Ecosystem Pyramid Worksheet
Are you a biology enthusiast looking to strengthen your understanding of ecosystem dynamics? If so, you're in the right place! In this blog post, we will introduce you to the world of ecosystem pyramid worksheets, a valuable resource for learning about the interconnections and hierarchy within ecosystems. These worksheets provide a structured way to explore various ecological relationships, understand the flow of energy, and identify different organisms' roles within an ecosystem.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
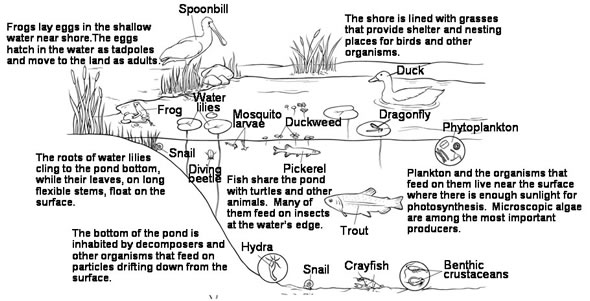
What is an ecosystem pyramid?
An ecosystem pyramid, also known as an ecological pyramid, is a graphical representation of the trophic levels within an ecosystem, illustrating the flow of energy or biomass from one level to another. It typically shows the relationship between producers, primary consumers, secondary consumers, and tertiary consumers, with each level representing a decrease in energy or biomass as it moves up the pyramid. This visual representation helps to demonstrate the interconnectedness and complexity of energy transfer within an ecosystem.
What are the different levels or trophic levels in an ecosystem pyramid?
The trophic levels in an ecosystem pyramid are typically categorized into four main levels: producers (autotrophs), primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and tertiary consumers (top predators). Producers, such as plants, generate energy through photosynthesis. Primary consumers, like rabbits, feed on producers. Secondary consumers, like foxes, prey on primary consumers. Tertiary consumers, such as eagles, are at the top of the food chain and consume other consumers. Each trophic level plays a critical role in the transfer of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem.
Describe the producers in an ecosystem pyramid.
Producers are the base of an ecosystem pyramid, responsible for converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. They include plants, algae, and some types of bacteria that provide food for other organisms. Producers play a crucial role in transferring energy from the sun to the rest of the ecosystem, serving as the foundation for all other trophic levels.
What do primary consumers feed on in an ecosystem pyramid?
Primary consumers, located at the second trophic level of an ecosystem pyramid, feed on producers. These consumers are typically herbivores that consume plants and algae as their primary source of energy and nutrients in the food chain. This transfer of energy from producers to primary consumers represents the beginning of the flow of energy through the ecosystem.
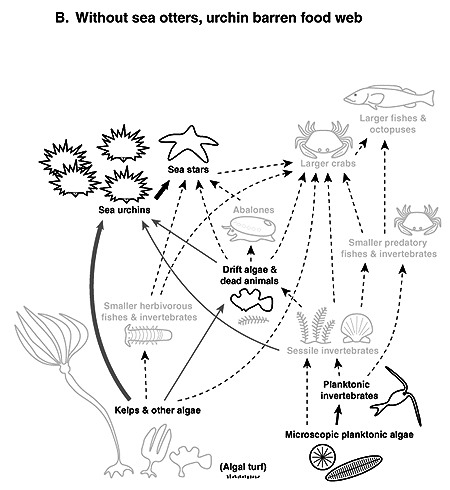
Explain the role of secondary consumers in an ecosystem pyramid.
Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in an ecosystem pyramid, playing a crucial role in regulating the populations of primary consumers and contributing to the energy flow within the ecosystem. These consumers primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, and in turn are preyed upon by tertiary consumers. By controlling the population of primary consumers, secondary consumers help maintain the balance of species within the ecosystem. Their presence also transfers energy from one trophic level to another, ultimately supporting the overall biodiversity and health of the ecosystem.
Describe the tertiary consumers in an ecosystem pyramid.
Tertiary consumers in an ecosystem pyramid are the top predators that feed on secondary consumers, which in turn feed on primary consumers. They are typically apex predators, such as lions, killer whales, or eagles, that are at the highest trophic level in the food chain. Tertiary consumers play a crucial role in regulating the population levels of other species and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
What are decomposers and how do they fit into the ecosystem pyramid?
Decomposers are organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead organic matter into smaller molecules, releasing nutrients back into the environment. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem pyramid by recycling nutrients and energy from dead organisms, which then becomes available to primary producers like plants. This process of decomposition is essential for maintaining the balance of nutrients in the ecosystem and supporting the overall health and functioning of the ecosystem.
What is the significance of energy transfer in an ecosystem pyramid?
Energy transfer in an ecosystem pyramid is significant because it illustrates the flow of energy through different trophic levels of an ecosystem, showing how energy is transferred from producers to herbivores to carnivores. This transfer of energy is essential for sustaining life within the ecosystem, as energy is needed for all biological processes such as growth, reproduction, and movement. The pyramid shape represents the decrease in available energy as it moves up the trophic levels, with the majority of energy being lost as heat during each transfer. Understanding energy transfer in an ecosystem pyramid helps ecologists study the efficiency and dynamics of energy flow within ecosystems, which is crucial for maintaining balance and stability in natural environments.
How does the biomass change as you move up the trophic levels in an ecosystem pyramid?
As you move up the trophic levels in an ecosystem pyramid, the biomass generally decreases. This is because each trophic level only retains about 10% of the energy from the level below, with the rest being lost as heat during metabolism. Therefore, as energy is transferred from producers (first trophic level) to herbivores (second trophic level) to carnivores (higher trophic levels), the amount of biomass decreases due to this energy loss, resulting in a pyramid-shaped distribution of biomass in an ecosystem.
What are the potential consequences of disruption or imbalance in an ecosystem pyramid?
Disruption or imbalance in an ecosystem pyramid can have significant consequences, such as a decline in biodiversity, loss of key species, disruption of food chains, and a decrease in ecosystem stability. This can lead to an increase in invasive species, spread of diseases, and ultimately, ecosystem collapse. Additionally, it can impact the availability of resources, such as food and water, for both wildlife and humans, leading to negative effects on the entire ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments