6th Grade Cell Theory Worksheet
The cell theory is a fundamental concept in biology, explaining the structure and function of living organisms at the microscopic level. As a 6th-grade student, understanding the key principles of the cell theory is crucial for building a strong foundation in biology. In order to reinforce your knowledge and test your comprehension, a cell theory worksheet can provide a valuable learning resource. By engaging with activities and questions related to this topic, you can enhance your understanding of cells, their functions, and the principles that govern their existence.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
Who is credited with discovering cells?
The first to observe and describe cells accurately under a microscope was the English scientist Robert Hooke in 1665.
What is the basic unit of life?
The basic unit of life is a cell. Cells are the smallest structural and functional unit of living organisms, capable of carrying out essential life processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
What are the three main principles of the cell theory?
The three main principles of the cell theory are: 1) All living organisms are composed of one or more cells, 2) The cell is the basic unit of structure and function in organisms, and 3) Cells arise from pre-existing cells through cell division.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane serves as a protective barrier, regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell. It also helps maintain the cell's shape and provides structural support. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in cell communication and signaling processes.
How do prokaryotic cells differ from eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotic cells have a defined nucleus and membrane-bound organelles like mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum. Prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and simpler in structure compared to eukaryotic cells, which are larger and more complex. Additionally, prokaryotic cells have circular DNA, while eukaryotic cells have linear DNA organized into chromosomes.
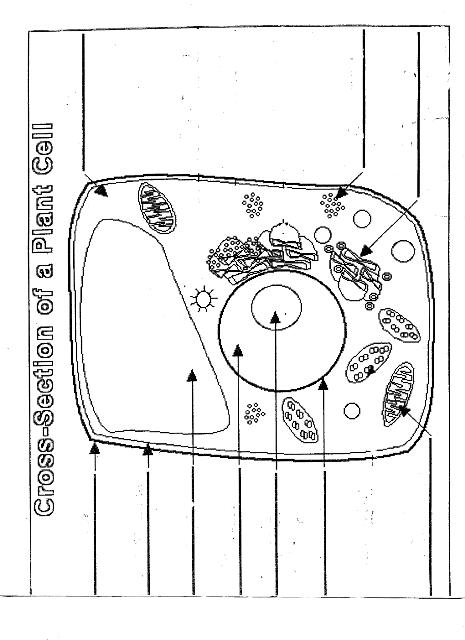
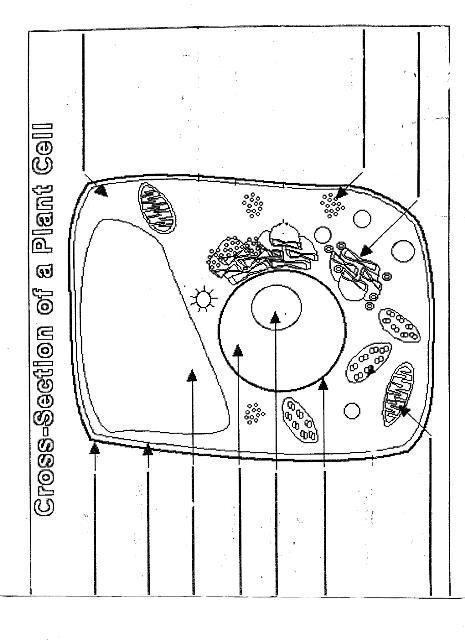
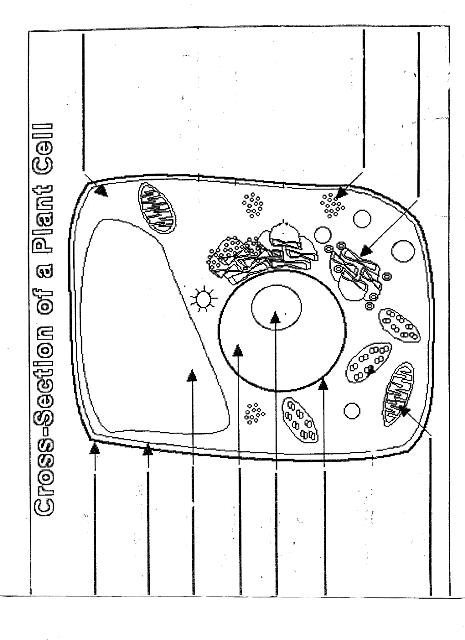
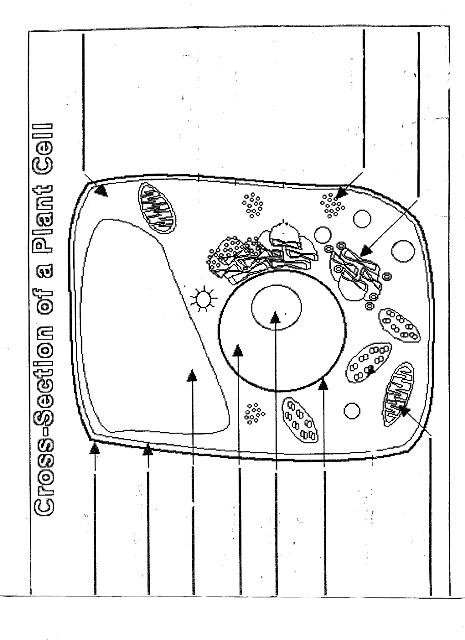
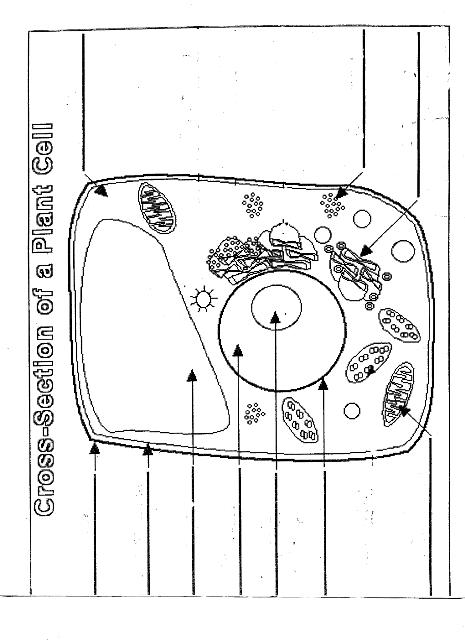
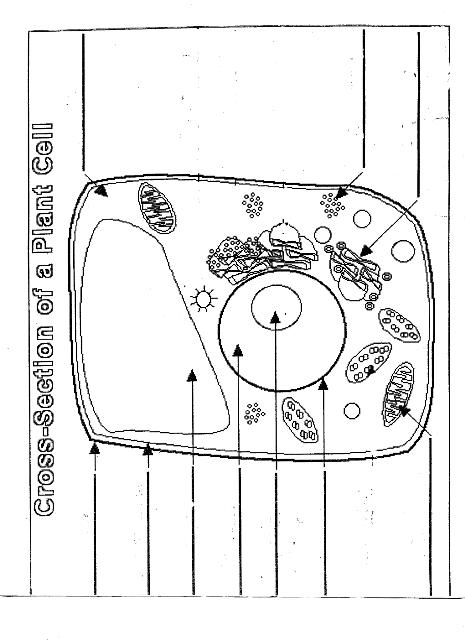
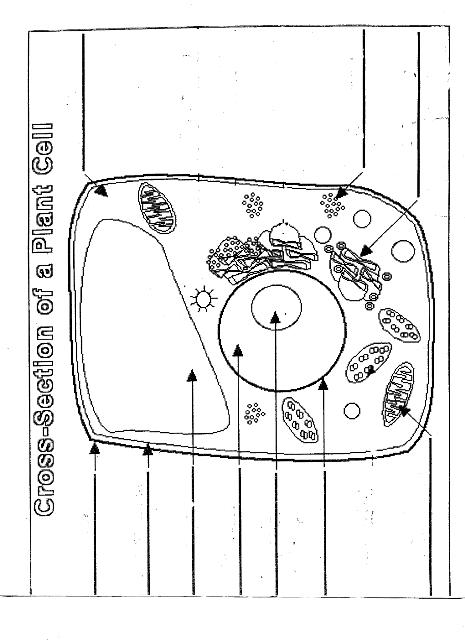
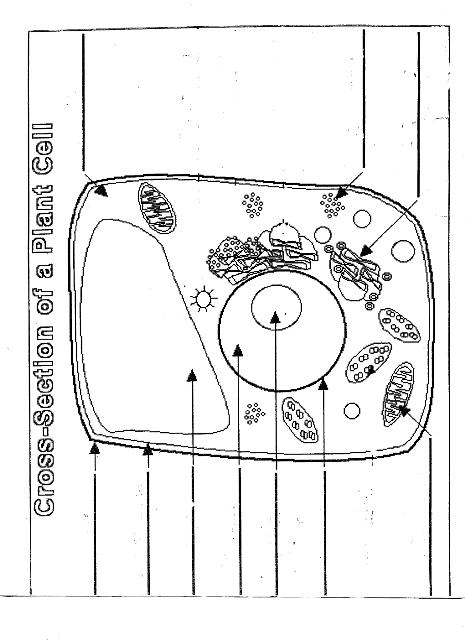
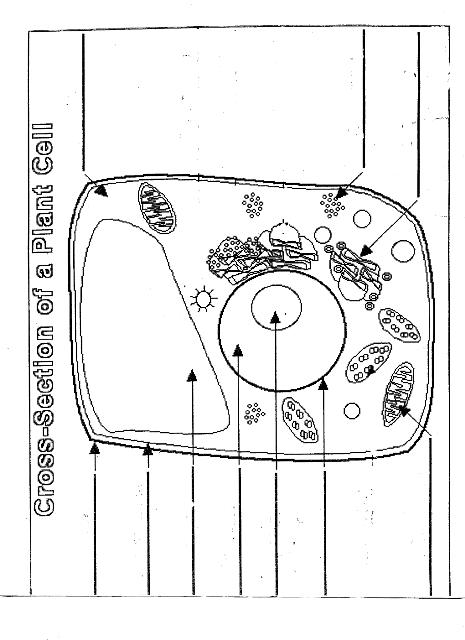
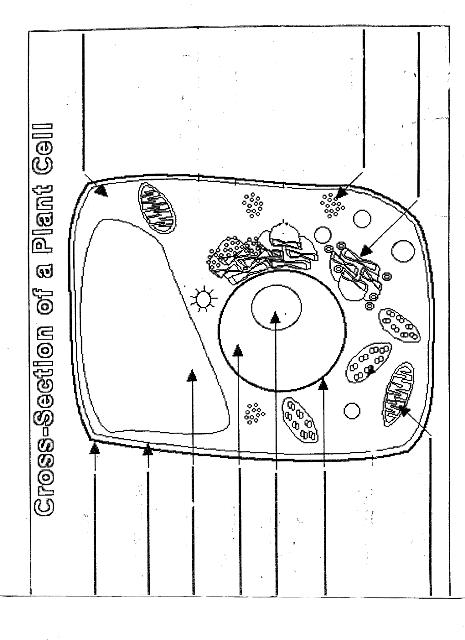
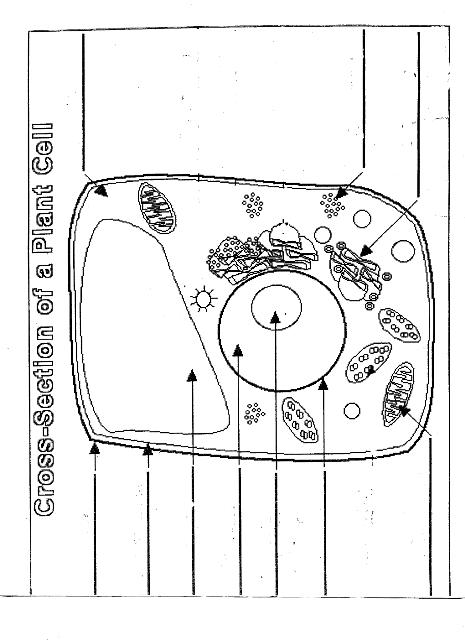
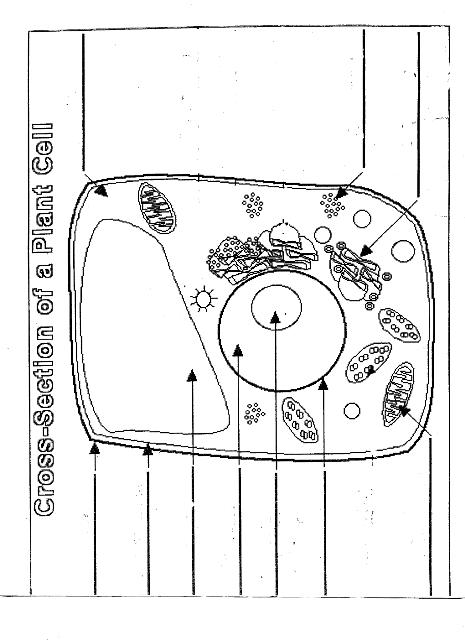
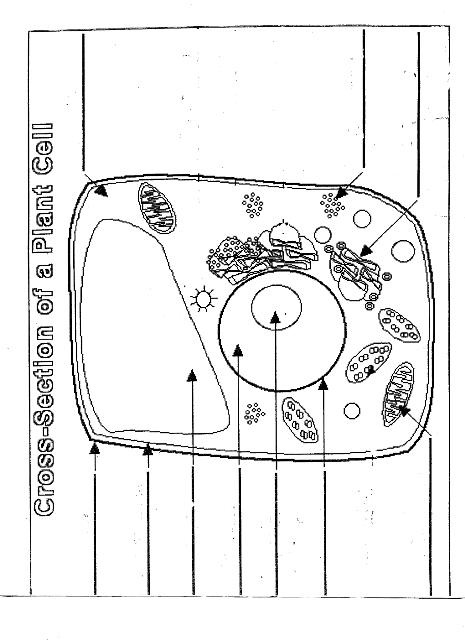
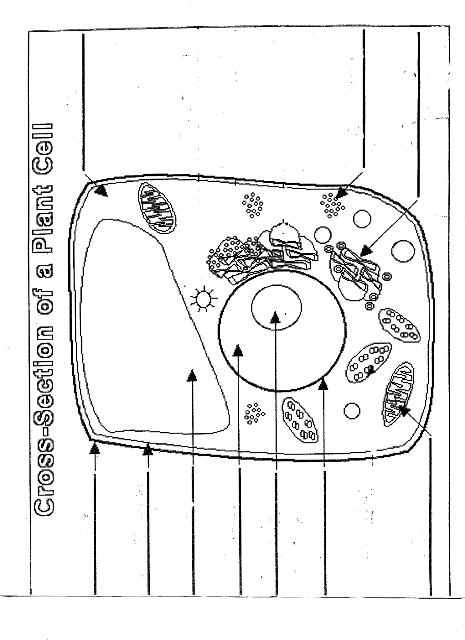
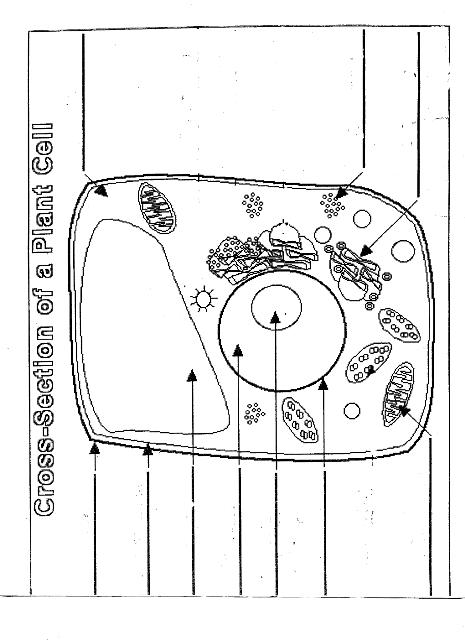
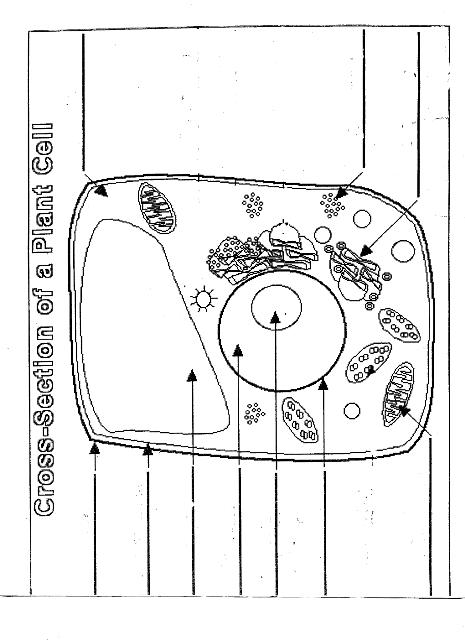
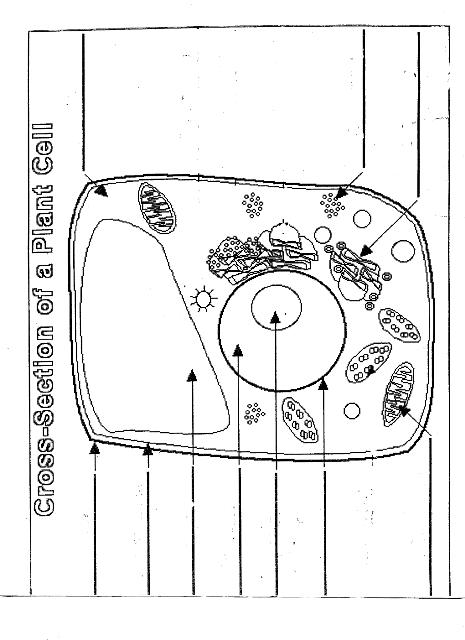
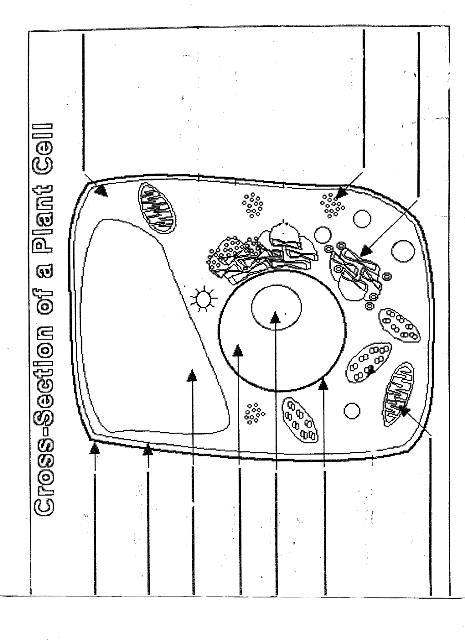
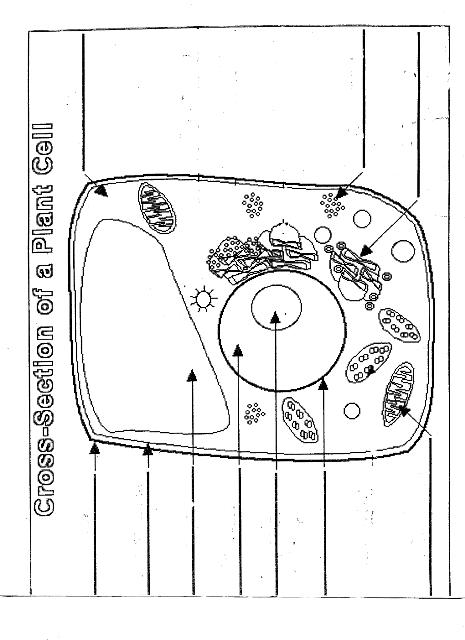
Name two organelles found in plant cells but not in animal cells.
Two organelles found in plant cells but not in animal cells are chloroplasts, responsible for photosynthesis, and central vacuoles, which store water, nutrients, and waste products in plant cells.
What is the role of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus in a cell serves as the control center, containing the cell's DNA and regulating gene expression. It is responsible for coordinating essential cellular activities, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction, by determining which proteins are synthesized and when. Additionally, the nucleus plays a crucial role in storing and protecting genetic information, ensuring the transmission of genetic material to future generations.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Mitochondria are known as the powerhouse of the cell. Their main function is to generate energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through the process of cellular respiration. This is achieved by breaking down nutrients from the food we eat and converting it into ATP, which serves as the primary energy source for various cellular functions and activities.
Explain the process of photosynthesis in plant cells.
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants, algae, and some bacteria convert light energy into chemical energy stored in glucose. It occurs in the chloroplasts of plant cells and involves two main stages: light-dependent reactions and light-independent reactions. During the light-dependent reactions, light energy is captured by chlorophyll and converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH. The light-independent reactions, also known as the Calvin cycle, use ATP and NADPH to convert carbon dioxide into glucose through a series of enzyme-controlled reactions. Overall, photosynthesis is a vital process that sustains life on Earth by producing oxygen as a byproduct and providing energy-rich organic compounds for plants and organisms that consume them.
How do cells communicate with each other in multicellular organisms?
Cells in multicellular organisms communicate through chemical signals, including hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors. These signals are released by one cell and received by another cell, which then responds accordingly. Additionally, cells can communicate through direct contact via gap junctions or cell adhesion molecules. This communication is essential for coordinating various processes in the organism, such as development, immune responses, and maintaining homeostasis.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


















Comments