Building Macromolecules Worksheet
If you're a biology student or enthusiast looking to better understand the intricate world of macromolecules, this blog post is for you. In this comprehensive worksheet, we will explore the fundamental entities and subjects related to macromolecules, providing you with the knowledge and practice needed to master this complex topic.
Table of Images 👆
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
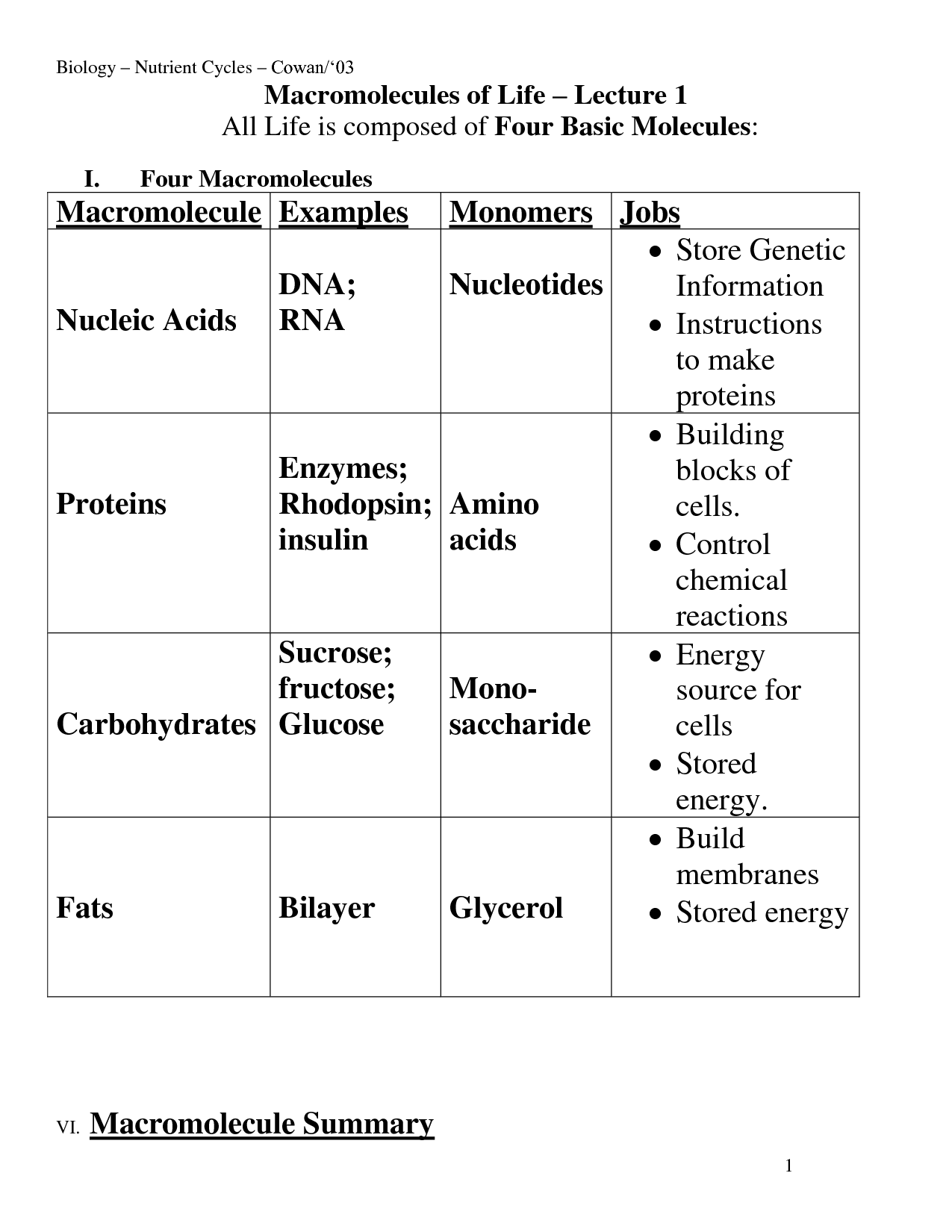
- 4 Macromolecules and Their Functions
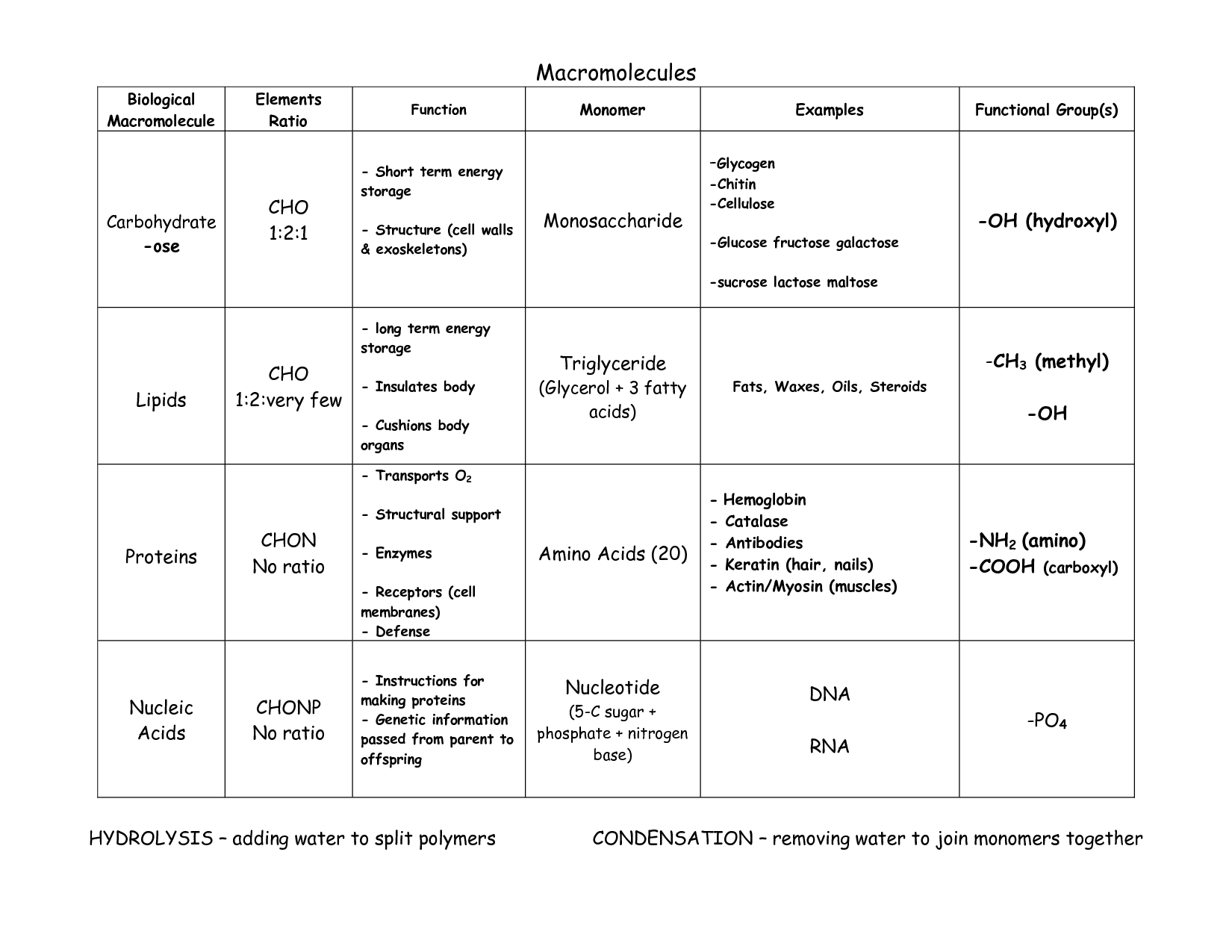
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
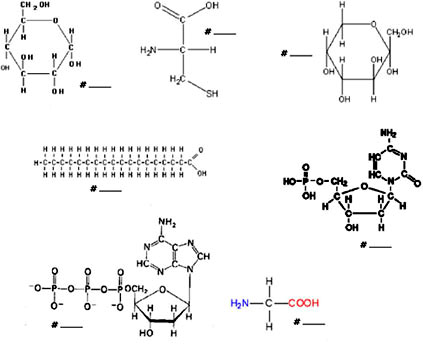
- Macromolecule Structure Worksheet
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Composite Figures Worksheet
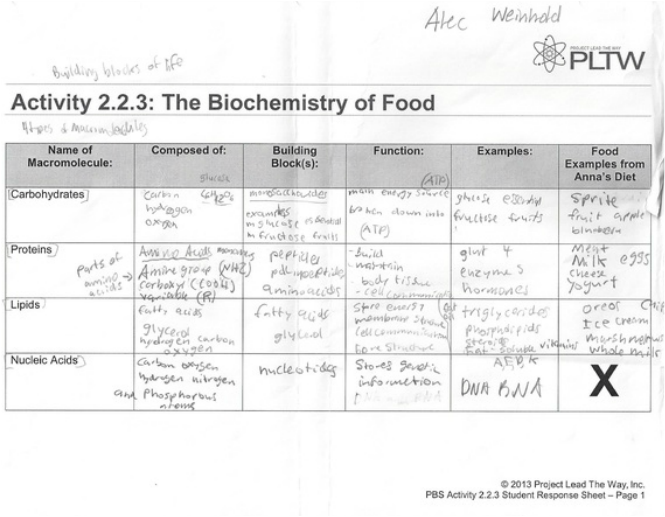
- Building Blocks of Life Worksheet Answers
- Building Blocks Worksheet Answers
- Shark Dichotomous Key Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Organelle Quiz Worksheet
- Hydrophobic Molecules Examples
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large molecules made up of smaller subunits called monomers, which are connected together through chemical bonds. These include essential biological molecules such as proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), carbohydrates, and lipids. These macromolecules play crucial roles in various cellular processes, serving as building blocks, energy sources, and information carriers in living organisms.
What are the four main classes of macromolecules?
The four main classes of macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. These molecules are essential for the structure and function of cells and play important roles in various biological processes within living organisms.
What is the function of carbohydrates?
Carbohydrates primarily serve as the body's main source of energy. When consumed, they are broken down into glucose, which is used as fuel by the body's cells for various functions such as metabolism, physical activity, and brain function. Additionally, carbohydrates play a role in supporting digestive health, regulating blood sugar levels, and providing fiber for maintaining a healthy gut.
What are the monomers of proteins?
The monomers of proteins are amino acids. These molecules contain an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable side chain, which distinguishes each amino acid from one another. When amino acids link together through peptide bonds, they form long chains known as polypeptides, which then fold into specific three-dimensional structures to create proteins with various functions in biological systems.
How are amino acids connected to form proteins?
Amino acids are connected to form proteins through peptide bonds. A peptide bond is a covalent bond that forms between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another amino acid, resulting in the formation of a dipeptide. This process repeats, with additional amino acids being added one by one, forming a chain known as a polypeptide. This polypeptide chain then folds and twists into a specific three-dimensional structure, which determines the protein's function.
What is the structure and function of lipids?
Lipids are molecules composed of hydrocarbons that form the building blocks of biological membranes. They are crucial for energy storage, providing insulation, and serving as signaling molecules in the body. Lipids can be classified into groups such as fats, phospholipids, and steroids. Fats are primarily used for long-term energy storage, while phospholipids make up the structural components of cell membranes. Steroids, such as hormones like estrogen and testosterone, have important regulatory functions in the body. Overall, lipids play essential roles in maintaining cell structure and function, as well as in various physiological processes.
What are the three main types of lipids?
The three main types of lipids are triglycerides, phospholipids, and steroids. Triglycerides are the most common type and function as a source of energy. Phospholipids are essential components of cell membranes, helping to create a barrier between the cell and its environment. Steroids, like cholesterol and hormones, play crucial roles in various physiological processes within the body.
What are nucleic acids and what is their function?
Nucleic acids are complex molecules made up of nucleotides that carry genetic information. There are two main types of nucleic acids: DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and RNA (ribonucleic acid). Their function is to store, transmit, and express genetic information in living organisms. DNA holds the genetic blueprint for an organism, while RNA is involved in protein synthesis and other cellular processes. Overall, nucleic acids play a crucial role in the inheritance of traits and the functioning of cells.
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
The monomers of nucleic acids are nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of three components: a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (ribose in RNA and deoxyribose in DNA), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine in DNA, and uracil in RNA). These nucleotides are the building blocks that make up the long chains of DNA and RNA molecules, which are essential for encoding genetic information and carrying out various cellular functions.
How are nucleotides connected to form nucleic acids?
Nucleotides are connected to form nucleic acids through phosphodiester bonds. This bond forms between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the sugar of another nucleotide. This process creates a sugar-phosphate backbone, with the nitrogenous bases extending off of the backbone. Multiple nucleotides are linked together through these phosphodiester bonds to form a linear chain, ultimately creating the structure of DNA or RNA.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments