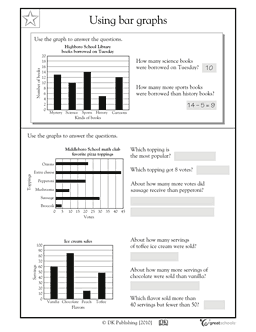
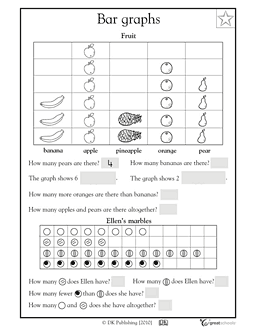
Comparing Bar Graphs Worksheet
Bar graphs are a useful tool for visual representation of data sets, making them a valuable resource for students or individuals who want to develop their data analysis and interpretation skills. Understanding the patterns and trends in bar graphs can help students grasp concepts relating to statistics, business, and social sciences. In this blog post, we will explore a worksheet that focuses on comparing bar graphs, allowing students to enhance their ability to analyze and draw conclusions from various types of data.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a bar graph?
A bar graph is a visual representation of data using rectangular bars of different lengths to show the frequency or distribution of categories or values. The bars are typically drawn horizontally or vertically, with the length of each bar proportional to the value it represents, making it easy to compare and analyze data at a glance.
How are bar graphs used to compare data?
Bar graphs are used to visually represent and compare data by showing the relationships and differences between different variables or categories. Each bar in the graph represents a category, with the length or height of the bar corresponding to the value of that category. By looking at the lengths of the bars, viewers can easily compare the data and identify patterns, trends, and relative sizes of the different categories being compared.
What are the key components of a bar graph?
The key components of a bar graph include the x-axis (horizontal axis) representing categories or groups being compared, the y-axis (vertical axis) representing the values being measured, bars that visually display the data for each category, spacing between the bars to separate categories, and a title to describe the data being presented. Additionally, labels on the axes and bars, a key or legend for different colors or patterns used in the bars, and numerical values or percentages on the bars may also be included to enhance understanding.
How can you determine the scale of a bar graph?
To determine the scale of a bar graph, you need to look at the range of values being represented in the data being plotted on the graph. Calculate the difference between the highest and lowest values in your data set, and then determine an appropriate scale that clearly represents this range while also fitting neatly and evenly across the axis of your graph. Make sure to label your axes appropriately and use increments that are easy to read and interpret for the viewer.
What are the advantages of using a bar graph for data comparison?
Bar graphs are advantageous for data comparison because they provide a visual representation of data that is easy to interpret at a glance. They allow for quick and straightforward comparisons between different categories or groups of data, making it simple to identify trends, patterns, and relationships. Additionally, bar graphs are effective in highlighting differences in the data and are especially useful for showcasing relative sizes and proportions of each category, making them a popular choice for presenting data in a clear and concise manner.
How are different categories or variables represented on a bar graph?
Different categories or variables are represented on a bar graph by using the horizontal axis to represent the categories or variables, and the vertical axis to represent the numerical values associated with each category or variable. Each category or variable is represented by a separate bar on the graph, with the length or height of the bar corresponding to the value being represented. This visual representation allows for easy comparison between different categories or variables.
How can you interpret the height of a bar on a graph?
The height of a bar on a graph typically represents a specific value or quantity being measured or compared. It can convey information such as frequency, magnitude, quantity, or any other numerical data relevant to the context of the graph. The taller the bar, the higher the value it represents, while shorter bars indicate lower values. By comparing the heights of the bars in a graph, one can easily visualize and understand patterns, trends, or comparisons within the data set being presented.
How can you compare data using multiple bar graphs?
To compare data using multiple bar graphs, you can visually examine the height or length of the bars for each category or group being compared across the different graphs. Look for patterns, differences, and similarities in the shape, size, and positioning of the bars to identify trends or variations in the data. Pay attention to any differences in scale or axes between the graphs to ensure accurate and fair comparisons.
What are some common mistakes to avoid when comparing bar graphs?
When comparing bar graphs, common mistakes to avoid include not ensuring the bars are proportional to the data they represent, not using a consistent scale or axis labels that can misrepresent the data, comparing bars that do not start from a common baseline, comparing bars that represent different categories or units, and not providing enough context or explanation for the comparison being made. It is important to accurately represent the data in a clear and understandable way to draw valid conclusions from the comparison.
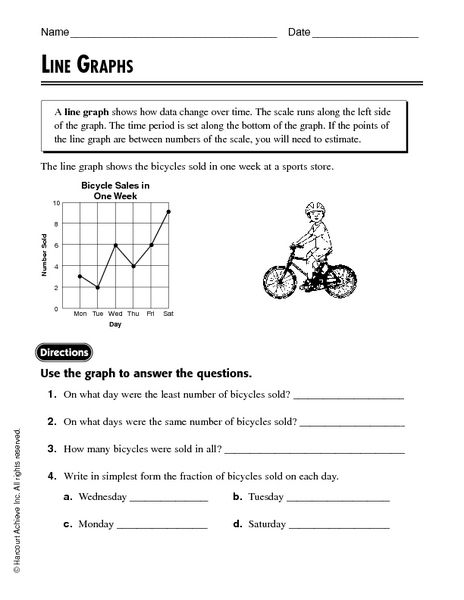
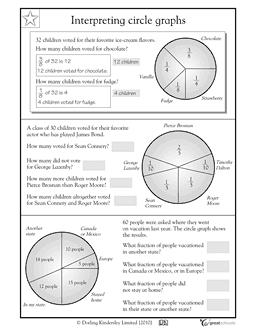
In what situations would it be more appropriate to use a different type of graph instead of a bar graph?
Different types of graphs are more appropriate in various situations depending on the data being presented. For example, line graphs are better suited for showing trends over time, pie charts are ideal for displaying proportions of a whole, and scatter plots are useful for illustrating the relationship between two variables. When the data requires comparison across categories, histogram or box plot may be more suitable to show distribution and variability. Choosing the most appropriate type of graph depends on the specific objective and the nature of the data being visualized.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments