DNA Code Worksheet
The DNA code is the means by which life communicates. The DNA code contains instructions for creating a living entity. The DNA Code Worksheet is an excellent resource for kids interested in learning about the structure and function of DNA. This interesting game is ideal for biology students seeking a thorough understanding of genetics and cellular processes.
Table of Images 👆
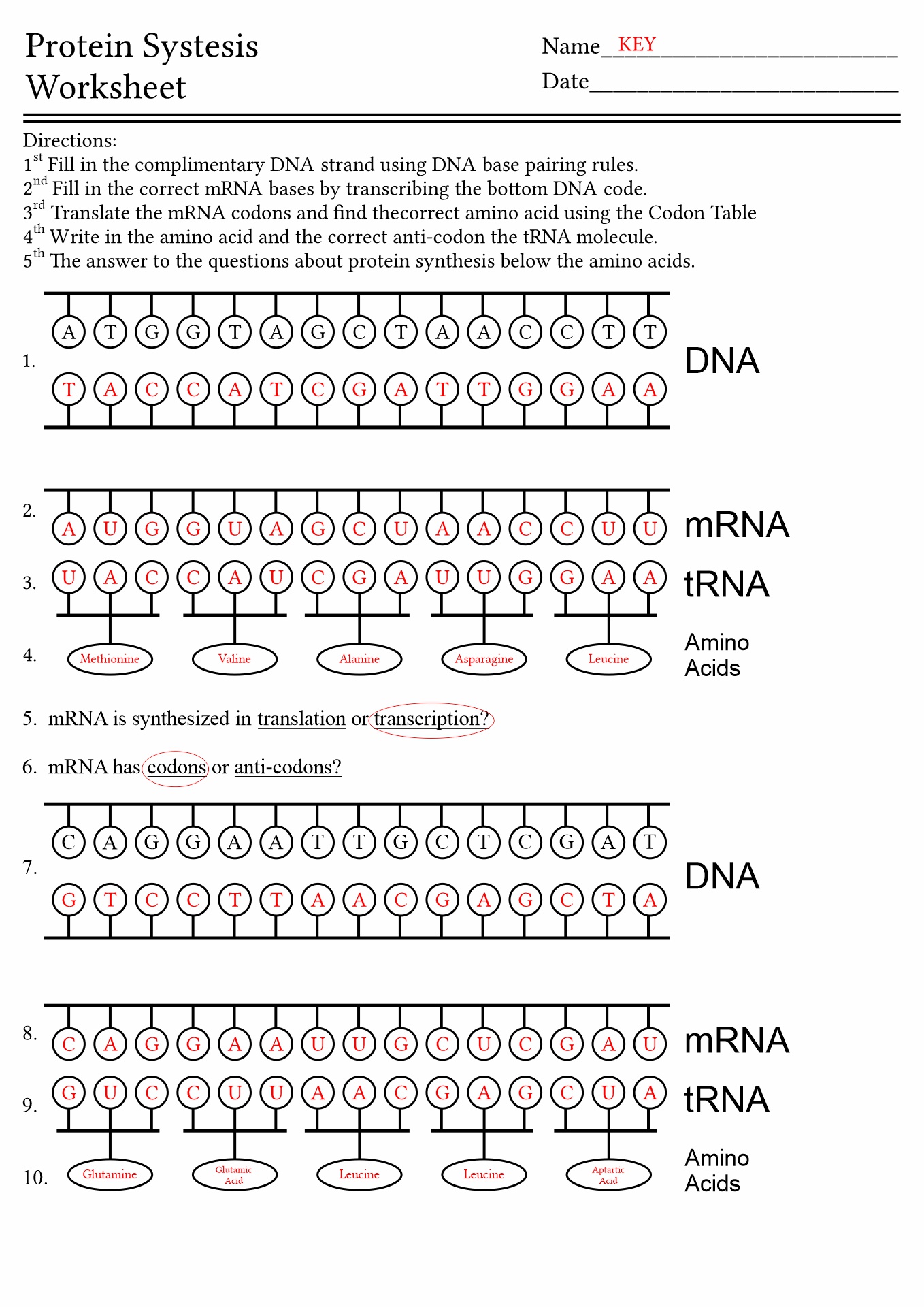
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Properties of Light Worksheet
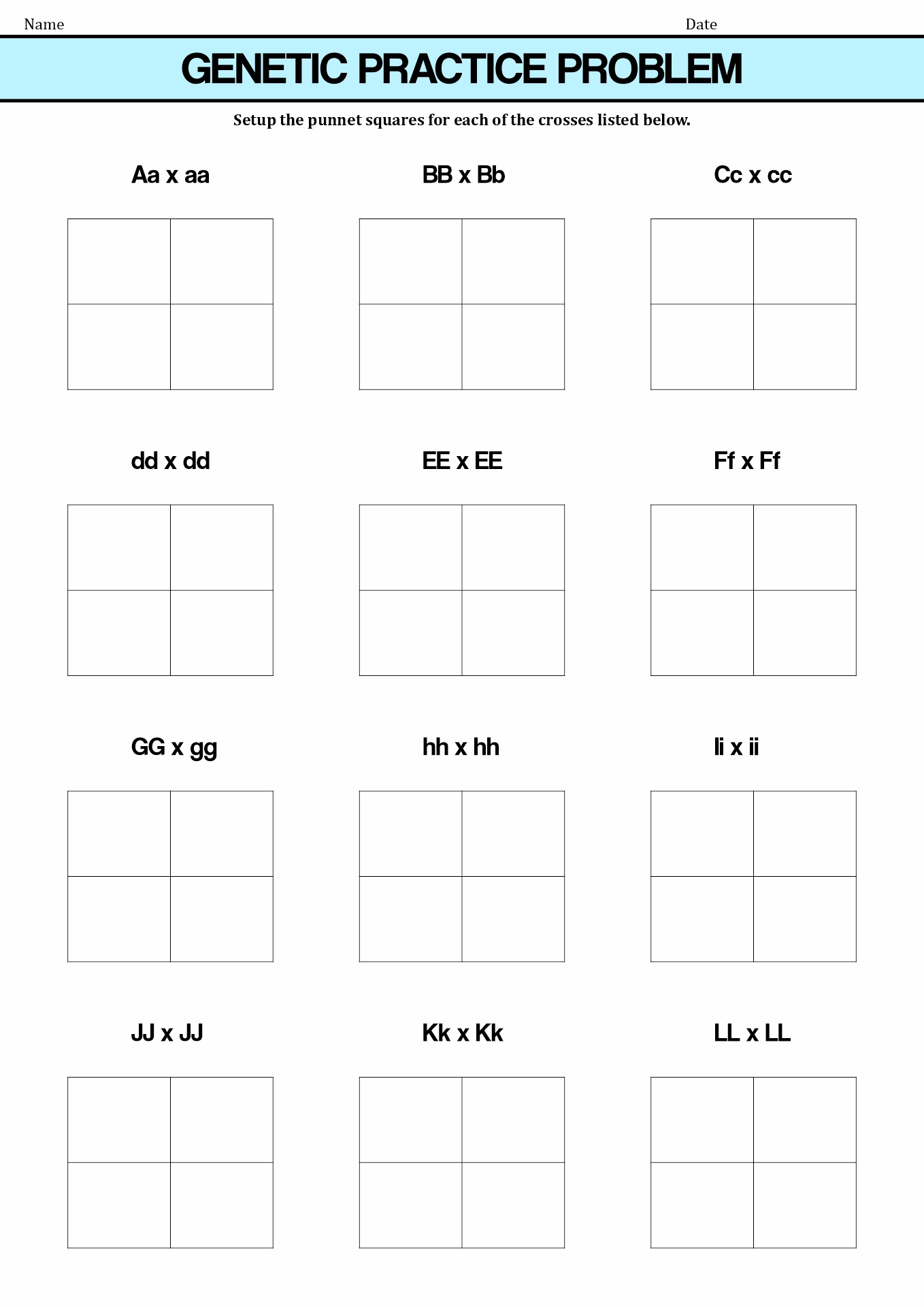
- Simple Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet
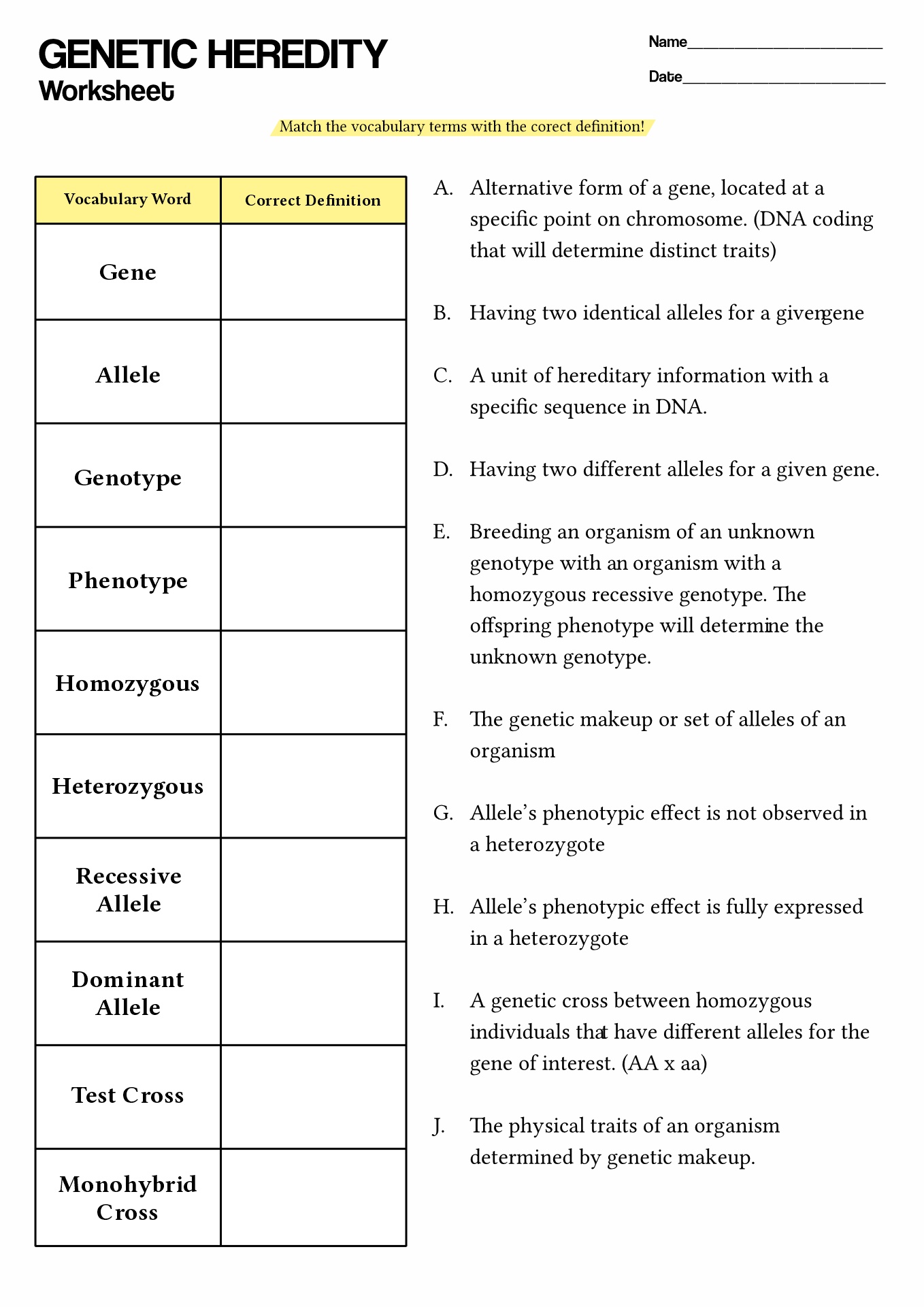
- Genetics Heredity Worksheet
- DNA Extraction Worksheet
- Population Genetics Worksheet
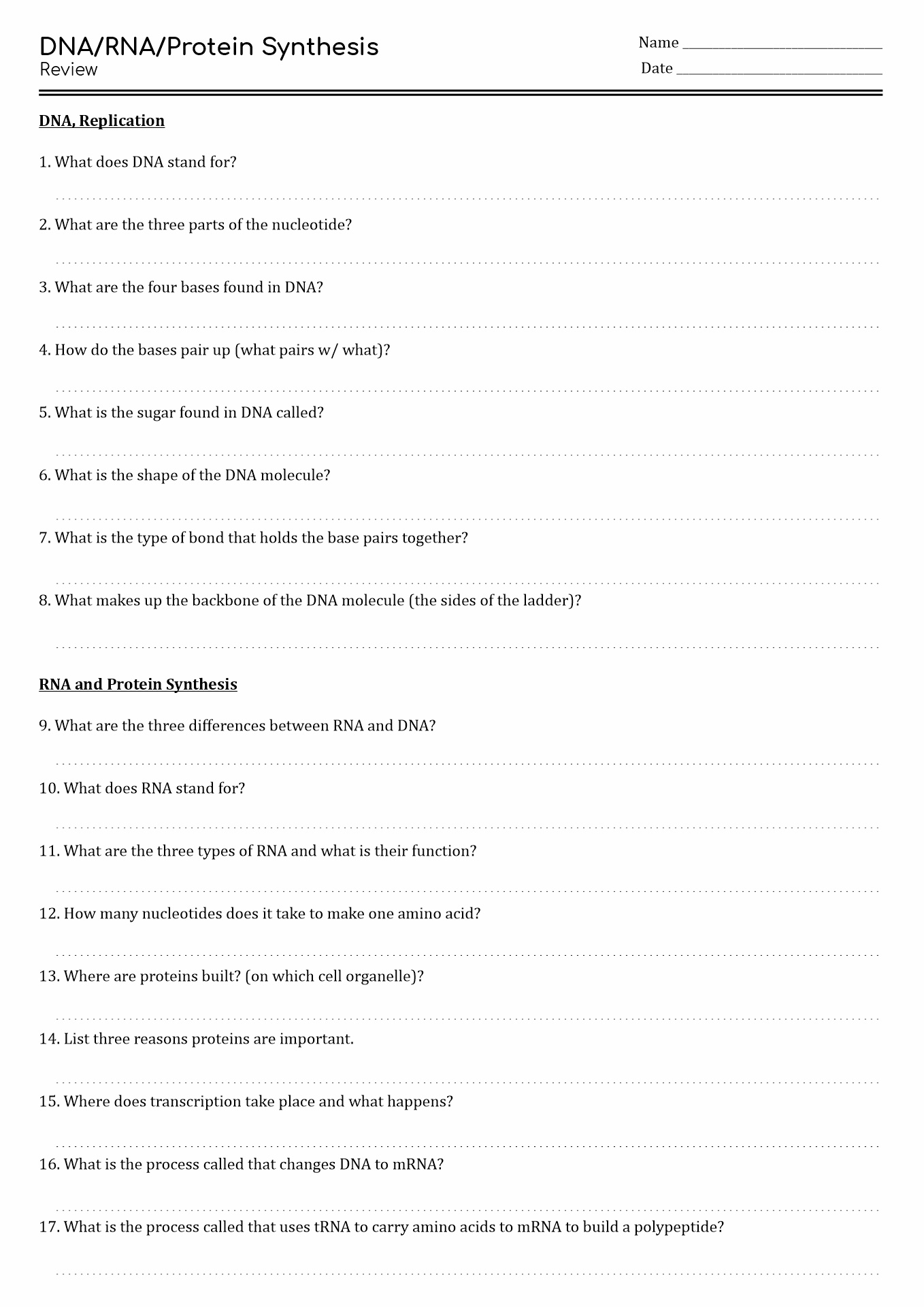
- DNA and RNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
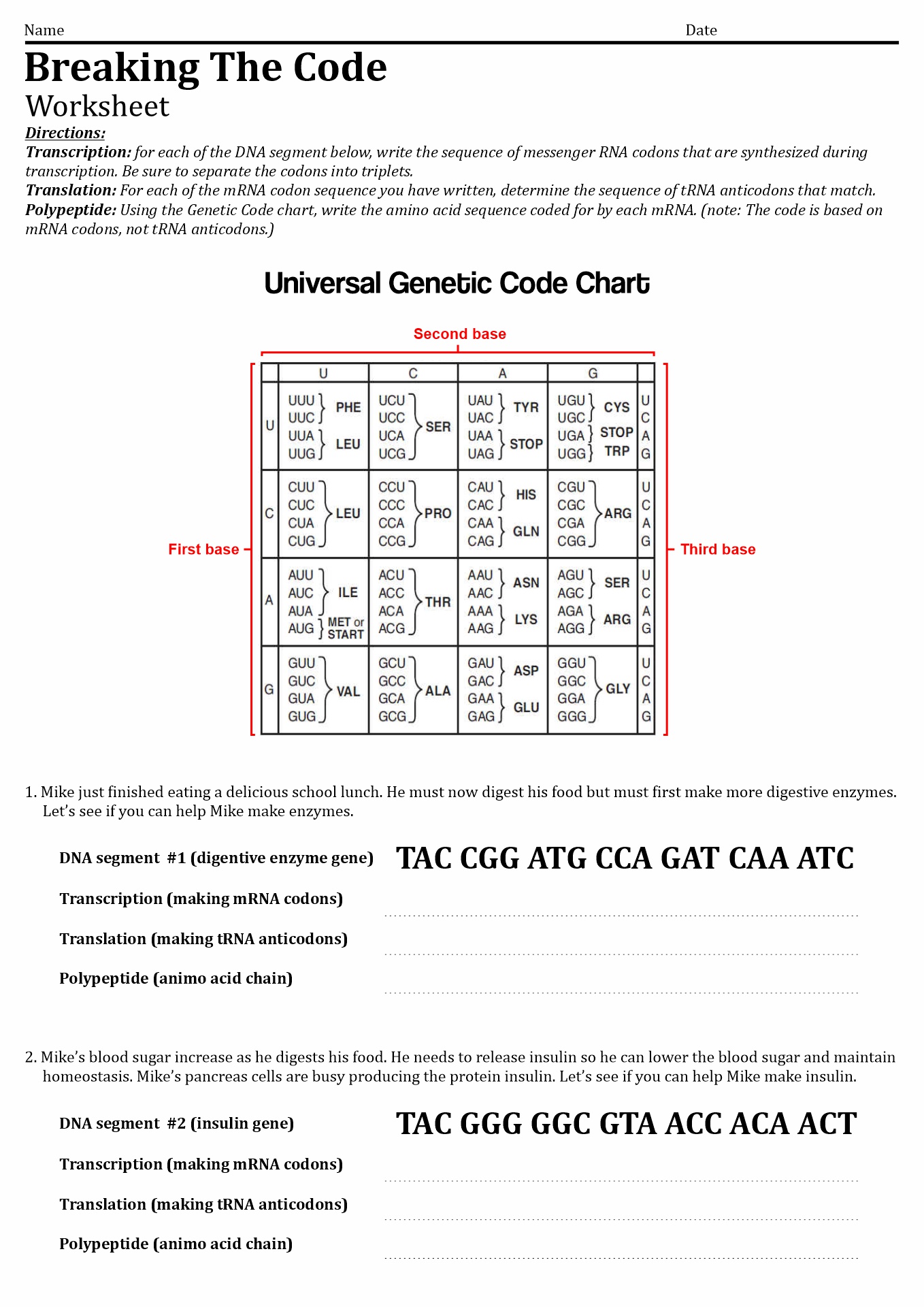
- Breaking the Code Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet
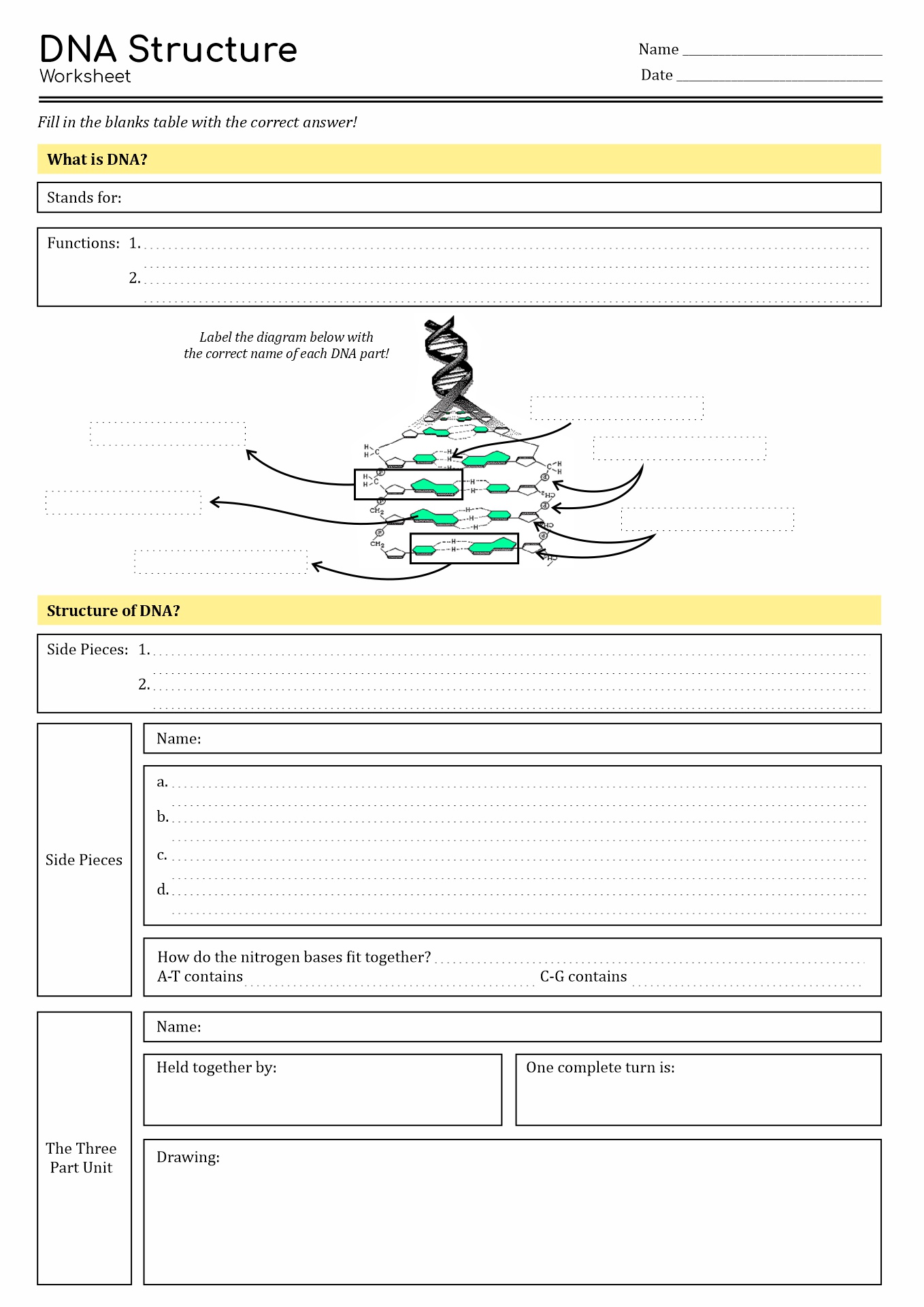
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- Genetic Variation Worksheet
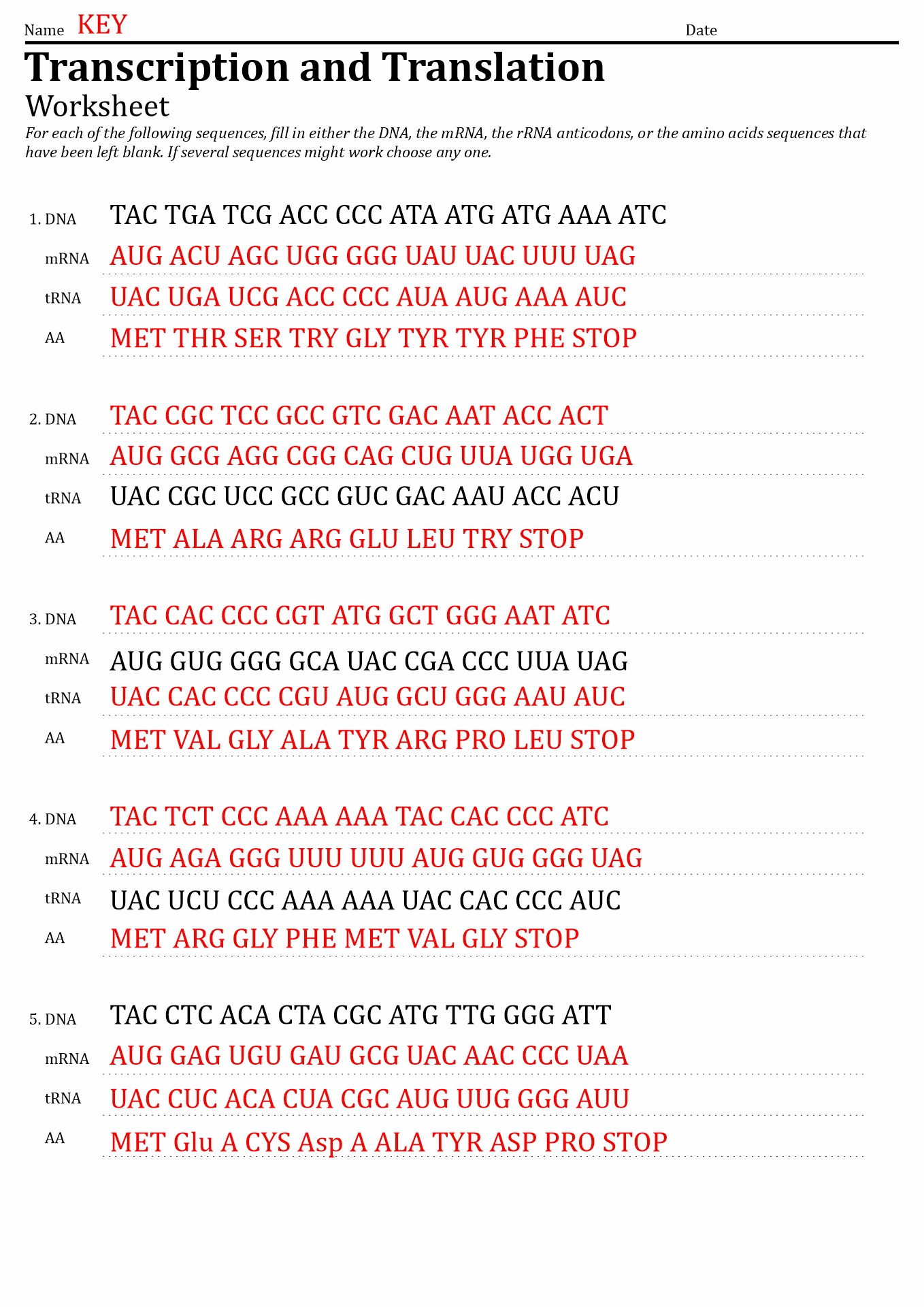
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Simple Genetics Practice Problems Worksheet

Understanding the basics of genetics is crucial for students; with our DNA Code Worksheet, you can provide an excellent resource for their studies.
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Spring Clothes Worksheet
For First Grade Phonics Worksheets
Hundreds Chart Missing Numbers Worksheet
Healthy Eating Plate Printable Worksheet
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
My Shadow Worksheet
Large Printable Blank Pyramid Worksheet
Relationship Circles Worksheet
The worksheet defines DNA, its role in inheritance, and how it codes for proteins. Working through this worksheet will help students understand the complexities and significance of the DNA molecule. Learn more about DNA!
What is DNA Code?
There are four code bases of DNA: Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), and Thymine (T) - different ways to spell the three-letter "codon" that indicates which amino acid needs at each position in the protein. Some experts also call the genetic code DNA code. The history of the genetic code developed in the 19th, 20th, and 21st centuries, its promises and dangers.
For example, Oswald Avery proved in 1944 that the genetic code (DNA) is indeed the carrier of genetic information, ending over 80 years of productive speculation. But just as important as DNA was to the so-called heroic age of molecular biology, which spanned generations of post-World War II scientific discoveries, it is essential to the revolutionary science of genetics and genomics. Neither your genes nor your DNA determines who you are or what you should do. Use our DNA Code Worksheets to study this topic.
What is Codon?
Codon is three ensuing nucleotides in the DNA or RNA molecule that rules for a particular amino acid. The codon will give a signal to show the start and the end of the DNA translation. When people talk about the genetic code, they refer to the phenomenon of DNA that contains the informational code for making the proteins that organisms need to function.
DNA serves as a template for making messenger RNA, and messenger RNA serves as a template for making specific proteins. A series of bases create the DNA and its corresponding messenger RNA. In RNA, these bases are represented by the letters A, U, C, and G.
A set of three foundations forms a codon. Messenger RNA contains various codons in a series of 3 bases, three more bases, three more bases, and so on. Each codon tells the cell to start forming a protein chain, add a specific amino acid to a growing protein chain, or stop forming a protein chain.
How Does the DNA Code Worksheet Used for Learning?
An instructional tool or resource intended to assist people in learning and comprehending the basic ideas around DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) and its function in genetics and biology is a DNA code worksheet for medical students and biologists. Most people use these worksheets for self-study or in educational environments like labs and classrooms.
What is the Relation between DNA and Codon?
DNA code is the way of life to communicate. The DNA code consists of guidance to create a living thing. Four simple alphabets and sixty-four three-letter 'words' (codons) make the DNA code. Those four letters represent four molecules: thymine (T), adenine (A), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
One of the ways DNA encodes information in cells is through genes. Each gene has instructions to make a specific protein, and each protein has a particular job in the cell. A codon is a progression of three nucleotides on a thread of DNA or RNA. Each codon is like a three-letter word, and all these codons together make up the instructions for DNA (or RNA).
DNA and RNA have only four nucleotides, so only 64 possible codons. From 64 codons, 61 codes for amino acids, which consist of blocks of proteins. A series of amino acids come together and create protein. Each protein is different based on the order and number of amino acids it has. Therefore, the DNA code is instructions for stringing together the correct number and type of amino acids in the appropriate order.
What are the Characteristics of the Genetic Code?
The sequence of nucleotides in the genetic code (DNA and RNA) determines the amino acid sequence of the proteins. Although the linear sequence of nucleotides in DNA contains the protein sequence information, proteins are not made directly from DNA. The process of genetic code has some essential characteristics that you should know:
- The genetic code is universal; all organisms have the same genetic code. This explanation indicates that all organisms share a common evolutionary history.
- The genetic code is apparent. Each codon codes for only one amino acid (or start or stop).
- The genetic code is redundant. Multiple codons encode the amino acids.
What is Protein Synthesis?
Protein synthesis is the method of producing proteins. This process consists of two steps: transcription and translation. In eukaryotic cells, the transcription process happens in the nucleus. In the transcription process, the DNA is used as a template to make messenger RNA (mRNA) molecules.
The mRNA molecule then leaves the cell nucleus and travels to the cytoplasmic ribosomes, where the translation is. During translation, the genetic code in mRNA is read and used to make polypeptides. Learn more about protein synthesis with our DNA Code Worksheets.
What is DNA Replication?
DNA replication is the process of duplicating and cloning DNA molecules. This procedure means that a new DNA molecule will consist of two strands. One is recreated, and the other is the original strand. DNA carries the genetic information that codes for specific proteins.
Therefore, DNA molecules must be replicated before cell division to ensure that the two cells have the same genetic content after cell division. During the early stages of mitosis (prophase) and meiosis (prophase I), DNA is replicated in preparation for the later stages when the cell divides, creating two cells containing copies of the DNA.
The DNA Code Worksheet is a crucial tool in understanding genetics and biology, providing instructions for creating proteins and RNA and addressing DNA replication. It teaches students the importance of DNA in genetics and biology, highlighting the role of DNA molecules in the development of genetic information.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments
This DNA Code Worksheet is incredibly helpful for understanding the intricacies of DNA codes in a simple and visually engaging way. It has made learning about genetics so much more enjoyable and easier to grasp. Thank you for providing such a valuable resource!
Thank you for providing the DNA Code Worksheet! It's a great resource to help visualize and understand the intricacies of DNA. Simple and effective, it's perfect for guiding students through the fascinating world of genetics.
Great resource! The DNA Code Worksheet is a helpful tool for understanding the basics of DNA and its importance. It's concise and user-friendly, making it perfect for learning and reviewing.
The printable DNA code worksheet helps students understand the structure of DNA and its functions, making it a valuable tool for learning and visualizing the complexity of genetic information.
I found the DNA Code Worksheet to be a helpful resource for understanding the fundamentals of genetic coding. The simple format and clear instructions made it easy to follow along and learn. Thank you!