Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
Are you a science teacher or a student wanting to improve your understanding of atomic structure? Look no further than the Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers! This comprehensive set of answers is designed to complement the Atomic Structure Worksheet, providing clear and concise explanations for each question's entity and subject. With these correct answers at your disposal, you can enhance your knowledge and proficiency in this fundamental area of chemistry.
Table of Images 👆
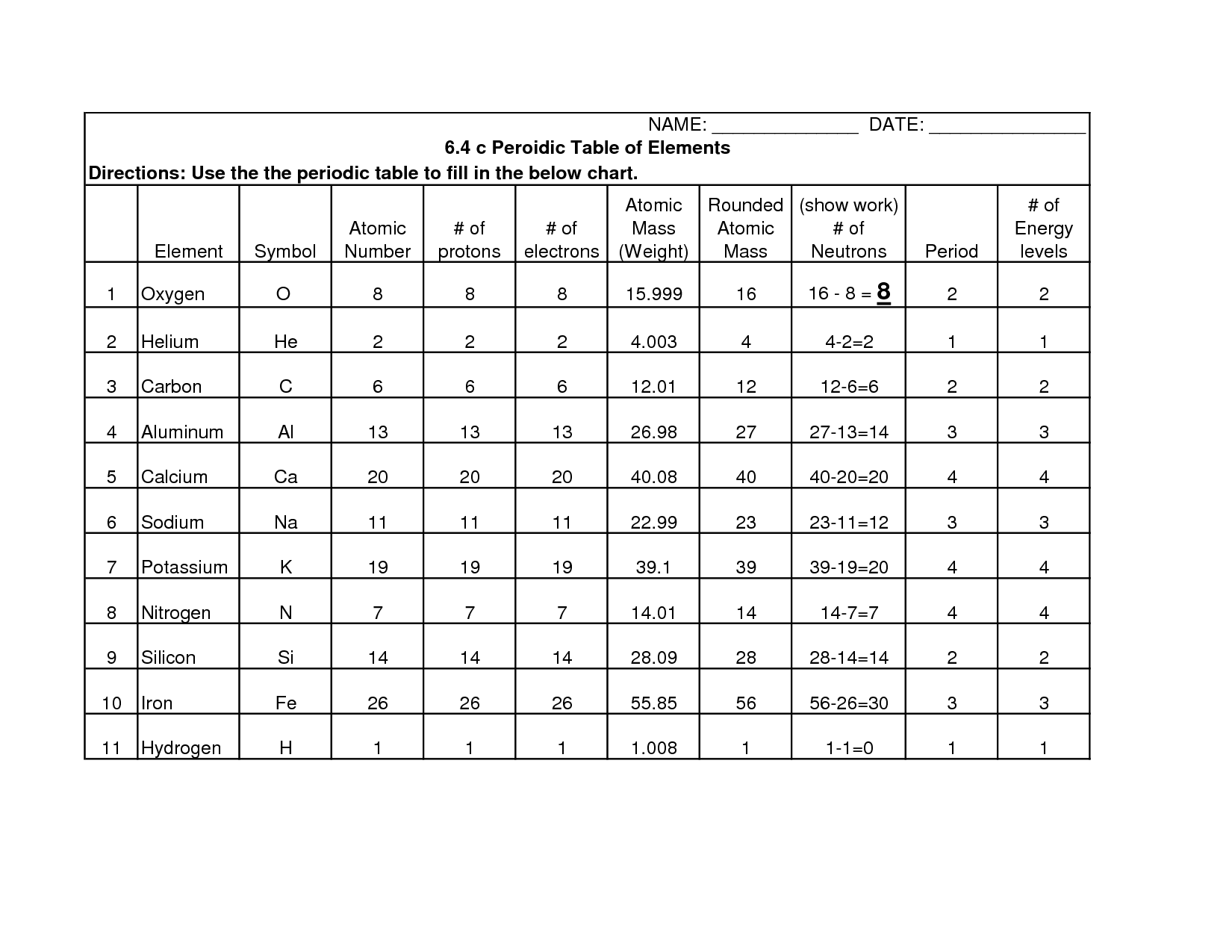
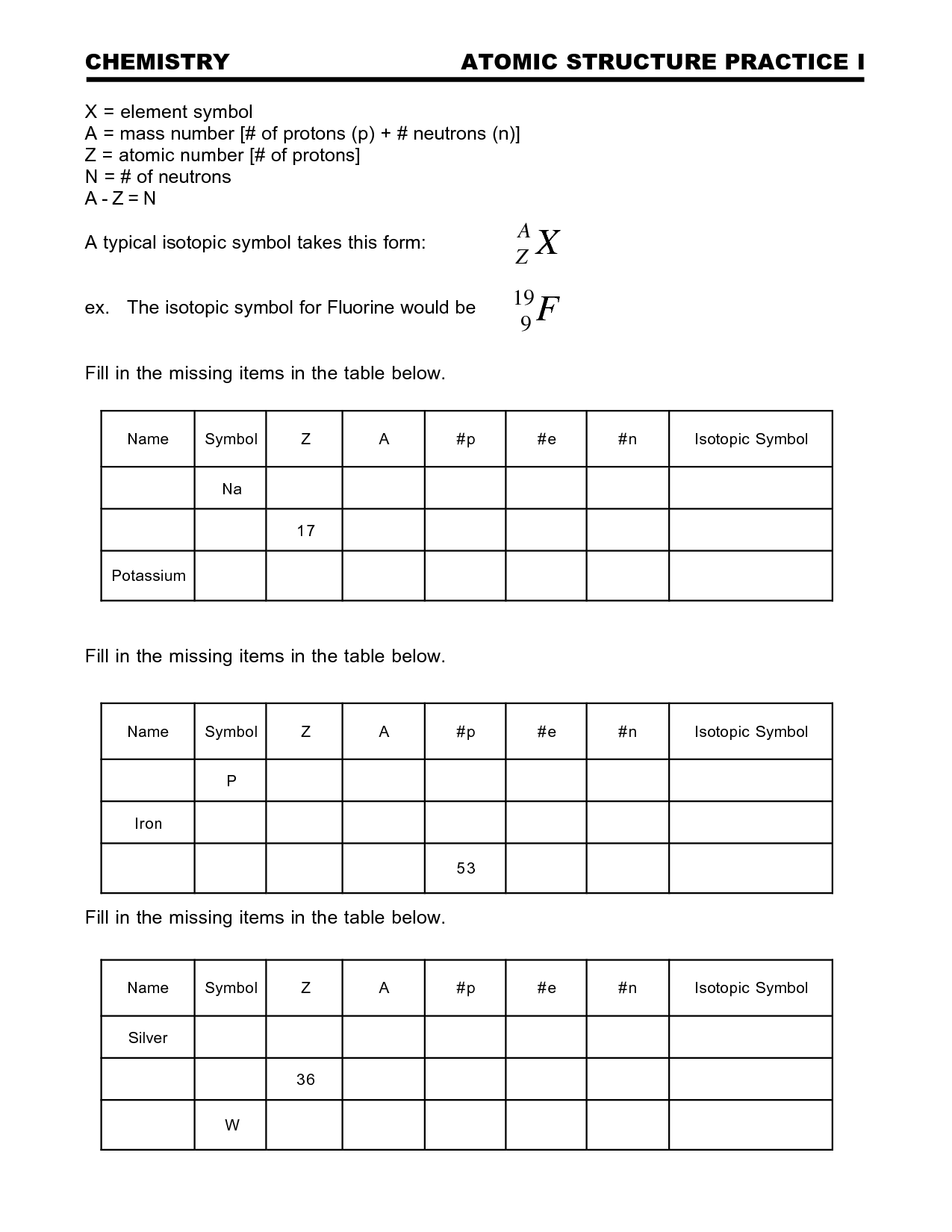
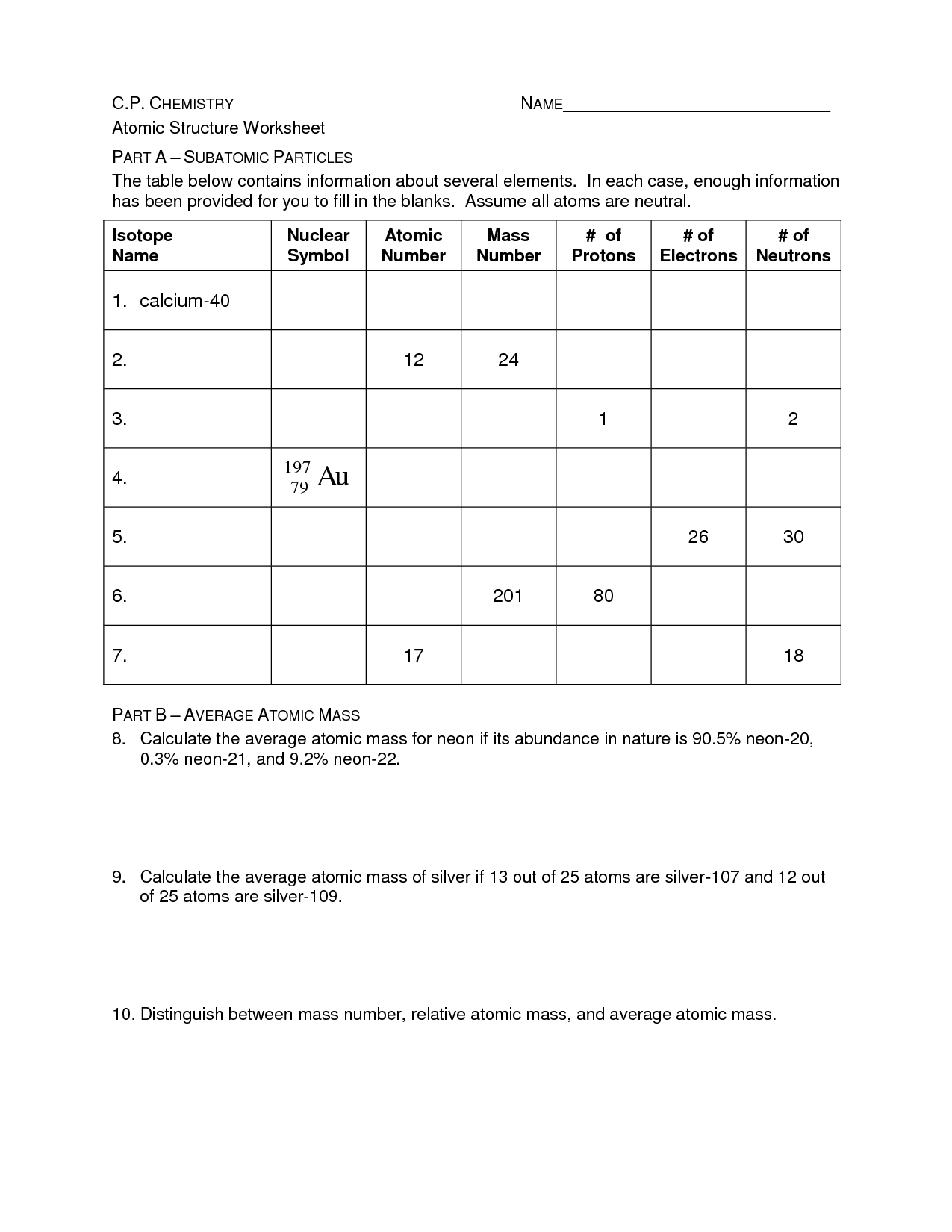
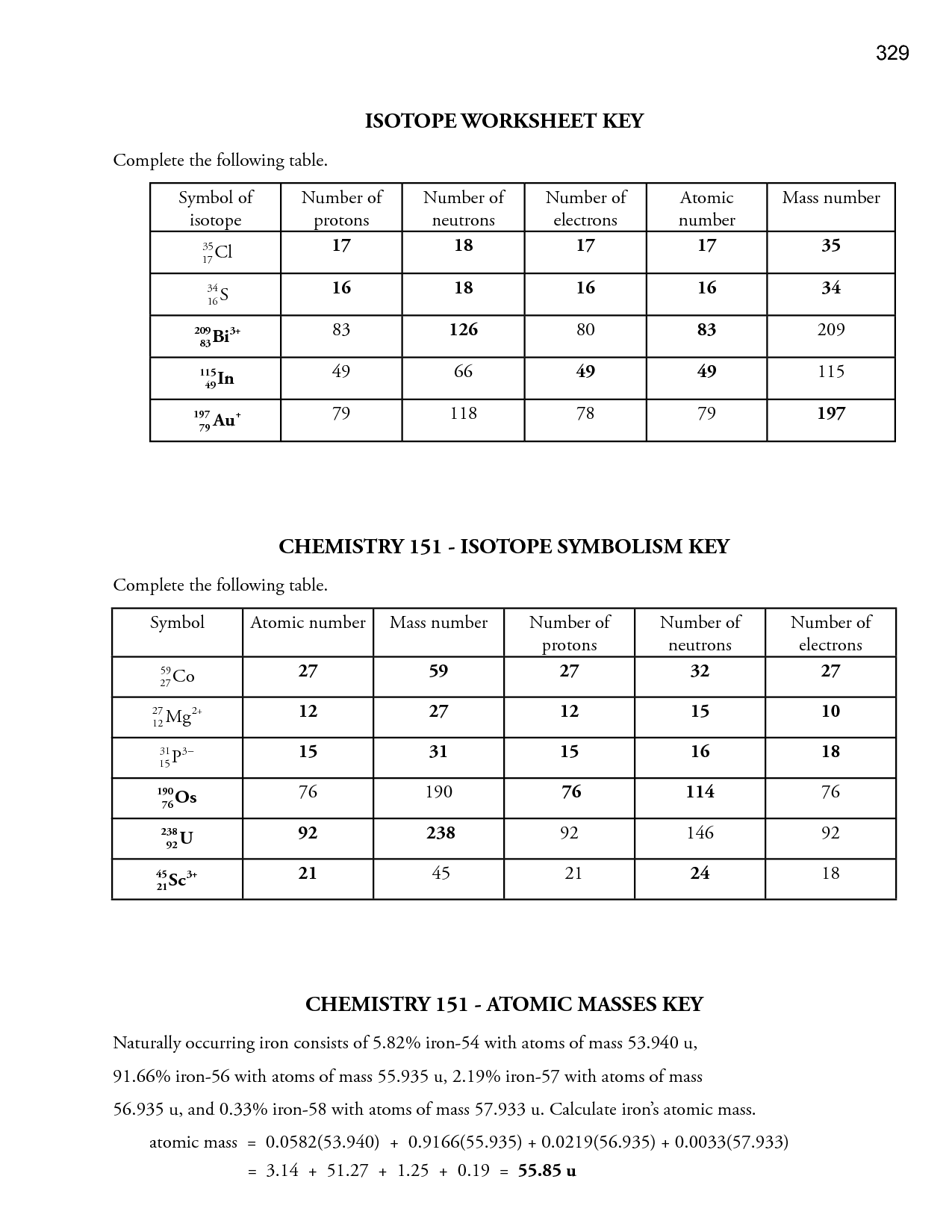
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Practice Worksheet
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Atomic Structure Worksheet
- Average Atomic Mass and Isotopes Worksheet Answer Key
- Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is an atom?
An atom is the smallest unit of matter that retains the properties of an element. It consists of a nucleus composed of positively charged protons and uncharged neutrons, surrounded by negatively charged electrons that orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels. Atoms combine to form molecules, which in turn make up all substances in the universe.
What are the subatomic particles of an atom?
The three main subatomic particles of an atom are protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons carry a positive charge, neutrons have no charge, and electrons carry a negative charge. Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus of the atom, while electrons orbit around the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells.
How are protons and electrons different?
Protons are positively charged particles found in the nucleus of an atom, while electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus. Protons have a much larger mass compared to electrons, with electrons being about 1,800 times lighter than protons. Additionally, protons are involved in determining the element of an atom due to their positive charge, while electrons are responsible for chemical bonding and determining the reactivity of an atom.
What is the role of neutrons in an atom?
Neutrons play a crucial role in an atom by providing stability to the nucleus. They help bind protons together through the strong nuclear force, preventing them from repelling each other due to their positive charges. Neutrons also contribute to the mass of the nucleus without adding any electrical charge, thus helping to balance the overall charge of the atom. Additionally, the number of neutrons in an atom can affect its stability and isotopic identity.
How is the atomic number of an element determined?
The atomic number of an element is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom. It is a unique identifier for each element on the periodic table and is used to classify elements based on their properties. The atomic number is typically found on the top left corner of each element's square on the periodic table.
What is the atomic mass of an element?
The atomic mass of an element is the average mass of all the isotopes of that element, taking into account the abundance of each isotope. It is usually expressed in atomic mass units (amu) and is found on the periodic table beneath the element's symbol.
What is an isotope?
An isotope is a variant of a chemical element that contains a different number of neutrons in its atomic nucleus, leading to variations in atomic mass. Isotopes of an element exhibit similar chemical properties but may have different physical properties such as stability, radioactivity, and behavior in chemical reactions based on their neutron content.
How are ions formed?
Ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons. If an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged and is called an anion. Conversely, if an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged and is called a cation. This process of gaining or losing electrons creates an imbalance in the number of protons and electrons, resulting in the formation of ions.
What is an electron shell?
An electron shell is the grouping of electrons around the nucleus of an atom. Electrons occupy various energy levels or shells, with each shell being associated with a specific energy level and distance from the nucleus. The shells are labeled with numbers (e.g., 1, 2, 3) and can hold a specific maximum number of electrons. The outermost shell, known as the valence shell, is particularly important in determining an atom's chemical properties and its ability to bond with other atoms.
What is the significance of valence electrons in chemical bonding?
Valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom and play a crucial role in chemical bonding. The number of valence electrons determines an atom's reactivity and ability to form bonds with other atoms. Atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to achieve a full outer electron shell (usually 8 electrons), following the octet rule. This process helps atoms attain a more stable and lower energy state, leading to the formation of chemical bonds in molecules and compounds, which ultimately determines the properties and behavior of substances.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments