Waves Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a science teacher or student looking for a comprehensive resource to reinforce your understanding of waves? Well, you're in luck! In this blog post, we will provide you with an answer key for a waves worksheet that covers various topics related to wave properties and behaviors. By using this answer key, you will gain a better grasp of the concepts and principles involved in the study of waves. So, let's dive right in and explore the fascinating world of waves together!
Table of Images 👆
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Sound Wave Worksheet Answer
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answer Key
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answer Key
- 8 Answer Key Science Worksheet Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Wave Characteristics Answer Key Worksheet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet
- Chemistry Stoichiometry Worksheet Answer Key
- Speed Frequency Wavelength Worksheet Answers
- 6th Grade Science Worksheets with Answer Key
- Potential Kinetic Energy Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a wave?
A wave is a disturbance that propagates through a medium or space, carrying energy without the transport of matter. It is characterized by oscillations or vibrations of particles in the medium, causing a transfer of energy from one point to another. Waves are found in various forms, such as electromagnetic waves (light), sound waves, water waves, and seismic waves.
What are the two main types of waves?
The two main types of waves are mechanical waves, which require a medium to travel through, and electromagnetic waves, which can travel through a vacuum. Mechanical waves include water waves and sound waves, while electromagnetic waves include visible light, radio waves, and X-rays.
What is the difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave?
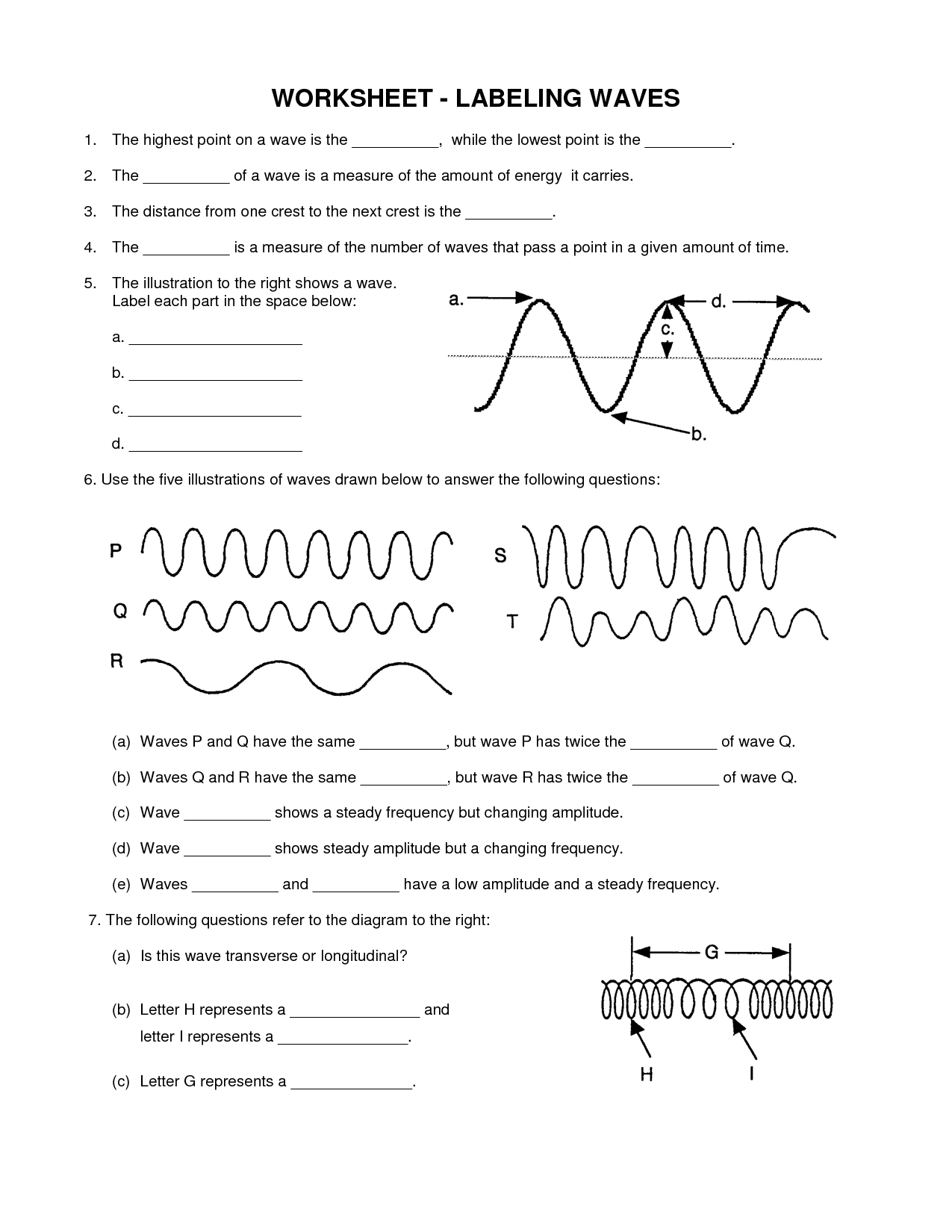
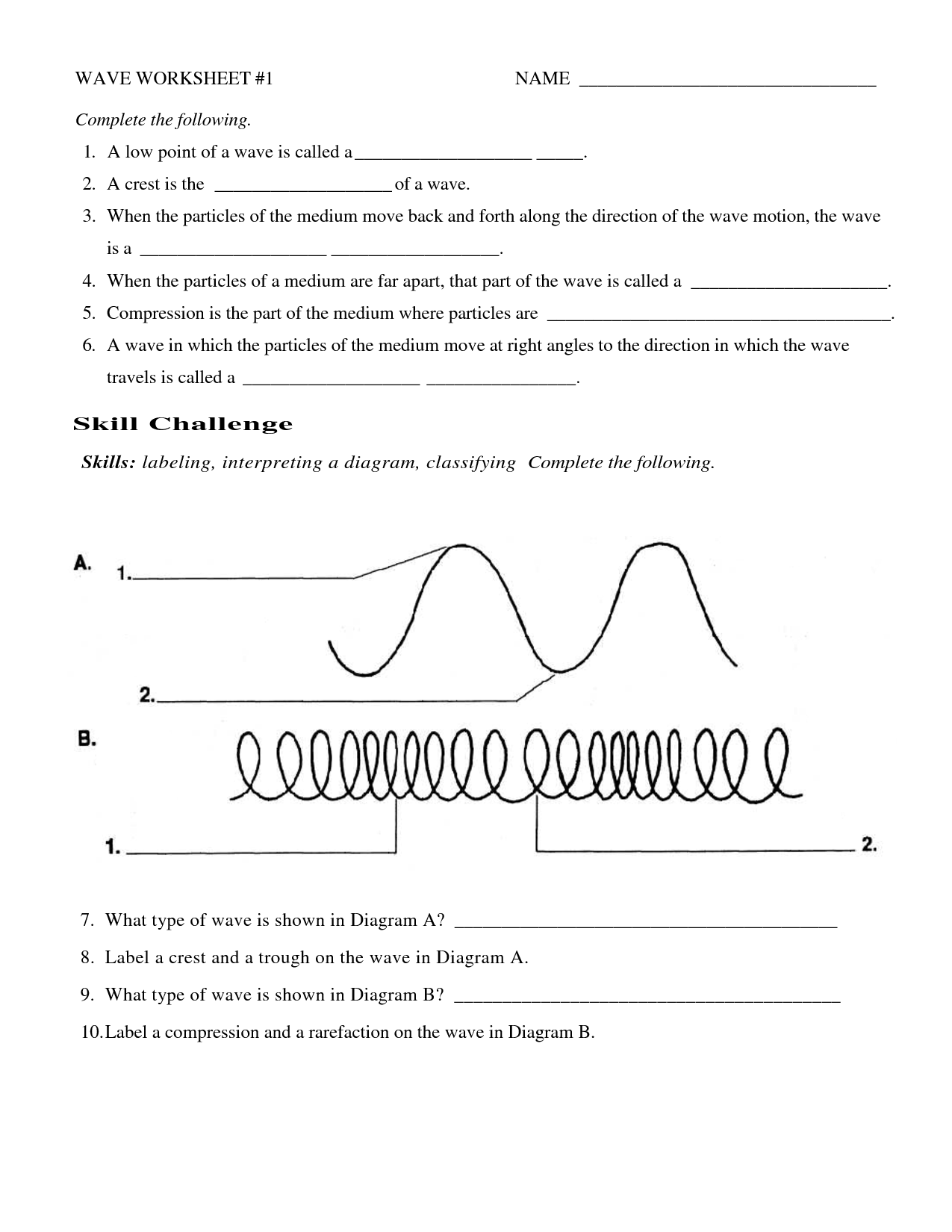
The main difference between a transverse and longitudinal wave lies in the direction of the vibrations relative to the direction of the wave propagation. In a transverse wave, the particles move perpendicular to the direction of the wave, forming crests and troughs. On the other hand, in a longitudinal wave, the particles vibrate parallel to the direction of the wave, causing compressions and rarefactions. Examples of transverse waves include light waves and water waves, while sound waves are a common example of longitudinal waves.
What is the amplitude of a wave?
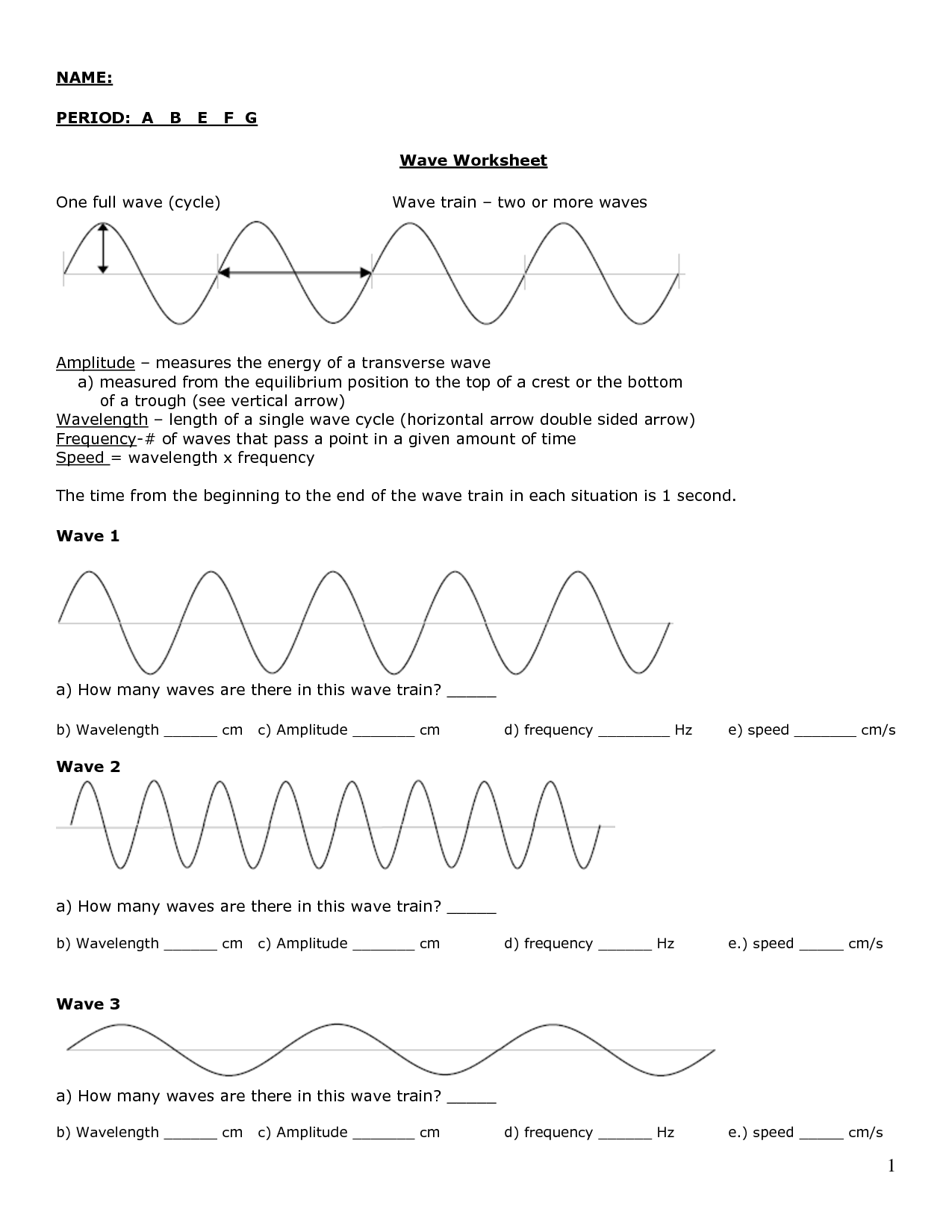
The amplitude of a wave is the measurement of the maximum displacement of a particle in the medium from its equilibrium position when the wave passes through it. It is the maximum height or depth of the wave from the resting position to the peak or trough of the wave.
How is wavelength defined?
Wavelength is defined as the distance between two successive points of a wave that are in phase, such as two crests or two troughs. It is usually measured in units of meters and is used to describe the length of a complete cycle of a wave, including electromagnetic waves like light or sound waves.
What is the frequency of a wave?
The frequency of a wave is the number of complete oscillations or cycles of the wave that occur in a given unit of time, usually measured in hertz (Hz), which represents cycles per second.
What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength?
Frequency and wavelength are inversely proportional to each other. This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is described by the formula: speed of light = frequency x wavelength. So, when the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength must decrease in order to maintain a constant speed of light.
How is wave speed calculated?
Wave speed is calculated by dividing the distance traveled by a wave by the time it takes to travel that distance. The formula to calculate wave speed is speed = distance/time. This can be applied to any type of wave, including sound waves, water waves, and electromagnetic waves.
How do waves transfer energy?
Waves transfer energy through the vibration or movement of particles in a medium, such as water or air. As the wave travels, it causes the particles in the medium to oscillate or move in a back-and-forth motion, transferring energy from one particle to the next. This propagation of energy continues along the wave's path until it reaches its destination.
What are some examples of common waves in everyday life?
Some examples of common waves in everyday life include light waves (such as those from the sun or artificial lights), sound waves (from speaking or music), water waves (in oceans, rivers, or ponds), and radio waves (used in communication devices like radios and cell phones).
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments