Standard Form Algebra 1 Worksheets
Are you an Algebra 1 student or teacher in search of reliable, comprehensive worksheets? Look no further! Our Standard Form Algebra 1 Worksheets are designed to help you master the concepts and skills necessary for success in this subject. With a wide variety of exercises and practice problems, these worksheets provide the perfect tool for enhancing your understanding of standard form equations and their applications.
Table of Images 👆
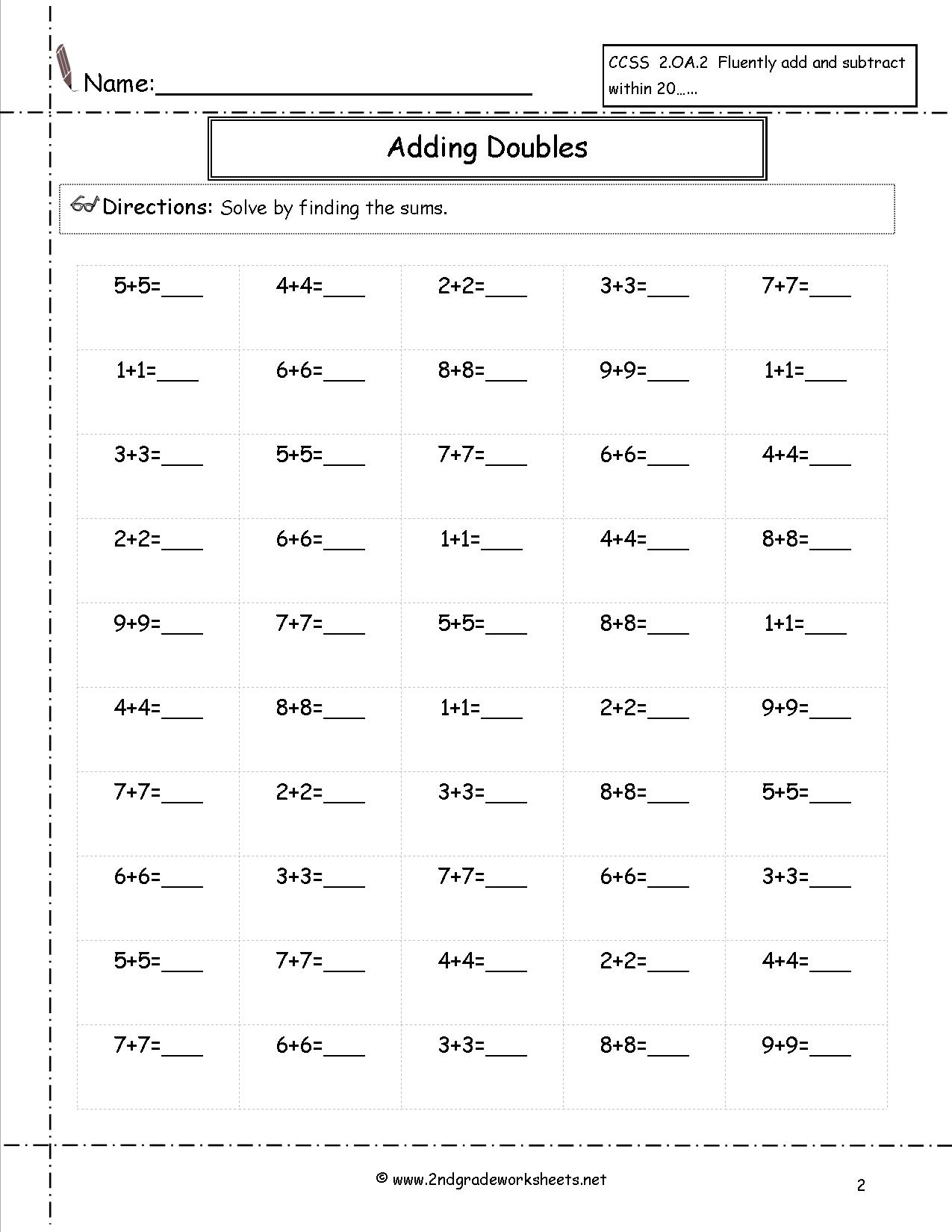
- Math Addition Worksheets 2nd Grade
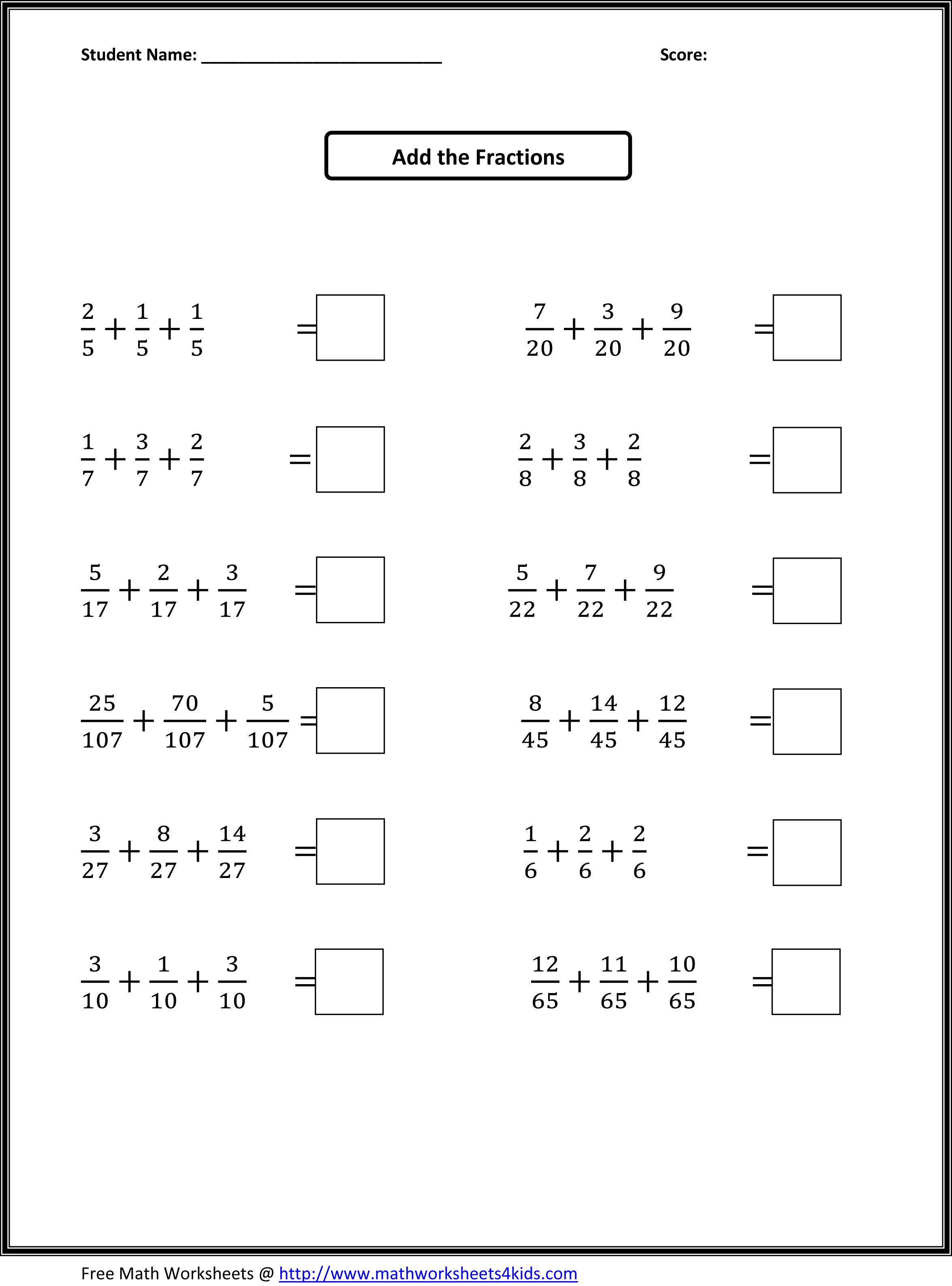
- 4th Grade Math Worksheets Fractions
- Factoring Polynomials with Leading Coefficient Worksheet
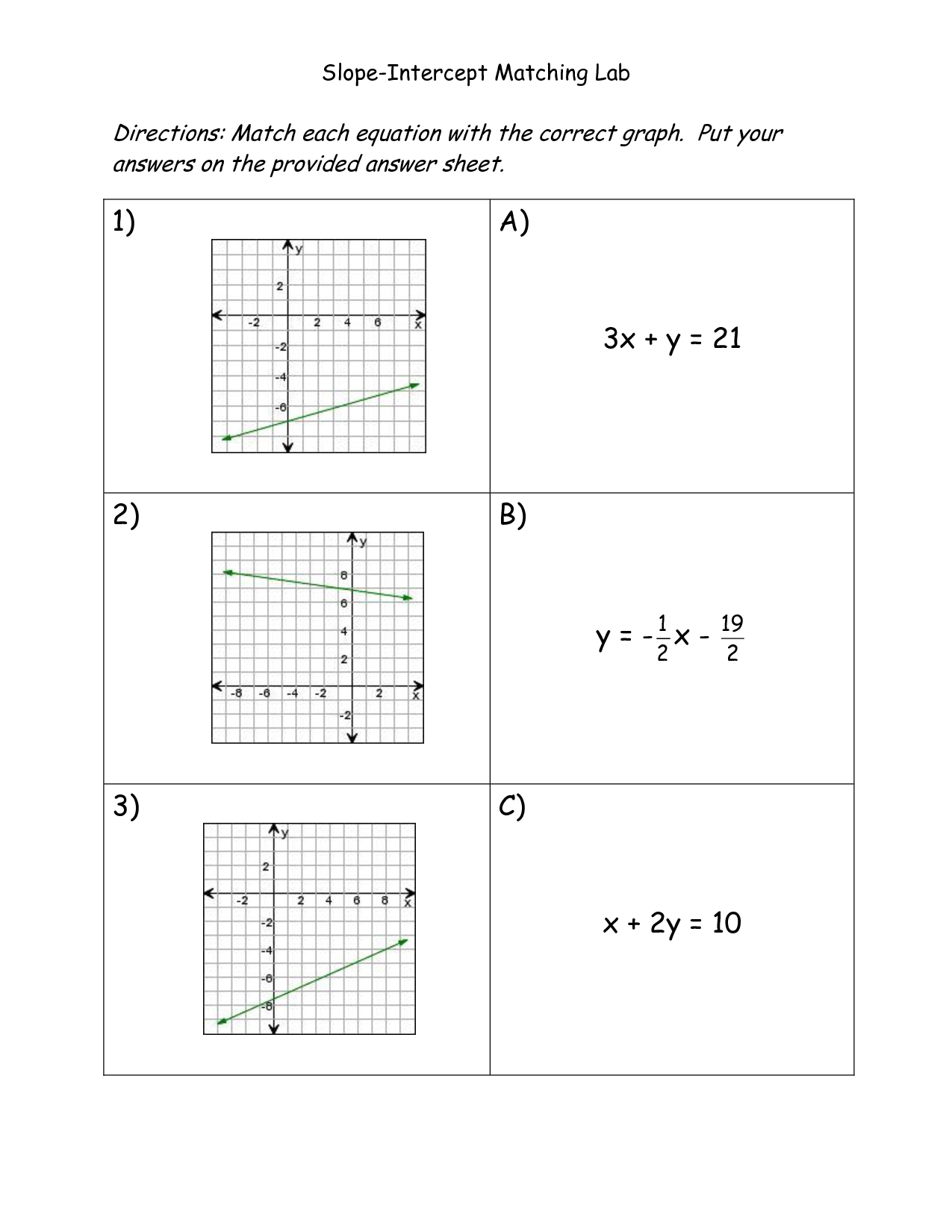
- Slope-Intercept Form Worksheet and Answers
- Scientific Notation Worksheet
- Polynomial Long Division
- Glencoe Algebra 2 Answer Key Chapter 4
- College Algebra Math Worksheets
- Prime and Composite Numbers Worksheets
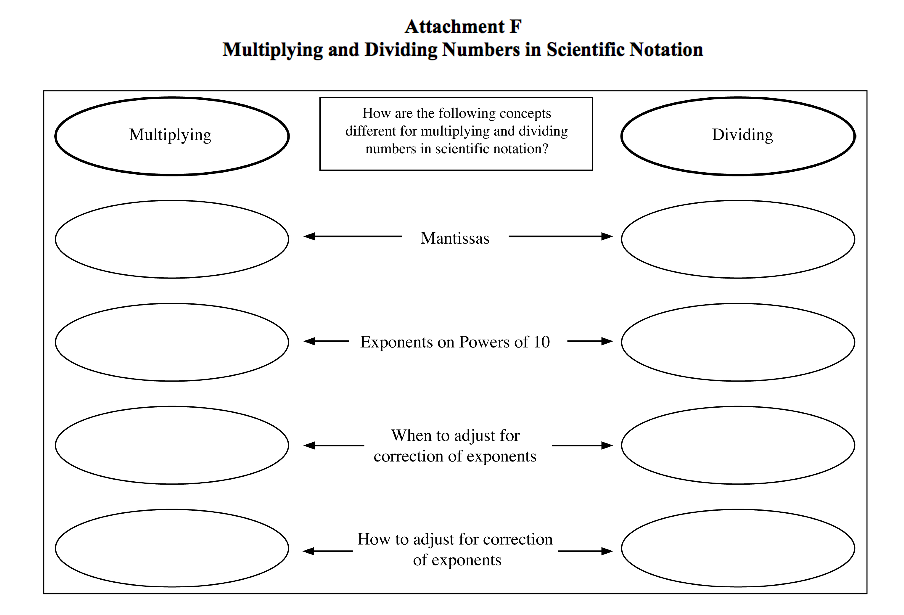
- Scientific Notation Graphic Organizer
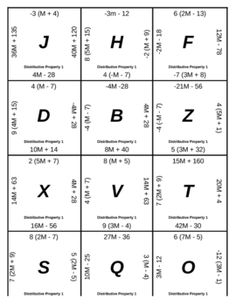
- Distributive Property Matching Game
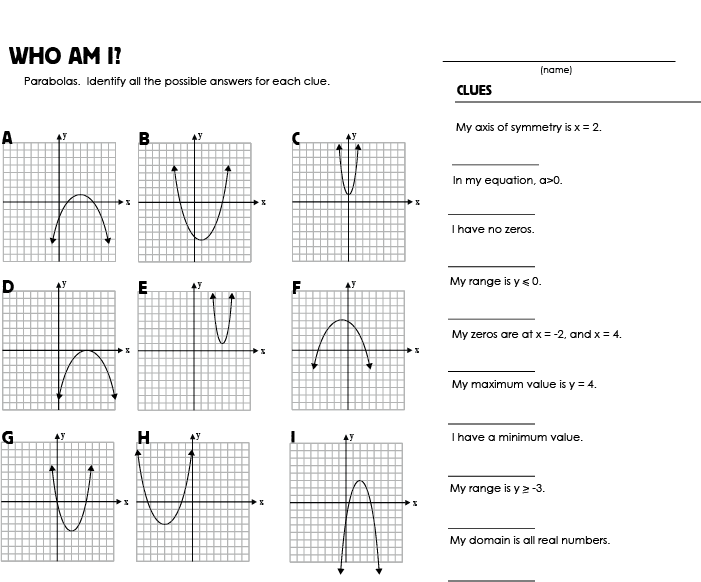
- Graphing Quadratic Functions Worksheet Answers
- Distance Formula Algebra
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
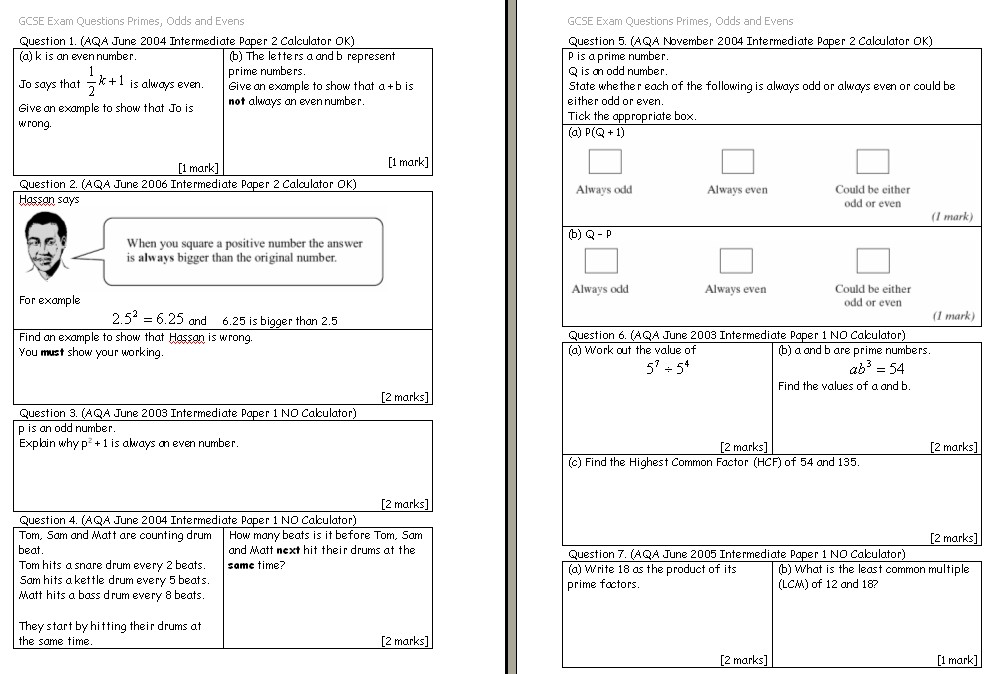
What is standard form in algebra 1?
Standard form in algebra 1 refers to the standard way of writing linear equations, which is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are constants, x and y are variables, and A is typically a positive integer. This form allows for easy identification of the coefficients and constants in the equation.
How do you convert an equation from slope-intercept form to standard form?
To convert an equation from slope-intercept form, y = mx + b, to standard form, Ax + By = C, first multiply the entire equation by the denominator of the slope m to eliminate fractions. Next, rearrange the equation so that all terms are on one side of the equation and the constant term on the other side, which will result in the equation being in the form Ax + By = C. Make sure to maintain the general form where A, B, and C are integers and A is positive.
What is the role of the coefficients in standard form equations?
The coefficients in standard form equations represent the numerical values that are multiplied by the variables in the equation. They determine the scale or size of each variable's contribution to the overall relationship described by the equation. By adjusting the coefficients, you can change the slope, intercept, and overall characteristics of the equation, providing insight into how the variables are related and how they impact each other within the equation.
Can standard form equations have negative coefficients? Why or why not?
Yes, standard form equations can have negative coefficients. The standard form of a linear equation is Ax + By = C, where A, B, and C are constants. These constants can be positive, negative, or zero, allowing for negative coefficients in the equation. Negative coefficients simply indicate a decrease in the value of the corresponding variable as it is multiplied by a negative number in the equation.
How do you determine the x and y-intercepts from a standard form equation?
To determine the x-intercept, set y to zero and solve for x. The x-intercept will be a point on the x-axis where the graph of the equation crosses it. To find the y-intercept, set x to zero and solve for y. The y-intercept will be a point on the y-axis where the graph crosses it. These intercepts give you specific points on the graph to help understand its behavior and shape.
What is the significance of the constant term in standard form equations?
The constant term in standard form equations represents the y-intercept of the graph of the equation, which is the point where the graph intersects the y-axis. It indicates the value of y when x is equal to zero, providing important information about the starting point and overall shape of the graph. The constant term helps in understanding the behavior of the function and how it relates to the coordinate axes.
Are standard form equations always linear equations?
No, standard form equations are not always linear equations. Standard form is a way of writing numeric equations that can represent various types of functions, including linear, quadratic, cubic, and other types of equations. Linear equations are a specific type of standard form equation where the highest exponent of the variable is 1.
How do you graph a standard form equation on a coordinate plane?
To graph a standard form equation (Ax + By = C) on a coordinate plane, first solve for y to get the equation in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) by isolating y. Then, identify the y-intercept (b) and the slope (m). Plot the y-intercept on the y-axis and use the slope to find additional points to draw the line. Connect the points to create a straight line that represents the graph of the standard form equation on the coordinate plane.
How does the graph of a standard form equation differ from a graph in slope-intercept form?
The graph of a standard form equation Ax + By = C is typically a straight line, but it is presented in a different format compared to slope-intercept form y = mx + b. In standard form, the coefficients A, B, and C determine the slope and y-intercept indirectly, while in slope-intercept form, the slope m and y-intercept b are explicitly given. Overall, both forms represent linear equations and have their own advantages depending on the context in which they are used.
How can you determine if two standard form equations represent parallel lines?
Two standard form equations can be determined to represent parallel lines if they have the same slope but different y-intercepts. In standard form, ax + by = c, the slope can be found by solving for y to get the equation in slope-intercept form (y = mx + b), where m is the slope. If the two equations in standard form have the same slope but different y-intercepts, they are parallel lines.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






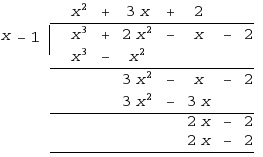



















Comments