Right Triangle Trig Worksheets
Are you a high school student struggling to understand right triangle trigonometry? Look no further, as we have the perfect solution for you! Our collection of right triangle trig worksheets is specifically designed to help you grasp the concepts of sine, cosine, and tangent effortlessly. With carefully crafted exercises and step-by-step explanations, these worksheets will make learning trigonometry an enjoyable and rewarding experience. Whether you need to practice finding side lengths, angles, or solving word problems, our worksheets provide ample opportunities to master these skills. Get ready to conquer right triangle trigonometry with our comprehensive worksheets!
Table of Images 👆
- Right Triangle Trig Word Problems Worksheet
- Right Triangle Word Problems Worksheet
- Right Triangle Trigonometry Worksheet
- Right Triangles in Trig Ratios Worksheet Answers
- Right Angle Trigonometry Worksheet
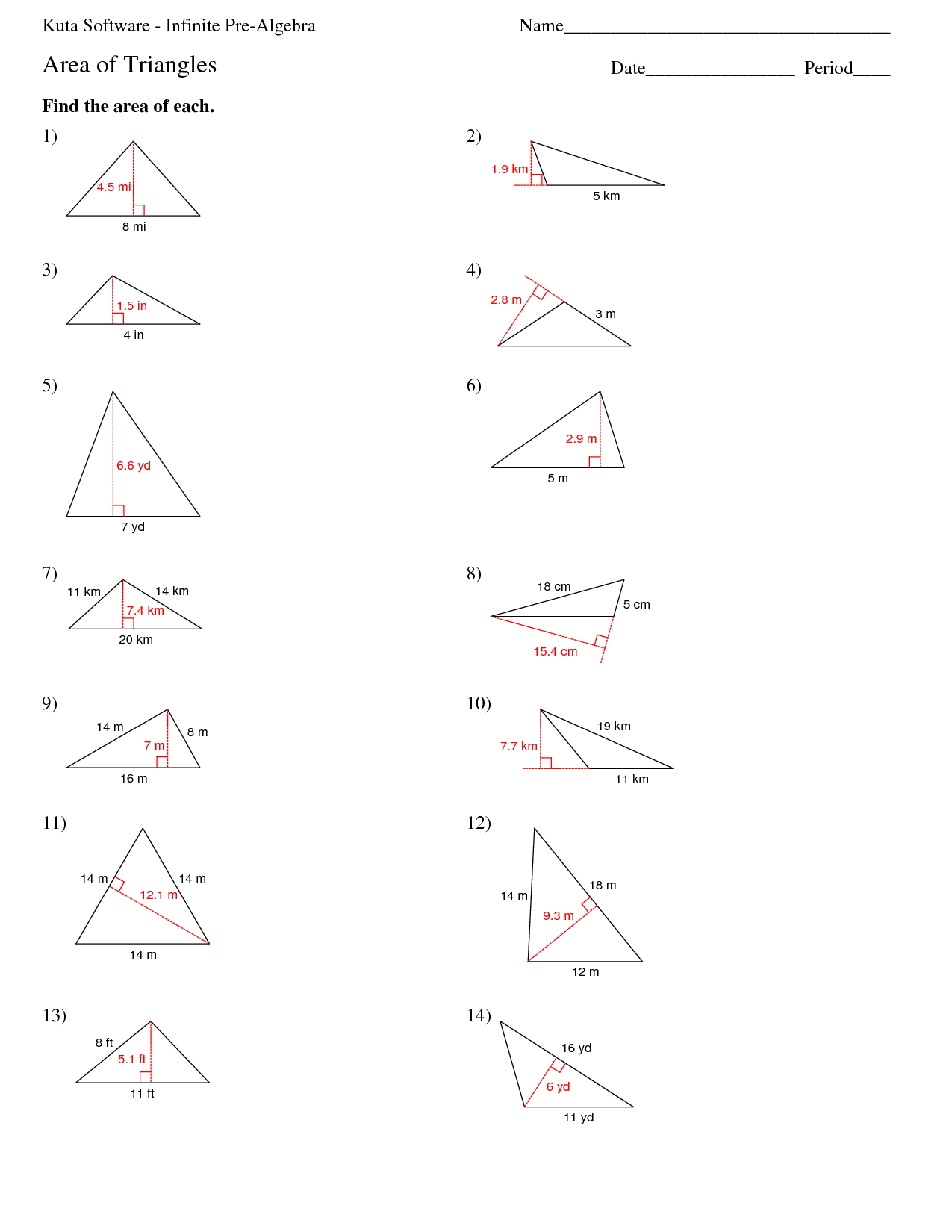
- Area of Triangle Worksheets PDF
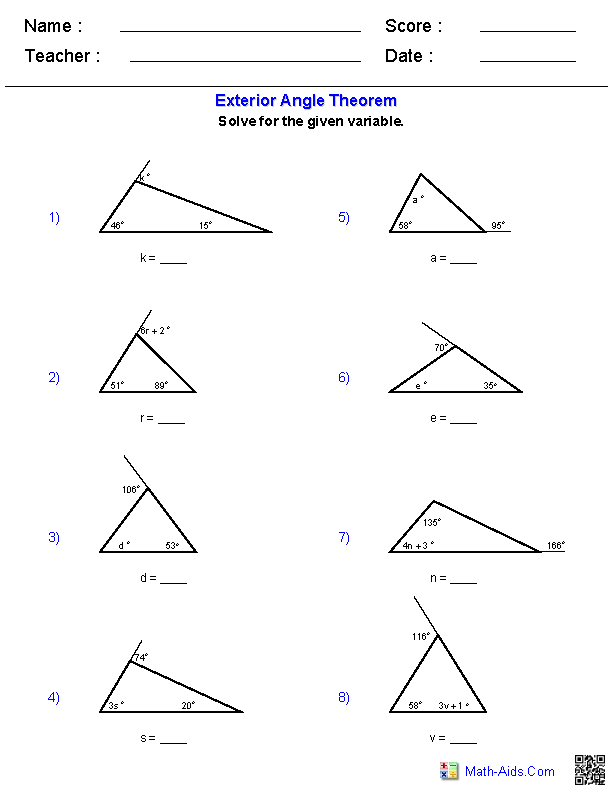
- Triangle Angle Sum Theorem Worksheet
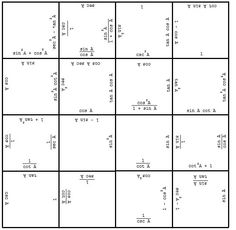
- Identities Trig Worksheet Puzzle
- Pythagorean Theorem Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
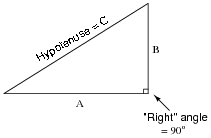
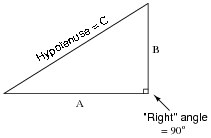
What is the Pythagorean Theorem and how is it used to solve right triangles?
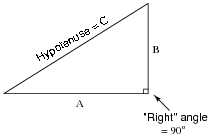
The Pythagorean Theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry that states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. Mathematically, it can be written as a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where 'c' is the length of the hypotenuse, and 'a' and 'b' are the lengths of the other two sides. This theorem is used to find missing side lengths of right triangles when the lengths of the other two sides are known. It provides a quick and reliable method for solving problems involving right triangles in various real-world applications.
How do you find the missing side length of a right triangle using trigonometry?
To find the missing side length of a right triangle using trigonometry, you can use the sine, cosine, or tangent functions based on the information you have. For example, if you know the measure of an acute angle and the length of one side, you can use the sine or cosine function to calculate the missing side length. If you know the lengths of two sides, you can use the tangent function to find the missing side length. Just remember to use the appropriate function based on the information given and apply the trigonometric ratio to solve for the missing side length.
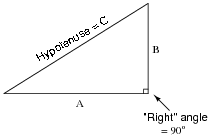
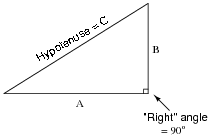
What are the primary trigonometric ratios (sine, cosine, tangent) and how are they used in right triangle trigonometry?
The primary trigonometric ratios are sine, cosine, and tangent. In right triangle trigonometry, these ratios are used to relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of its sides. The sine of an angle is the ratio of the length of the side opposite to the angle to the hypotenuse, the cosine is the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to the angle to the hypotenuse, and the tangent is the ratio of the length of the side opposite to the angle to the side adjacent to the angle. These ratios are essential for solving for missing sides or angles in right triangles using trigonometric functions.
How do you use the trigonometric ratios to find the measure of an angle in a right triangle?
To find the measure of an angle in a right triangle using trigonometric ratios, you can use SOH-CAH-TOA. If you know the lengths of two sides of a right triangle, you can use sine, cosine, or tangent (depending on the given sides) to determine the angle measure by setting up the appropriate ratio. For example, if you know the lengths of the opposite and adjacent sides of an angle, you would use the tangent ratio (opposite/adjacent) to find the angle measure.
What is the difference between the sine function and the cosine function in right triangle trigonometry?
In right triangle trigonometry, the sine function refers to the ratio of the length of the side opposite an angle to the length of the hypotenuse, denoted as sin(theta). Meanwhile, the cosine function refers to the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to an angle to the length of the hypotenuse, denoted as cos(theta). Essentially, the key difference between the sine and cosine functions lies in the sides of the right triangle they compare in relation to the angle being considered.
How do you determine whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent to solve a right triangle problem?
You determine whether to use sine, cosine, or tangent in a right triangle problem based on the information given and the specific sides or angles involved. If you have the lengths of two sides of the triangle and need to find an angle, you would typically use the inverse trigonometric functions sine, cosine, or tangent depending on which two sides are given. If you have an angle and need to find a side length, you would use the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, or tangent based on which side length is given and which you need to find.
How are right triangle trigonometry calculations used in real-world applications, such as architecture or engineering?
Right triangle trigonometry calculations are used in real-world applications like architecture and engineering to determine the dimensions and angles of structures. For example, in architecture, trigonometry is used to calculate the height of buildings, the slope of roofs, and the angles of staircases. In engineering, trigonometry is used to design bridges, calculate forces in structures, and determine the optimal angle for installing supports. Overall, these calculations help ensure that buildings and structures are designed and built accurately and safely.
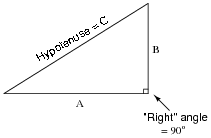
What is the relationship between the angle measures in a right triangle and the lengths of its sides?
In a right triangle, the relationship between the angle measures and the lengths of its sides is defined by trigonometric functions, such as sine, cosine, and tangent. These functions help relate the angles to the ratio of the lengths of the sides; for example, in a right triangle with angles ?, ?, and ?, the sine of angle ? is the ratio of the length of the side opposite angle ? to the length of the hypotenuse. Similarly, the cosine of angle ? is the ratio of the length of the side adjacent to angle ? to the length of the hypotenuse. Thus, trigonometric functions provide a way to express the relationship between angles and side lengths in a right triangle.
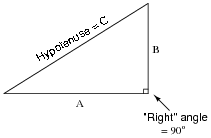
How do you determine whether a given set of side lengths can form a right triangle?
You can determine if a set of side lengths can form a right triangle by using the Pythagorean theorem. If the sum of the squares of the two shorter sides is equal to the square of the longest side, then the triangle can form a right angle. In other words, if a² + b² = c², where a and b are the shorter sides and c is the longest side, then the triangle is a right triangle.
What is the purpose of special right triangles (30-60-90 and 45-45-90) and how are they used in right triangle trigonometry?
Special right triangles, such as the 30-60-90 and 45-45-90 triangles, have specific angles and side ratios that make calculations easier in trigonometry. The purpose of these triangles is to provide convenient reference points for common angles, allowing for quicker and simpler calculations of trigonometric functions like sine, cosine, and tangent. By using the known side lengths and angle relationships of these special triangles, trigonometric functions can be calculated without needing to resort to memorizing or calculating complicated values.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments