Protein Synthesis Coloring Worksheet
Are you a biology teacher or student looking for a fun and engaging way to learn about protein synthesis? Look no further! Our Protein Synthesis Coloring Worksheet is the perfect educational tool for understanding this complex biological process. Whether you're completely new to the subject or just need a refresher, this worksheet is designed to make learning about protein synthesis easy and enjoyable.
Table of Images 👆
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- DNA Model Cut Out Worksheets
- Photosynthesis Coloring Worksheet
- DNA and Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
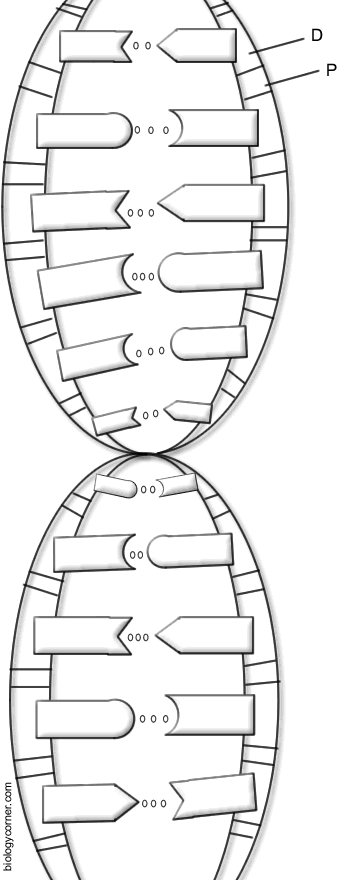
- DNA Double Helix Coloring Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Diagram Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Enzymes Worksheet Review Answer Key
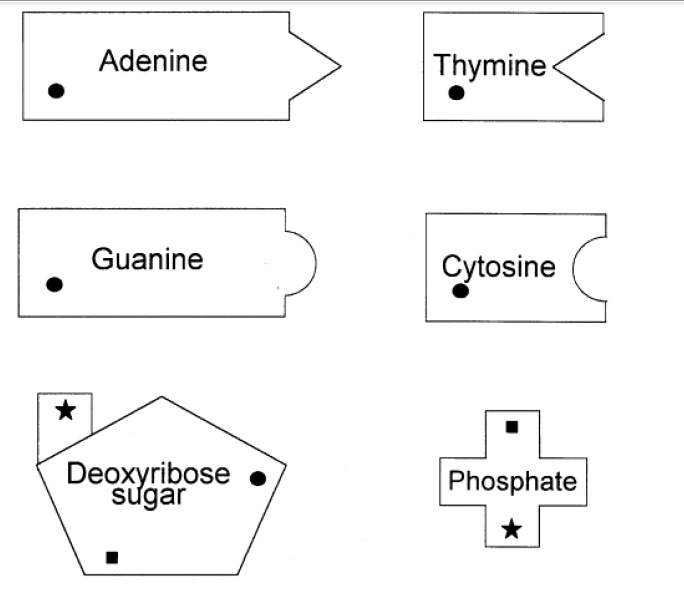
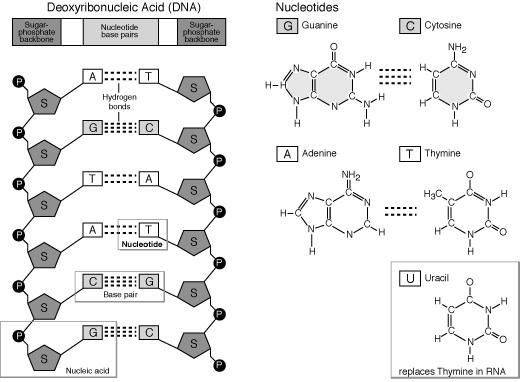
- DNA Nucleotide Structure
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of protein synthesis?
The purpose of protein synthesis is to produce proteins, which are essential molecules in the body that play a crucial role in various functions such as building and repairing tissues, regulating chemical processes, and carrying out biological reactions. Protein synthesis allows cells to create specific proteins by translating the genetic information encoded in DNA into functional proteins that perform specific tasks within the body.
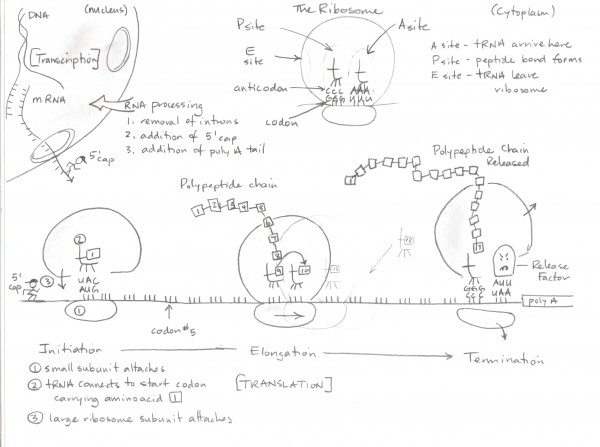
Where does protein synthesis occur in the cell?
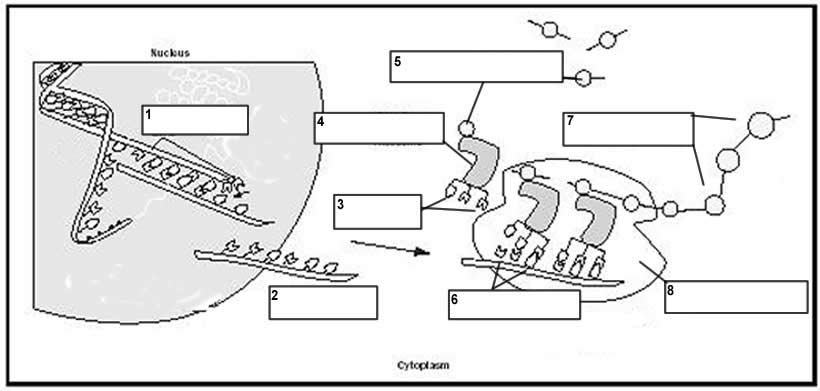
Protein synthesis occurs in the ribosomes of the cell. Ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm, as well as on the endoplasmic reticulum in eukaryotic cells. This process involves the translation of messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins by linking together amino acids in a specific sequence according to the mRNA instructions.
What is the starting molecule in protein synthesis?
The starting molecule in protein synthesis is messenger RNA (mRNA), which carries the genetic information from the DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm where protein synthesis occurs.
What is the process called when DNA is used as a template to produce an RNA molecule?
The process is called transcription.
What is the role of mRNA in protein synthesis?
mRNA, or messenger RNA, plays a crucial role in protein synthesis by carrying the genetic information from the DNA in the cell's nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm. It serves as a template for translating the genetic code into specific amino acids, which are then linked together to form proteins through a process known as translation. Thus, mRNA acts as a messenger that conveys the instructions required for protein synthesis, ultimately contributing to the production of proteins that are essential for various cellular functions.
What is the function of tRNA during protein synthesis?
tRNA, or transfer RNA, functions during protein synthesis by carrying amino acids to the ribosome based on the codons of mRNA. Each tRNA molecule is specific to a particular amino acid, and it recognizes the codon on the mRNA through its anticodon sequence. This ensures that the correct amino acid is added to the growing polypeptide chain according to the genetic code, allowing for precise and accurate protein synthesis.
What are codons and what is their significance in protein synthesis?
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides in mRNA that code for a specific amino acid during protein synthesis. They play a crucial role in the translation process, where the genetic information stored in DNA is transcribed into mRNA and then translated into proteins. Each codon corresponds to a specific amino acid, allowing the correct sequence of amino acids to be assembled to form a functional protein. Additionally, codons also include start and stop signals, initiating and terminating protein synthesis. The genetic code is universal, meaning the same codons code for the same amino acids in all organisms, highlighting the significance of codons in understanding and manipulating genetic information.
What is the site where amino acids are joined together to form a protein?
The site where amino acids are joined together to form a protein is the ribosome, which is a cellular organelle responsible for protein synthesis.
How does protein synthesis differ in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Protein synthesis in eukaryotic cells is more complex and occurs in the nucleus and cytoplasm, involving processes such as mRNA processing and export from the nucleus. In contrast, protein synthesis in prokaryotic cells takes place in the cytoplasm and is a simpler process without a nucleus, often involving simultaneous transcription and translation. Additionally, eukaryotic cells have membrane-bound organelles like ribosomes in the rough endoplasmic reticulum that contribute to protein synthesis, while prokaryotic cells lack these organelles.
Are all protein synthesis processes the same in every cell in the body?
No, all protein synthesis processes are not the same in every cell in the body. Different cell types express different sets of genes and produce different proteins based on their specific functions and requirements. Additionally, variations in gene expression, regulation, and post-translational modifications can result in unique protein synthesis processes in different cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments