Basic Distributive Property Worksheets
The Basic Distributive Property Worksheets are designed to help students understand and practice the fundamental concept of the distributive property in a straightforward and engaging way. Whether you're a teacher looking for supplemental materials for your classroom or a parent seeking additional practice for your child, these worksheets offer a structured and comprehensive approach to mastering this essential math concept.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the basic distributive property?
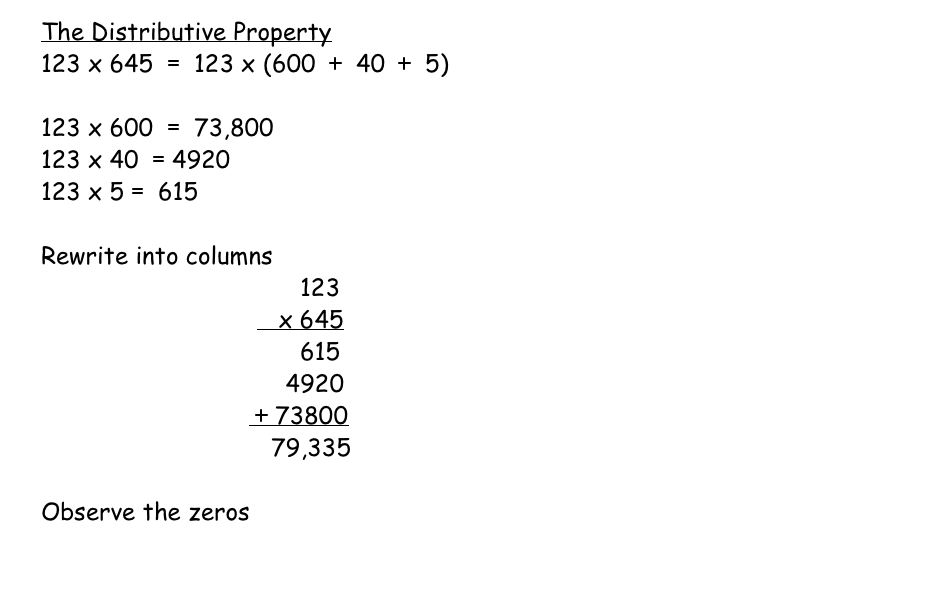
The basic distributive property states that when you multiply a number by a sum, you can distribute the multiplication to each term inside the parentheses. In other words, a(b + c) = ab + ac. This property is fundamental in algebraic manipulation and simplification, allowing us to break down complex expressions into simpler forms.
How can the basic distributive property be applied to simplify expressions?
The basic distributive property states that for any real numbers a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac. This property can be used to simplify expressions by distributing the multiplication operation over the terms inside the parentheses. By applying the distributive property, you can multiply each term inside the parentheses by the constant outside the parentheses, which helps in combining like terms and ultimately simplifying the expression.
Give an example of applying the basic distributive property to expand an expression.
Sure! An example of applying the basic distributive property to expand an expression is: 3(2x + 4). Using distribution, we would multiply 3 by each term inside the parentheses to get 6x + 12.
Can the basic distributive property be used with variables or only with numbers?
The basic distributive property can be used with variables as well as with numbers. This principle states that for any real numbers a, b, and c, the product of a and the sum (or difference) of b and c is equal to the sum (or difference) of the products of a and b, and a and c. This concept applies to variables as well, allowing you to distribute a variable across the sum or difference of other variables in an algebraic expression.
How does the basic distributive property relate to multiplication and addition or subtraction?
The basic distributive property states that when multiplying a number by a sum or difference of two other numbers, the product is the same as multiplying the number by each of the two numbers in the sum or difference and then adding or subtracting the two products. In other words, it relates to both multiplication and addition/subtraction by showing how multiplication can be distributed over addition or subtraction to simplify expressions and calculations.
When simplifying an expression using the basic distributive property, what should be done first?
When simplifying an expression using the basic distributive property, you should first multiply the term outside the parentheses by each term inside the parentheses. This involves distributing the value of the outside term to each term inside the parentheses before combining like terms to simplify the expression.
Can the basic distributive property be used in reverse to factorize an expression?
Yes, the basic distributive property can be used in reverse to factorize an expression. This involves looking for common factors within the terms of the expression and then factoring out those common factors to rewrite the expression in a simplified form. By using the distributive property in reverse, you can break down a given expression into its factors and simplify it to make it easier to work with.
How can the basic distributive property be used to solve equations?
The basic distributive property can be used to solve equations by distributing terms inside parentheses to simplify expressions. This helps to isolate variables on one side of the equation and constants on the other side. By applying the distributive property correctly, one can manipulate the terms in an equation to eventually solve for the unknown variable.
How is the basic distributive property different from the advanced distributive property?
The basic distributive property states that a(b + c) = ab + ac, where a, b, and c are any numbers. In contrast, the advanced distributive property, also known as the expanded form of distributive property, applies to more complex expressions involving multiple terms and parentheses. It allows for distributing a factor across several terms inside parentheses, such as a(b + c + d) = ab + ac + ad. This property is useful in simplifying and expanding expressions in algebraic equations.
Provide a real-world example where the basic distributive property can be applied.
When shopping for groceries, the distributive property can be applied when calculating the total cost of purchasing multiple items at different prices. For example, if you are buying 3 apples at $1.50 each and 2 oranges at $0.75 each, you can use the distributive property to find the total cost by multiplying the number of each fruit by its price and then adding them together, which would be (3 x $1.50) + (2 x $0.75) = $6.00.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments