Ecosystem Scavenger Hunt Worksheet
The Ecosystem Scavenger Hunt Worksheet is a helpful tool for educators and parents seeking to engage students in hands-on learning about different elements of an ecosystem. This worksheet focuses on its entity and subject - the ecosystem - and offers a variety of activities and questions to encourage students to explore and identify the various components found within a specific ecosystem.
Table of Images 👆
- Scavenger Hunt Worksheet
- Textbook Scavenger Hunt
- Cleverbot Ben
- Beach Scavenger Hunt List
- Food Nutrient Cycle Worksheet
- Topographic Maps Worksheets 8th Grade
- Ocean Printable Worksheets
- Endocrine System Worksheets
- Types of Ecosystems Foldable
- Diagrams Respiratory System Coloring Worksheets
- Diagram of Lateral Lower Leg
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of an ecosystem?
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their environment, interacting as a system. This includes plants, animals, and microorganisms interacting with each other and the physical environment they inhabit, such as soil, water, and air. Ecosystems can vary in size and complexity, but all are characterized by the interdependence of the organisms within them and the flow of energy and nutrients between the living and nonliving components.
Name three examples of biotic factors within an ecosystem.
Three examples of biotic factors within an ecosystem are plants, animals, and fungi. These living organisms interact with each other and their environment, playing crucial roles in the functioning and dynamics of the ecosystem.
What are two examples of abiotic factors within an ecosystem?
Two examples of abiotic factors within an ecosystem are sunlight and temperature. Sunlight is essential for photosynthesis, a process by which plants produce energy, while temperature plays a crucial role in determining the types of organisms that can thrive in a specific environment. Both of these factors have significant impacts on the overall structure and function of ecosystems.
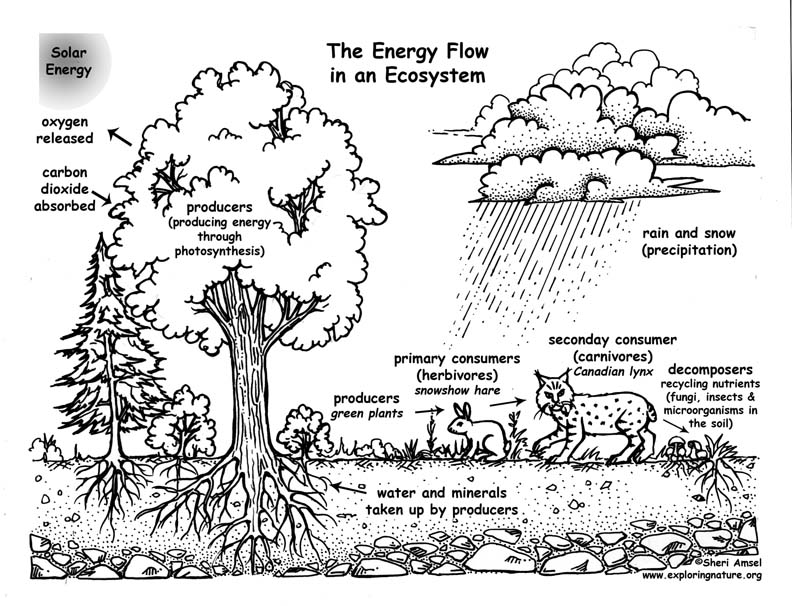
Describe the role of producers in an ecosystem.
Producers, such as plants and algae, play a crucial role in an ecosystem by converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. They are the foundation of the food chain, providing energy and nutrients for other organisms. Producers also release oxygen as a byproduct of photosynthesis, which is essential for the survival of many organisms. Their abundance and health directly affect the overall health and biodiversity of the ecosystem.
Explain the difference between a herbivore and a carnivore.
A herbivore is an animal that mainly consumes plant material as their primary source of food, while a carnivore is an animal that primarily feeds on other animals. Herbivores have evolved to efficiently digest plant matter, often possessing specialized teeth and digestive systems for processing plant cellulose. Carnivores, on the other hand, have sharp teeth and claws for hunting and tearing apart the flesh of other animals, as well as shorter digestive tracts suited for digesting high-protein animal tissues.
What is the purpose of decomposers within an ecosystem?
Decomposers play a vital role in the ecosystem by breaking down dead organic matter like plants and animals into simpler substances, such as minerals and nutrients. This process, known as decomposition, releases these essential nutrients back into the soil, making them available for uptake by plants for growth and productivity. Ultimately, decomposers help facilitate nutrient cycling and energy flow within ecosystems, contributing to the overall health and functioning of the environment.
Define the term "food chain" and provide an example.
A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms where each member serves as a source of food for the next. An example of a food chain is grass (producer) being eaten by a grasshopper (primary consumer), which is then consumed by a frog (secondary consumer), which in turn is preyed upon by a snake (tertiary consumer).
Describe the concept of a food web and why it is more realistic than a food chain.
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that illustrate the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. It is more realistic than a food chain because it accounts for the multiple interconnected relationships and interactions between various species in an ecosystem. In nature, organisms often have more than one source of food and are also consumed by multiple predators, creating a more intricate and realistic representation of the complexity of energy flow and ecosystem dynamics. This interconnectedness better reflects the true relationships in an ecosystem and the diversity of species that rely on each other for survival.
Explain the importance of energy flow within an ecosystem.
Energy flow within an ecosystem is crucial as it is the driving force behind all ecological processes. It involves the transfer of energy from one organism to another through food chains and food webs, ultimately sustaining life. Organisms use this energy for growth, reproduction, and metabolic processes, while also influencing the population dynamics and interactions within an ecosystem. Without this continuous flow of energy, ecosystems would collapse, leading to cascading effects on biodiversity and ecosystem stability. In essence, energy flow is essential for maintaining the balance and functioning of ecosystems.
Describe the relationship between predators and prey within an ecosystem.
Predators and prey have a dynamic and interdependent relationship within an ecosystem where predators hunt and consume prey as a source of food. This interaction plays a crucial role in controlling the population of prey species, ensuring a balance within the ecosystem. Predators help maintain the health and diversity of the ecosystem by controlling the population of prey species, preventing overgrazing and ensuring a sustainable food chain. Additionally, the presence of predators can influence the behavior, distribution, and evolution of prey species, leading to a complex and intricate web of interactions that shape the overall dynamics of the ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments