DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
In search of a reliable and comprehensive resource for the DNA the Molecule of Heredity worksheet answer key? You're in the right place! This blog post is dedicated to providing an entity and subject-focused discussion on worksheets that will prove to be an invaluable tool for students studying genetics, biology, or any related field. With a clear and concise approach, we aim to bring you the necessary information without exaggeration or unnecessary fluff. So, let's delve into the world of DNA and uncover the answers you've been seeking.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Molecule Label Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Mutations Worksheet Answers Biology
- Genetics and Heredity Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- Chapter 11 DNA and Genes Worksheet Answers
- DNA Molecule of Heredity Worksheet
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA and RNA Worksheet
- Pedigree Genetics Worksheet Answers
- DNA Structure Concept Map Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the structure of DNA?
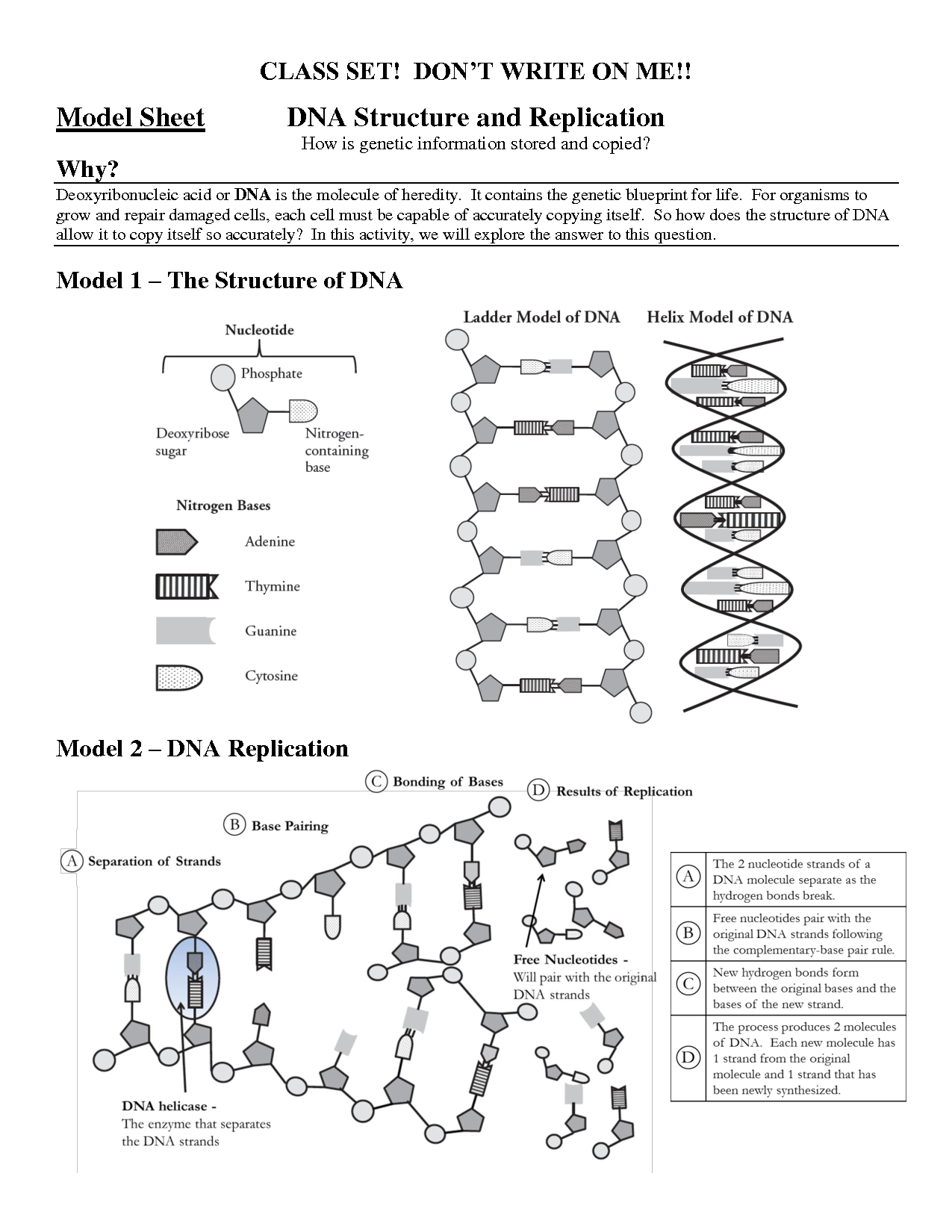
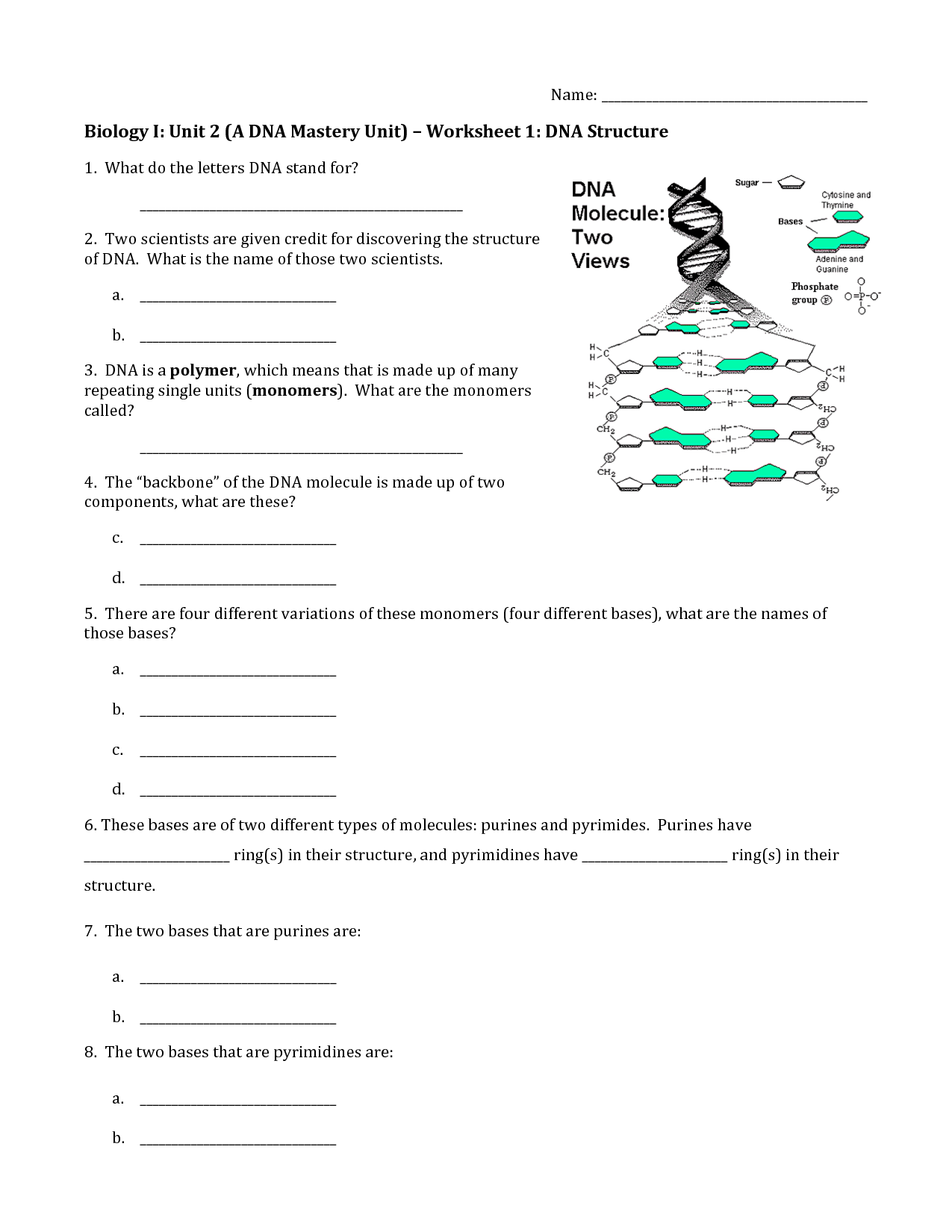
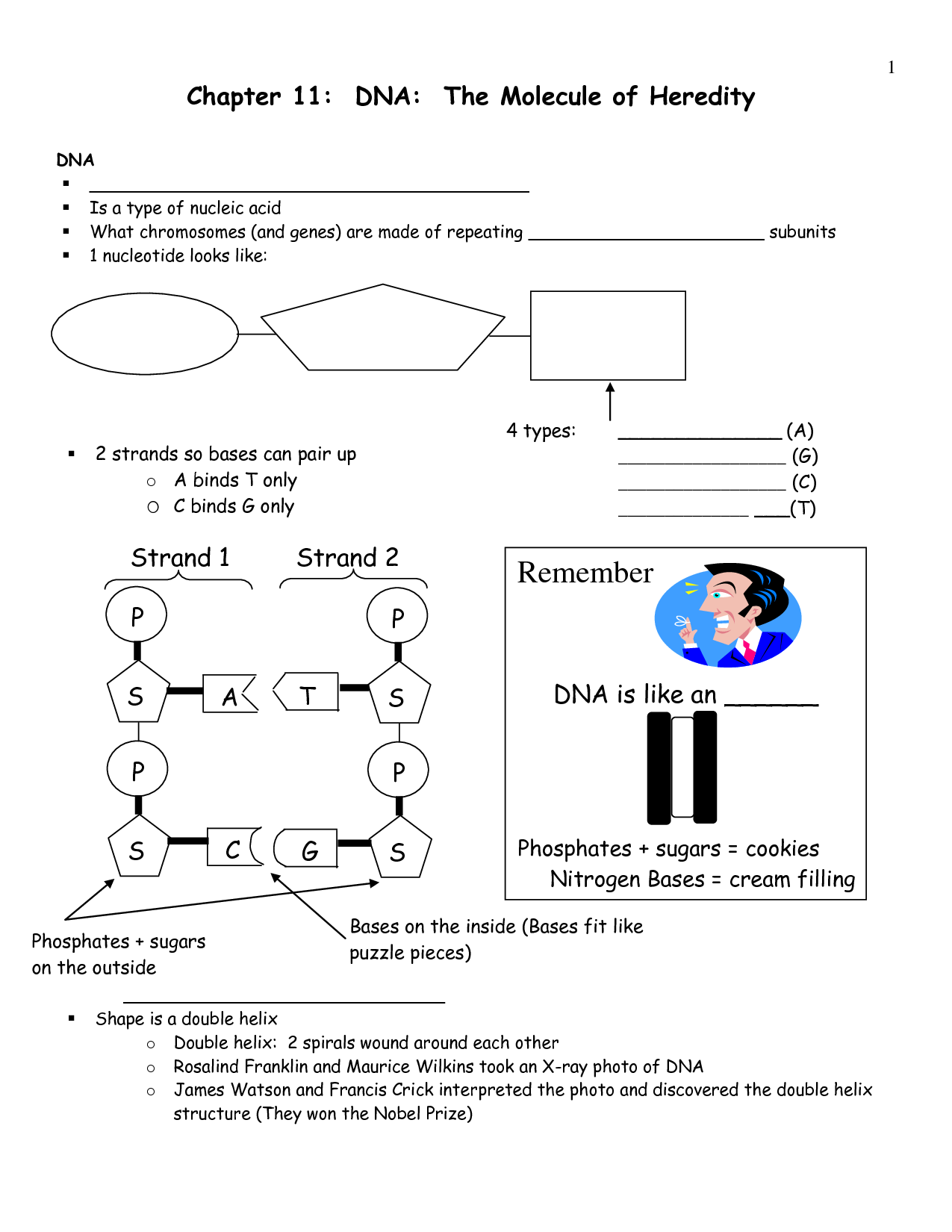
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double-helix structure composed of two long strands coiled around each other. Each strand is made up of nucleotides, which consist of a sugar-phosphate backbone with nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) attached. These bases pair up in a complementary manner, with adenine pairing with thymine and guanine pairing with cytosine, forming the rungs of the DNA ladder. The overall structure of DNA is crucial for storing genetic information and facilitating the process of gene expression.
DNA is a double-stranded helix made up of nucleotides.
Yes, DNA is a double-stranded helix molecule consisting of nucleotides. Each nucleotide in DNA comprises a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base, which can be adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), or guanine (G). The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs, with adenine forming hydrogen bonds with thymine and cytosine with guanine. This structure allows DNA to store genetic information and replicate accurately during cell division.
What are the four nitrogenous bases found in DNA?
The four nitrogenous bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up in specific combinations: A pairs with T, and C pairs with G, forming the building blocks of the double helix structure of DNA.
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine.
These are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA. Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine in the double helix structure of DNA. These base pairs are crucial for the accurate replication and transmission of genetic information during cell division.
How do these bases pair up in a DNA molecule?
In a DNA molecule, the bases pair up in a specific manner: adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T), and cytosine (C) pairs with guanine (G). This is known as complementary base pairing, where A-T and C-G bonds form between the respective bases, creating the double helix structure of DNA.
Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine.
Yes, that is correct. Adenine pairs with Thymine, and Guanine pairs with Cytosine in DNA molecules through hydrogen bonds, forming the complementary base pairs that contribute to the stability and structure of the double helix.
What is the role of DNA in heredity?
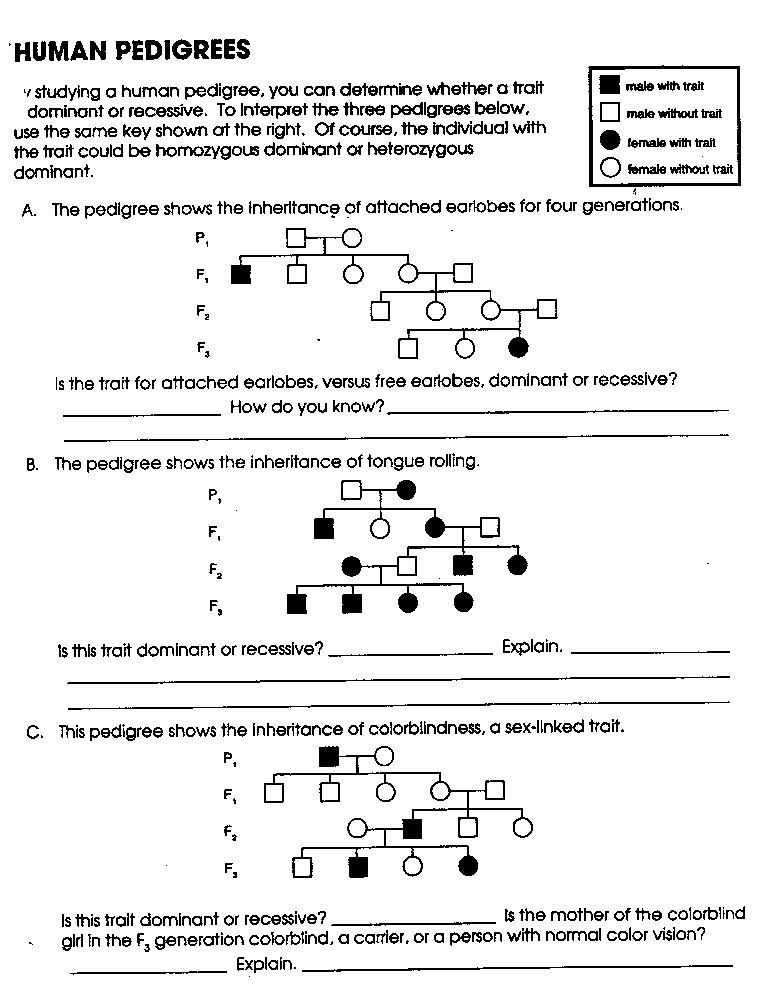
DNA plays a crucial role in heredity as it contains the genetic information that is passed down from one generation to the next. It carries the instructions for how an organism develops and functions, determining traits like eye color, height, and susceptibility to certain diseases. Through processes like replication and gene expression, DNA controls the production of proteins that carry out various functions in the body, ultimately influencing an individual's characteristics and traits that are inherited from their parents.
DNA carries the genetic information that is passed from parents to offspring.
Yes, DNA carries the genetic information that is passed from parents to offspring. It is a molecule that contains the instructions for building and maintaining an organism's cells, tissues, and organs. This information is responsible for determining an individual's traits and characteristics, making it crucial for inheritance and evolution.
How is DNA replicated?
DNA is replicated through a process called semi-conservative replication, where the double helix of DNA unwinds, and each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand. The enzyme DNA helicase unwinds the double helix, creating two single strands. DNA polymerase then adds nucleotides to each single strand according to the base-pairing rule (A pairs with T, and C pairs with G), resulting in two identical double-stranded DNA molecules.
DNA replication occurs through the separation of the two strands and the synthesis of new complementary strands.
DNA replication is the process of duplicating a DNA molecule by separating the two strands and using each strand as a template to create a new complementary strand. This process is essential for cell division and ensuring that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments