Basic Cell Labeling Worksheet
Worksheets are an invaluable resource for students who want to solidify their understanding of different subjects. Whether you are studying anatomy, chemistry, or any other subject that requires labeling diagrams and understanding key concepts, a basic cell labeling worksheet can be an excellent tool to aid in your learning journey. By providing a clear and organized format, these worksheets help students identify the various entities within a cell and enhance their subject knowledge at their own pace.
Table of Images 👆
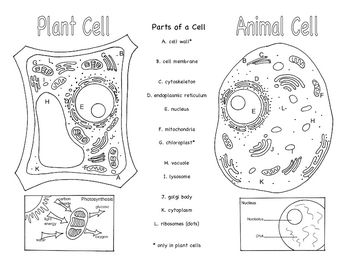
- Animal and Plant Cells Brochure
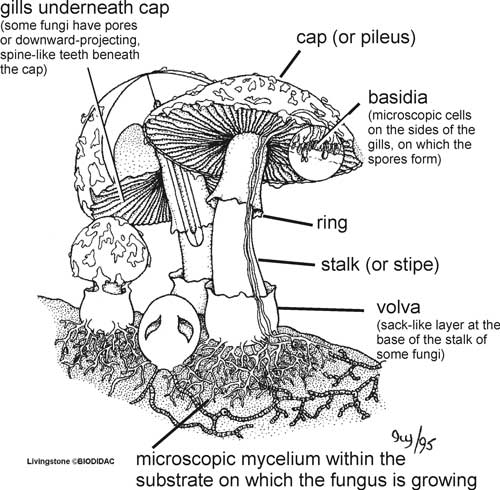
- Fungi Mushroom Diagram Labeled
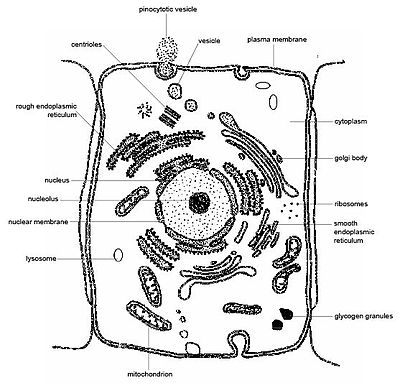
- Animal Cell Electron Microscope
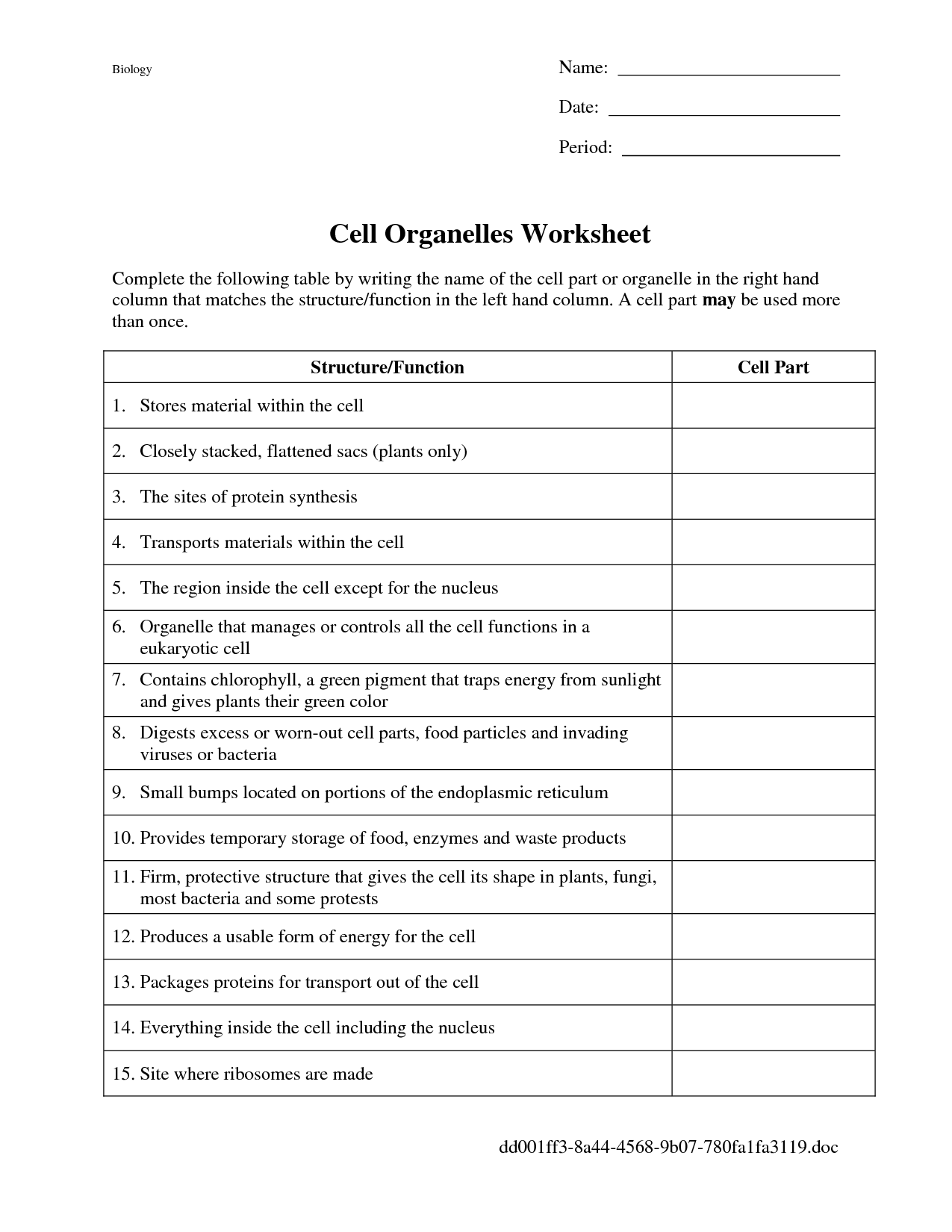
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Male Dog Reproductive System Diagram
- Plant Cell Diagram without Labels
- Animal Nervous System Diagram
- Biology Cell Organelles Worksheet
- Urinary System Diagram Blank Labels
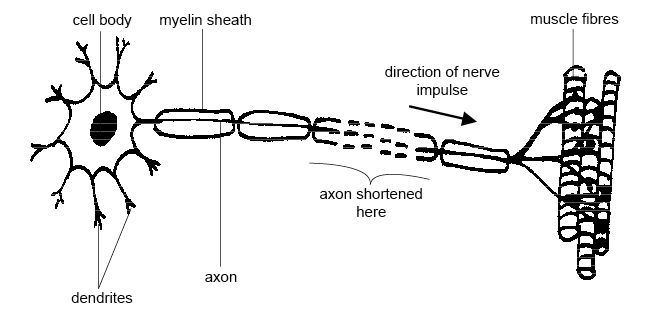
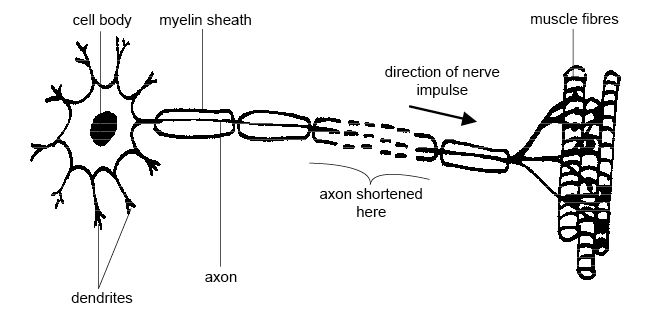
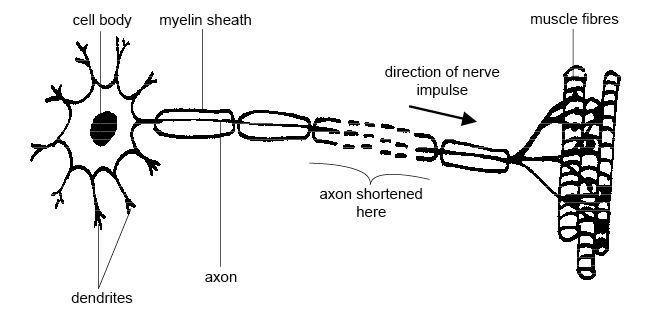
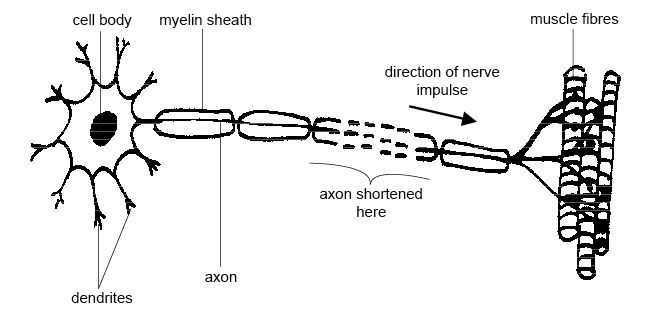
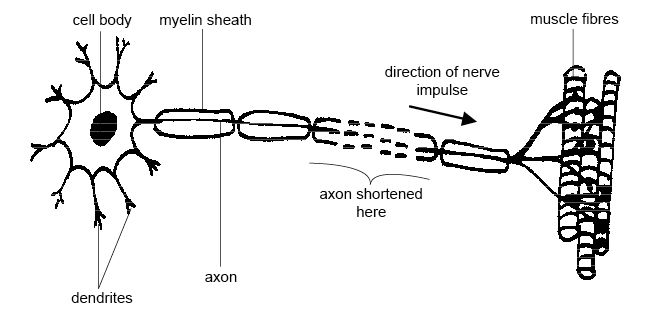
- Motor Neuron Diagram Unlabeled
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
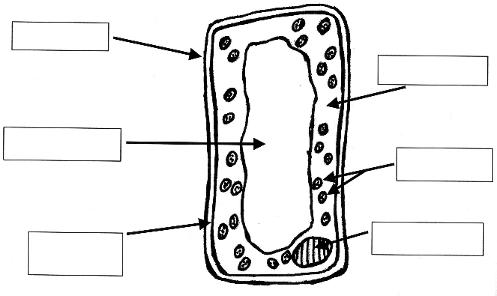
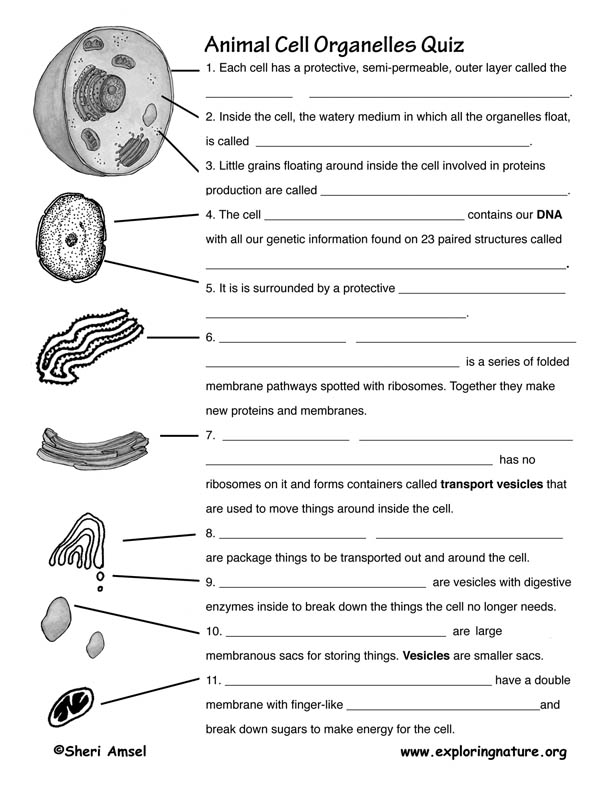
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer that surrounds the cell and acts as a protective barrier. It is made up of phospholipids and proteins and regulates the movement of molecules in and out of the cell, helping to maintain the cell's internal environment and allowing for communication with the external environment.
What is the function of the cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm serves as the medium for intracellular activities within the cell, providing a space for cellular organelles to float in and carry out their functions. It is involved in various processes, such as cell growth, metabolism, and cellular transport. Additionally, the cytoplasm helps maintain the shape and structure of the cell and plays a role in storing nutrients and waste products.
What is the role of the nucleus?
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells that serves as the control center for the cell. It contains the cell's genetic material in the form of chromosomes, including the DNA. The nucleus is responsible for regulating gene expression, cell growth, metabolism, and cell division. It also plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and stability of the genetic material, as well as in transmitting genetic information from one generation to the next.
What are mitochondria and what is their function?
Mitochondria are specialized structures found within cells that are responsible for producing energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration. Often referred to as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria play a crucial role in generating the energy needed for various cell functions and metabolic processes.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum and what does it do?
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranes found in eukaryotic cells that is involved in the synthesis, folding, and transport of proteins and lipids. It comes in two forms: rough ER, which has ribosomes attached and is involved in protein synthesis, and smooth ER, which lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification. The ER plays a crucial role in maintaining cell structure and function by ensuring the proper processing and packaging of molecules for secretion or use within the cell.
What is the Golgi apparatus and what is its function?
The Golgi apparatus is a cell organelle responsible for processing, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids produced by the endoplasmic reticulum before they are transported to their final destinations within or outside the cell. It plays a vital role in protein trafficking and secretion, as well as in the synthesis of certain complex molecules.
What are lysosomes and what is their role?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in animal cells that contain digestive enzymes. Their main role is to break down cellular waste, debris, and foreign materials, such as bacteria, viruses, and damaged organelles, through a process called hydrolysis. This breakdown helps in recycling the components for reuse by the cell or for energy production. Lysosomes also play a key role in maintaining cellular homeostasis by degrading and recycling cellular components.
What are ribosomes and what do they do?
Ribosomes are cellular structures found in all living cells that are responsible for protein synthesis. They are made up of RNA and proteins and can be found in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Ribosomes read the genetic information in mRNA and use it to assemble amino acids into proteins, which are essential for cell function and growth.
What is the function of the cell wall in plant cells?
The main function of the cell wall in plant cells is to provide structural support and protection. It helps maintain the shape of the cell, prevents excessive water uptake, and protects the cell from mechanical damage and pathogens. The cell wall is made up of cellulose fibers that form a rigid framework around the cell membrane, allowing plant cells to maintain their shape and withstand external pressures.
What is the vacuole and what is its purpose?
The vacuole is a membrane-bound organelle found in the cells of plants and some protists. Its main purpose is to store water, nutrients, and waste products, while also providing structural support for the cell. Additionally, the vacuole can help maintain the cell's turgor pressure, which is important for plant rigidity and growth.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments