Postulates and Theorems Worksheets
Postulates and theorems are fundamental concepts in mathematics, helping us to understand the rules and principles that govern geometric shapes and their properties. Whether you're a student looking to reinforce your knowledge or a teacher searching for additional resources for your classroom, these postulates and theorems worksheets are designed to provide an excellent learning experience for anyone looking to dive deeper into this intriguing subject.
Table of Images 👆
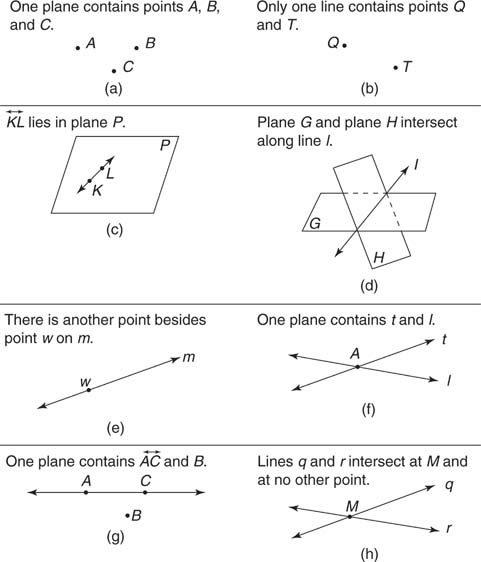
- Points Lines and Planes Worksheet
- Line Geometry Proofs Worksheets
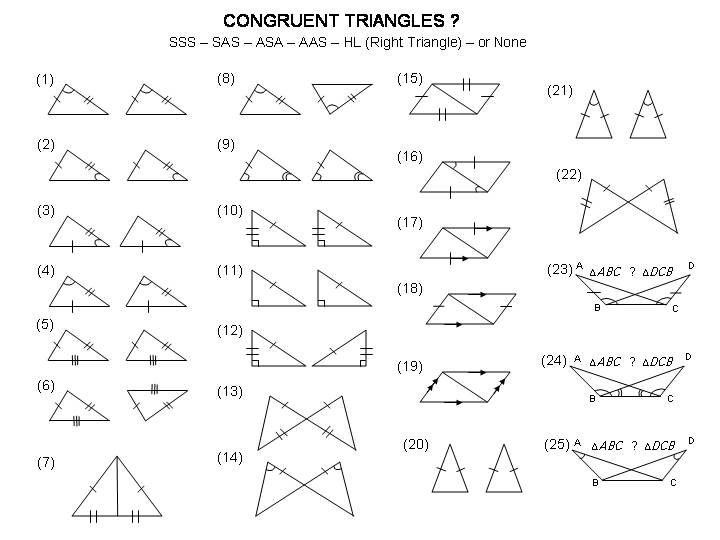
- Congruent and Similar Triangles Worksheet
- Triangle Exterior Angle Theorem Worksheet
- Parallel Lines Geometry Proofs Worksheets
- And Parallel Lines Proofs Worksheet
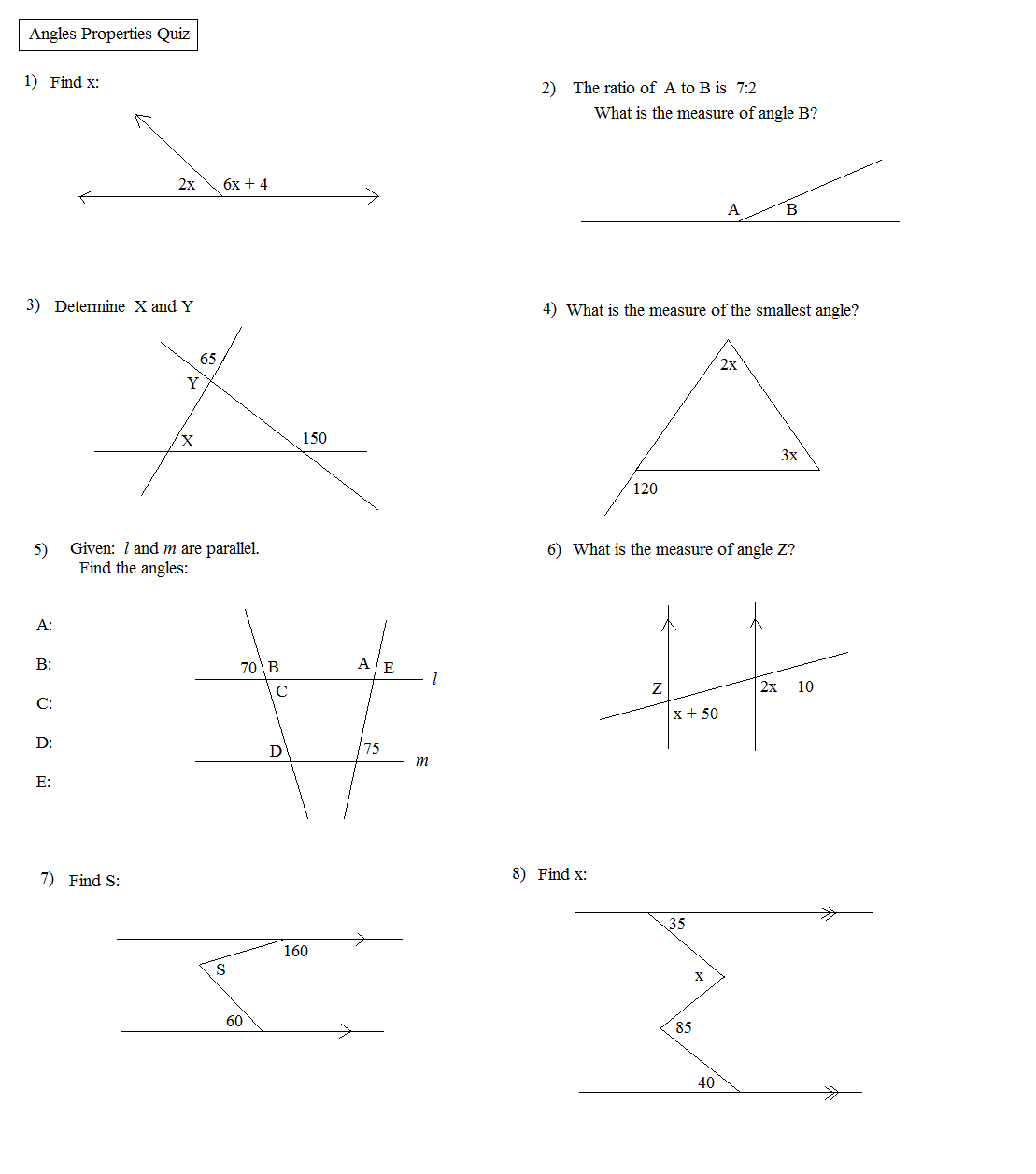
- Angle Properties Worksheet
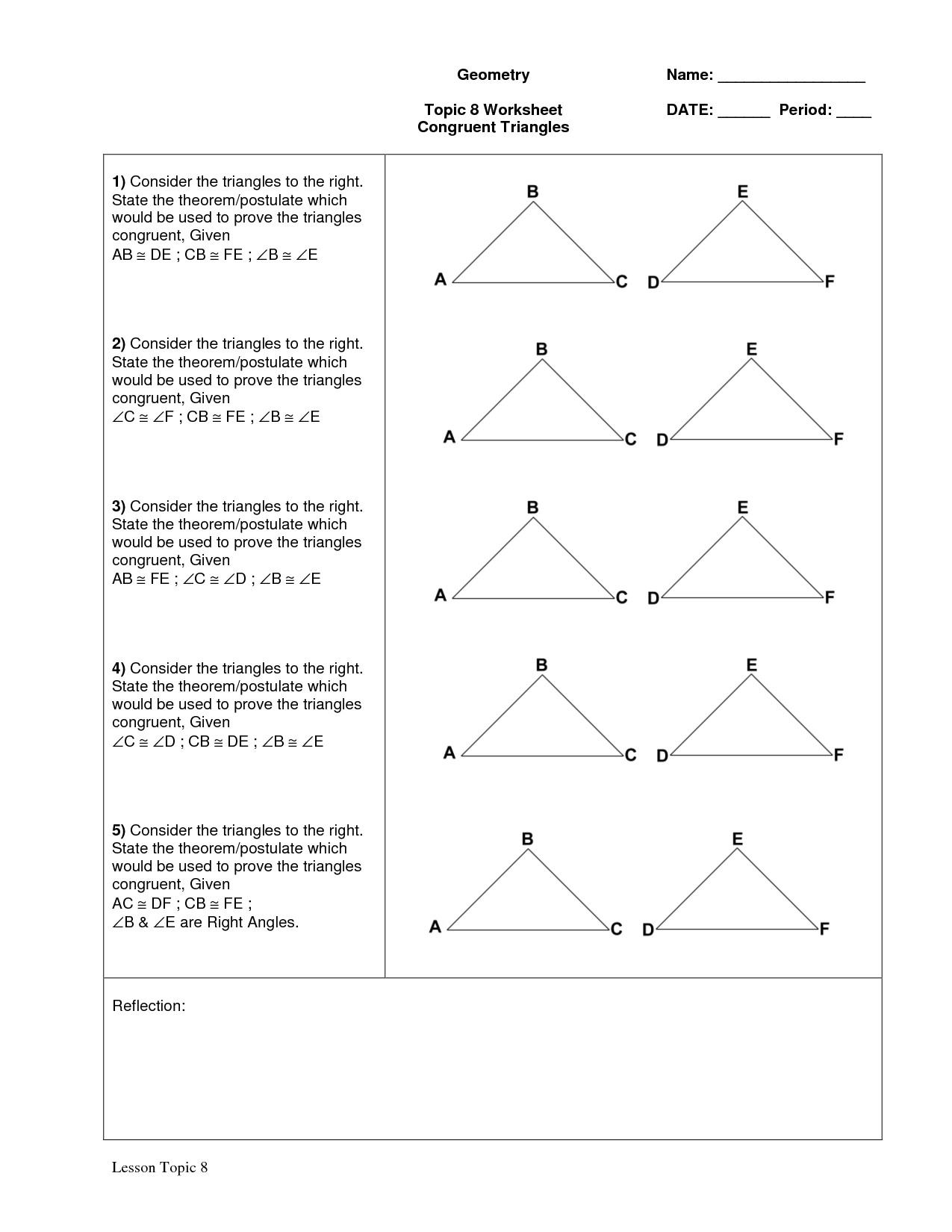
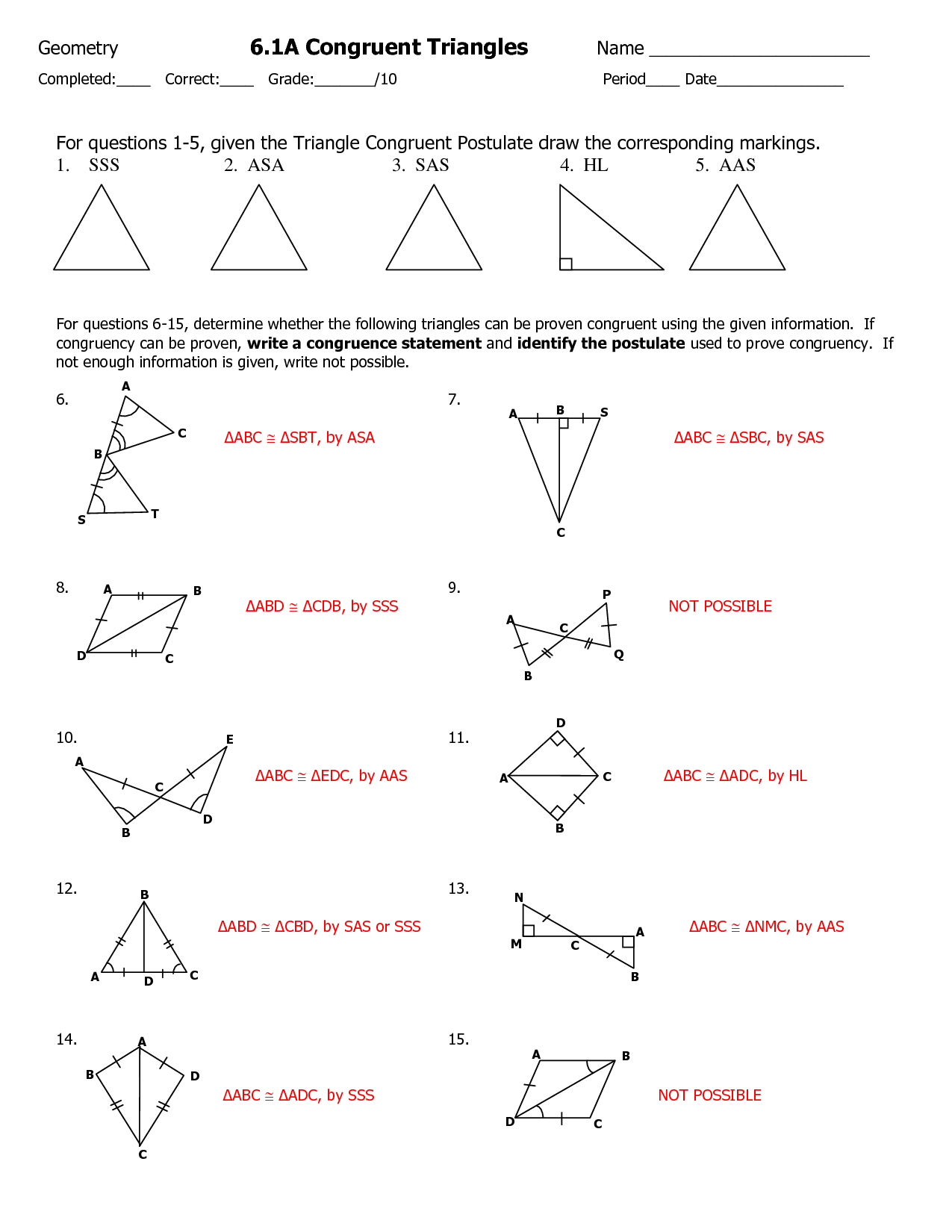
- SSS and SAS Congruent Triangles Worksheet
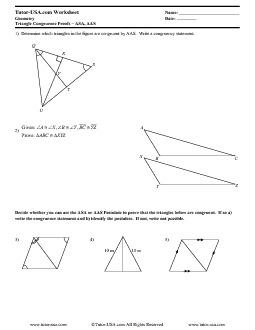
- Geometry Congruent Triangles Worksheet Answers
- Geometry Segment Addition Postulate Worksheet
- Lines Segments and Rays Worksheet
- Asa and AAS Triangle Congruence Proofs Worksheet
- Angle Postulates and Theorems Worksheets
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of postulates and theorems in geometry?
The purpose of postulates and theorems in geometry is to provide a set of fundamental assumptions and logical rules that form the basis for defining geometric concepts and proving geometric statements rigorously. Postulates, also known as axioms, are the basic assumptions that are accepted without proof, while theorems are statements that have been proven using these postulates. Together, postulates and theorems help to establish the logical foundation of geometry and enable mathematicians to deduce new results and properties based on established principles.
How do postulates differ from theorems?
Postulates are basic assumptions or statements that are accepted without proof in a mathematical system, serving as the foundation for further reasoning and deduction. On the other hand, theorems are statements that have been proven to be true based on logical reasoning from the postulates and previously established theorems. In summary, postulates are accepted as true without proof, while theorems are proven statements derived from these accepted assumptions.
What is the importance of understanding and using postulates in geometry?
Understanding and using postulates in geometry is crucial as they serve as the foundation for proving theorems and solving geometric problems. Postulates are fundamental assumptions that are accepted without proof, providing a starting point for developing logical arguments in geometry. By applying postulates correctly, mathematicians can derive new propositions, make connections between geometric concepts, and ultimately deepen their understanding of the spatial relationships and properties of geometric figures. In essence, postulates are like the building blocks of geometric reasoning, enabling mathematicians to construct logical arguments and advance their knowledge in the field of geometry.
How are postulates and theorems used to prove geometric statements?
Postulates are initial assumptions or basic truths accepted without proof, while theorems are statements that are proven using postulates, definitions, and previously proven theorems. In geometry, postulates serve as the foundation for logical reasoning, and theorems are derived from them through deductive reasoning. By using postulates as starting points and applying logical steps in a proof, geometric statements can be established as true based on the accepted truths and rules in the mathematical system.
Can you give an example of a postulate and explain how it is used in geometry?
One example of a postulate in geometry is the "line postulate", which states that two points determine a unique line. This postulate is used in geometry to describe the fundamental relationship between points and lines, allowing us to understand and work with concepts such as line segments, rays, and angles. By accepting this postulate as true, we can build upon it to derive more complex theorems and properties in geometric constructions and proofs.
What criteria must be met for a statement to be considered a theorem?
A statement must be proven based on a set of logical deductions and reasoning within a mathematical or logical system in order to be considered a theorem. It should be derived from previously established axioms, definitions, and other theorems, following a formal proof structure that demonstrates the truth of the statement beyond doubt.
How are theorems proven in geometry?
Theorems in geometry are typically proven using deductive reasoning, where logical arguments are made based on a set of axioms and previously proven theorems. These deductive proofs involve breaking down the given information into logical steps, applying geometric principles and properties, and providing a step-by-step explanation that leads to a valid conclusion. The use of logical reasoning and established rules of geometry ensures the validity and accuracy of the proof for a given theorem.
Can you provide an example of a theorem and explain how it is proved?
One example of a theorem is the Pythagorean Theorem, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. This can be proved using a variety of methods, such as algebraic, geometric, or trigonometric proofs. One common geometric proof involves constructing squares on each side of the triangle and using the properties of similar triangles to show that the areas of the squares satisfy the theorem. This visual and intuitive approach helps provide a clear understanding of why the theorem holds true.
How do postulates and theorems contribute to the overall understanding of geometry?
Postulates and theorems play a crucial role in advancing our understanding of geometry by providing the fundamental rules and principles upon which geometric concepts are built. Postulates serve as the basic assumptions that are accepted without proof, while theorems are statements that are proven using logical reasoning based on these postulates. By applying postulates and theorems, we can deduce new properties, relationships, and patterns within geometric shapes and structures, leading to a deeper comprehension of the principles governing the spatial relationships in our world. Overall, postulates and theorems form the backbone of geometric reasoning and analysis, enabling us to explore and understand the intricacies of shapes, sizes, angles, and dimensions within the domain of geometry.
Why is it important to study and practice with postulates and theorems in geometry?
Studying and practicing with postulates and theorems in geometry is important because they provide the fundamental principles and rules that govern geometric relationships and properties. By understanding and applying these postulates and theorems, students can develop critical thinking skills, logical reasoning abilities, and problem-solving strategies that are essential not only in geometry but also in various areas of mathematics and real-life applications. Moreover, postulates and theorems in geometry serve as the building blocks for constructing mathematical arguments and proofs, ultimately enhancing mathematical literacy and overall cognitive development.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments