Levels of Organization Ecology Worksheet
Worksheets are invaluable tools for students seeking to enhance their understanding of complex concepts. Among the wide variety of educational resources available, worksheets offer a structured format for learners to engage with specific topics. When it comes to the field of ecology, where comprehending the levels of organization is pivotal, a well-designed and informative worksheet can be a game changer. Whether you're a middle school student delving into the intricacies of ecosystems or a high schooler looking to grasp the scope of ecological interactions, a levels of organization ecology worksheet can serve as a helpful companion on your educational journey.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of ecology?
Ecology is the branch of biology that studies the relationships between living organisms and their physical environment, as well as the interactions among organisms within ecosystems.
What are the different levels of ecological organization?
The different levels of ecological organization include individual organisms, populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes, and the biosphere. Individual organisms are the smallest level, followed by populations of a single species in a specific area, then communities of multiple species interacting in the same area, ecosystems encompassing both biotic and abiotic factors, biomes that are large geographical areas with similar climates and vegetation, and finally the biosphere, which is the highest level and includes all living organisms and their environments on Earth.
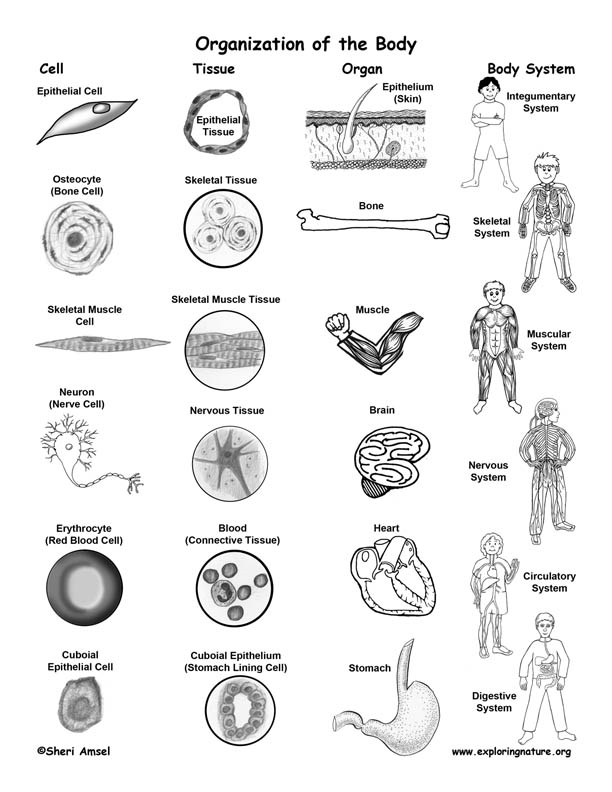
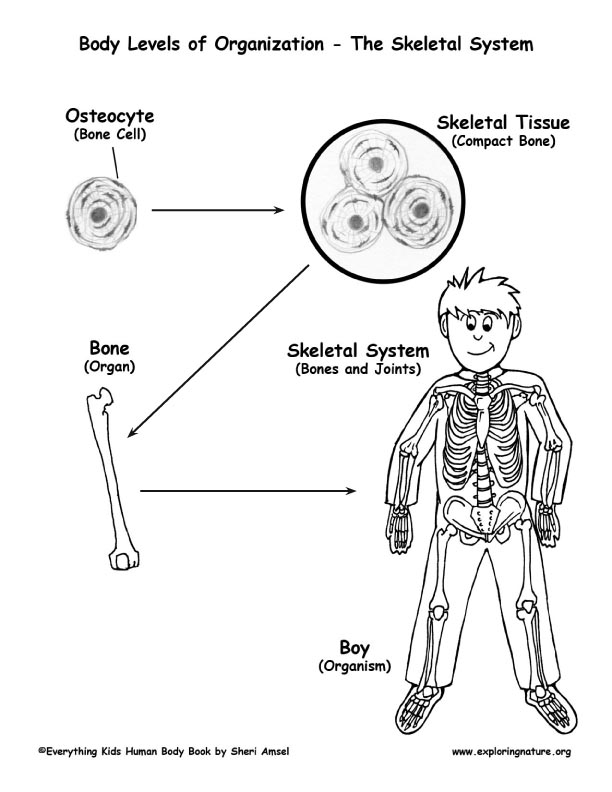
Describe the organization of an individual organism.
An individual organism is organized in a hierarchical structure, starting with cells as the basic unit of life. Cells group together to form tissues such as muscle and nerve tissues. These tissues then combine to create organs like the heart and brain, which work together in organ systems such as the circulatory and nervous systems. All these systems function in harmony to maintain the life processes of the organism, ultimately contributing to its overall health and survival.
Explain the organization of a population.
A population is a group of organisms of the same species that live in the same area and interact with one another. The organization of a population is based on factors such as the size of the population, the distribution of individuals within the area, the age structure of the population, and the dynamics of population growth and decline. Additionally, populations may be organized into smaller groups based on factors such as social structure, mating preferences, or resource availability. Understanding the organization of a population is important for studying ecological processes and for making informed decisions about conservation and management practices.
Discuss the organization of a community.
A community is typically organized through formal and informal structures that help facilitate communication, decision-making, and cooperation among its members. Formal organizations such as local governments, community committees, or non-profit groups often play a role in directing resources, implementing projects, and addressing issues within the community. Informal organizations such as neighborhood associations, social groups, and online communities also contribute to the cohesion and sense of identity within the community. Effective organization in a community is often characterized by open communication, inclusivity, shared goals, and a sense of collective responsibility among its members.
Describe the organization of an ecosystem.
An ecosystem is organized into different levels including individuals (organisms), populations (groups of individuals of the same species), communities (interactions between different populations in a given area), and ecosystems (communities along with abiotic factors such as air, water, and soil). These levels work together in a complex network of interactions where energy and nutrients flow through the system, supporting life and maintaining a balance within the ecosystem. Each organism plays a specific role within this structure, contributing to the overall functioning and stability of the ecosystem.
Explain the organization of a biome.
A biome is organized based on its specific climate, vegetation, and animal life. Biomes are typically classified into categories such as forests, grasslands, deserts, tundra, and aquatic biomes like freshwater and marine ecosystems. Each biome has distinct characteristics that influence the distribution of plants, animals, and microorganisms within it. These biomes are interconnected through complex food webs and nutrient cycles, with organisms adapting to their respective environments to survive and thrive within the biome's unique conditions. The organization of a biome is structured to create a balance and harmony among the different components that make up the ecosystem, ensuring the sustainability and resilience of life within that particular region.
Discuss the organization of the biosphere.
The biosphere is organized into various levels, starting from individual organisms to populations, communities, ecosystems, biomes, and the entire planet. At each level, organisms interact with each other and their environment in complex ways, forming a web of interconnected relationships. These interactions are key to the functioning of the biosphere, allowing for the transfer of energy and nutrients, as well as the maintenance of balance and stability. Overall, the organization of the biosphere reflects the intricate and dynamic nature of life on Earth, demonstrating the interconnectedness and interdependence of all living organisms.
Describe the organization of a food chain.
A food chain is a hierarchical series of organisms in an ecosystem, each dependent on the next as a source of food. At the base of the food chain are producers, such as plants, that make their own food through photosynthesis. Herbivores, or primary consumers, feed on producers. They are then eaten by carnivores, or secondary consumers. The chain continues with tertiary consumers, such as top predators, which are at the highest trophic level. Decomposers, like fungi and bacteria, break down dead organisms and organic matter, returning nutrients to the soil. This flow of energy and nutrients through different organisms in an ecosystem depicts the organization of a food chain.
Explain the organization of a food web.
A food web is a complex network of interconnected food chains that represent the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem. It consists of different organisms - like producers, consumers, and decomposers - arranged into trophic levels based on their position in the food chain. Producers (like plants) are at the base, followed by primary consumers (herbivores), secondary consumers (carnivores), and so on. Organisms can occupy multiple trophic levels, creating a web of interconnected relationships where energy and nutrients are transferred through predator-prey interactions. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of each organism in maintaining the balance and stability of the ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

































Comments