Bill Nye Cells Worksheet Answers
Are you a science teacher or a homeschooling parent in search of reliable worksheets on cells? Look no further! We have compiled a comprehensive collection of worksheets that will engage your students and help them understand the fascinating world of cells. Whether you are introducing the topic or reviewing the concepts, our worksheets provide a variety of exercises that focus on the key aspects of cells.
Table of Images 👆
- Bill Nye Cells Worksheet Answer Key
- Bill Nye Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Worksheets
- Bill Nye Video Worksheet Answer Key
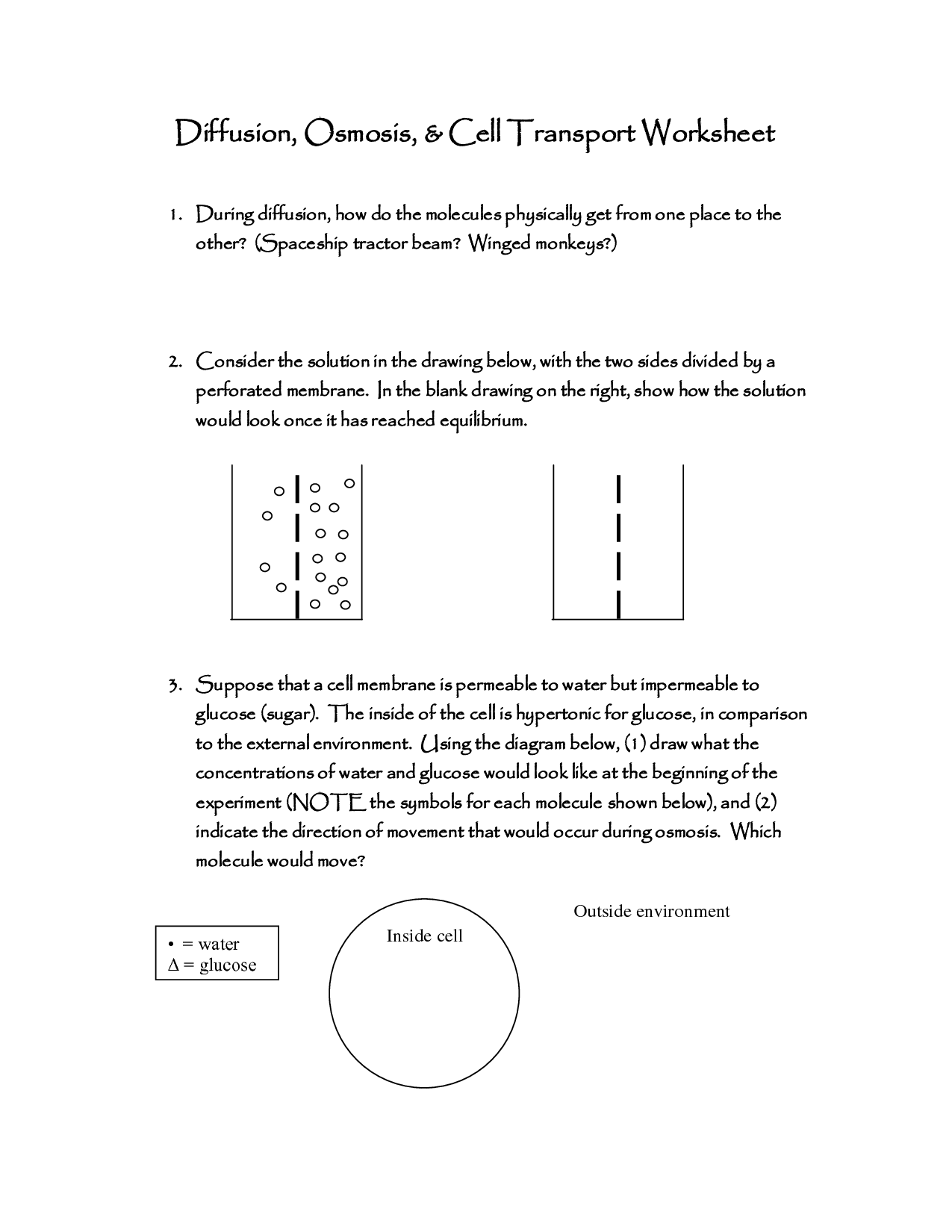
- Diffusion and Osmosis Worksheet Answers
- Bill Nye Atmosphere Worksheet
- Collisions and Momentum Worksheet Answers
- Specific Heat Worksheet Answer Key
- Bill Nye Periodic Table Worksheet
- Bill Nye Science Guy Water Cycle
- Chemical Changes in Matter Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a cell?
A cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that can carry out all the processes necessary for survival, growth, and reproduction. Cells contain organelles that perform specific functions, such as the nucleus which houses the genetic material, mitochondria which produce energy, and the cell membrane which regulates what enters and exits the cell.
What are the main functions of a cell?
The main functions of a cell include maintaining homeostasis, taking in and utilizing energy, replicating DNA for cell division, carrying out specific biochemical reactions, communication with other cells, and responding to external stimuli. Cells also have specialized roles depending on the type of cell, such as nerve cells transmitting signals, muscle cells contracting, and immune cells defending the body against pathogens.
What are the two types of cells and how do they differ?
The two main types of cells are eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are more complex and have a defined nucleus surrounded by a membrane, along with membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria and endoplasmic reticulum. In contrast, prokaryotic cells lack a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, and their genetic material is not enclosed within a nucleus but is instead found in a region called the nucleoid. These differences in structure and complexity lead to various distinctions in the functions and capabilities of these cell types.
What is the difference between plant and animal cells?
The main difference between plant and animal cells is that plant cells have a cell wall made of cellulose, chloroplasts for photosynthesis, and a large central vacuole, while animal cells do not have a cell wall, chloroplasts, or a central vacuole. Additionally, plant cells are generally rectangular in shape and have a rigid structure, while animal cells are typically round or irregular in shape and have a more flexible structure.
What are the three main parts of a cell?
The three main parts of a cell are the cell membrane, which controls what enters and exits the cell, the cytoplasm, which holds all the cell's organelles and is where most cellular processes occur, and the nucleus, which contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls cell activities.
What is the purpose of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane acts as a protective barrier that separates the interior of a cell from its external environment. It regulates the passage of molecules in and out of the cell, allowing for the maintenance of an internal environment conducive to cellular functions. Additionally, the cell membrane also plays a role in cell signaling, cell recognition, and adhesion to other cells or surfaces.
What is the function of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus is the control center of a cell, responsible for containing the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA. It regulates gene expression, coordinates cell activities, and plays a crucial role in cell division. The nucleus also helps protect and organize the DNA, ensuring that essential genetic information is passed on to daughter cells during cell division.
How does a cell obtain energy?
A cell obtains energy through a process called cellular respiration, which involves breaking down glucose molecules to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the primary energy currency of cells. This process occurs in the mitochondria of the cell and involves the step-by-step breakdown of glucose through glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation. ATP molecules generated during cellular respiration are used by the cell to power various biological processes and functions.
What is the role of mitochondria in a cell?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell because their main role is to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration. They also play a key role in regulating cell metabolism, calcium signaling, and apoptosis (programmed cell death). Mitochondria have their own DNA and reproduce independently of the cell through a process called fission. Overall, mitochondria are essential for the survival and functioning of eukaryotic cells.
What is the significance of DNA in a cell?
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a molecule that contains the genetic instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all living organisms. It serves as the blueprint for the synthesis of proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of cells. DNA also plays a crucial role in the inheritance of traits from one generation to the next, making it fundamental to the processes of evolution and diversity in organisms. In short, DNA is significant in a cell because it holds the essential information needed for the survival and functioning of an organism.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments