Writing Ionic Formulas and Naming Worksheet
Are you struggling to grasp the concept of writing ionic formulas and naming compounds? Look no further! This worksheet is designed to help you master this essential skill. Whether you're a student studying chemistry for the first time or a teacher looking for interactive resources to engage your students, this worksheet is here to provide you with a comprehensive practice in identifying and naming entities within chemical compounds.
Table of Images 👆
- Naming Acids Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemical Formula Writing Worksheet
- Formulas with Polyatomic Ions Worksheet Answers
- Practice Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Chemistry Nomenclature Naming Compounds Flowchart
- Ionic Compounds Formulas and Names
- Writing Formulas Criss Cross Method Worksheet Answers
- Binary Ionic Compounds Formulas Worksheet
- Naming Compounds Mixed Ionic and Covalent
- Polyatomic Ions Formulas
- Chemistry Theory and Atomic Structure Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of writing ionic formulas and naming compounds?
The purpose of writing ionic formulas and naming compounds is to accurately represent the chemical composition of substances and to communicate this information effectively to others. Writing formulas allows chemists to show the ratio of atoms in a compound, while naming compounds provides a universal and standardized way to identify different chemical substances. This helps to avoid confusion and ensures clear communication in the field of chemistry.
What are the key components of an ionic formula?
The key components of an ionic formula are the ions involved, their charges, and the subscript numbers indicating the ratio in which the ions combine to form a neutral compound. Ionic formulas represent the combination of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions in specific proportions to ensure electrical neutrality. The charges on the cations and anions determine how they combine to maintain overall charge balance in the compound.
How do you determine the charges of ions in an ionic compound?
The charges of ions in an ionic compound are determined based on the principle of charge neutrality, where the total positive charge of cations must be equal to the total negative charge of anions. This is achieved by balancing the charges of the ions to form a stable compound. The charges of common ions are typically known or can be determined based on their position in the periodic table. By balancing the charges of the ions involved, the formula of the ionic compound can be determined.
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
A cation is a positively charged ion, meaning it has lost electrons, while an anion is a negatively charged ion, meaning it has gained electrons. Cations are formed by elements that tend to lose electrons, such as metals, whereas anions are formed by elements that tend to gain electrons, such as nonmetals. In general, cations are smaller than their parent atoms, while anions are larger due to the added electrons.
What are the rules for naming cations and anions in ionic compounds?
When naming cations and anions in ionic compounds, the cation is named first followed by the anion. Cations typically keep their elemental name, while anions have an -ide ending (e.g. chloride, oxide). If a cation can have more than one possible charge, Roman numerals are used in parentheses to indicate the charge (e.g. iron(II) or iron(III)). Prefixes such as mono-, di-, tri-, etc. are used to denote the number of atoms present in the compound.
How do you write the formula for an ionic compound with a given set of ions?
To write the formula for an ionic compound with a given set of ions, you need to determine the charges of the ions involved. Then, write the symbols of the cation (positively charged ion) first, followed by the anion (negatively charged ion). The charges on each ion should balance out so that the overall charge of the compound is neutral. If the charges are not equal, you will need to use subscripts to balance the charges.
What is the role of subscripts in ionic formulas?
Subscripts in ionic formulas are used to indicate the ratio of ions in a compound. They show the number of each type of ion that combines to form a neutral compound. The subscripts are written as small numbers to the right of the ion symbol and help balance the charges to ensure the overall compound is electrically neutral.
How do you name binary ionic compounds?
Binary ionic compounds are named by writing the name of the cation (metal) first and then the name of the anion (non-metal) with an -ide ending. For example, sodium chloride is named by combining the names of sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl) to form sodium chloride (NaCl).
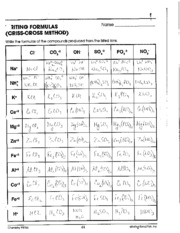
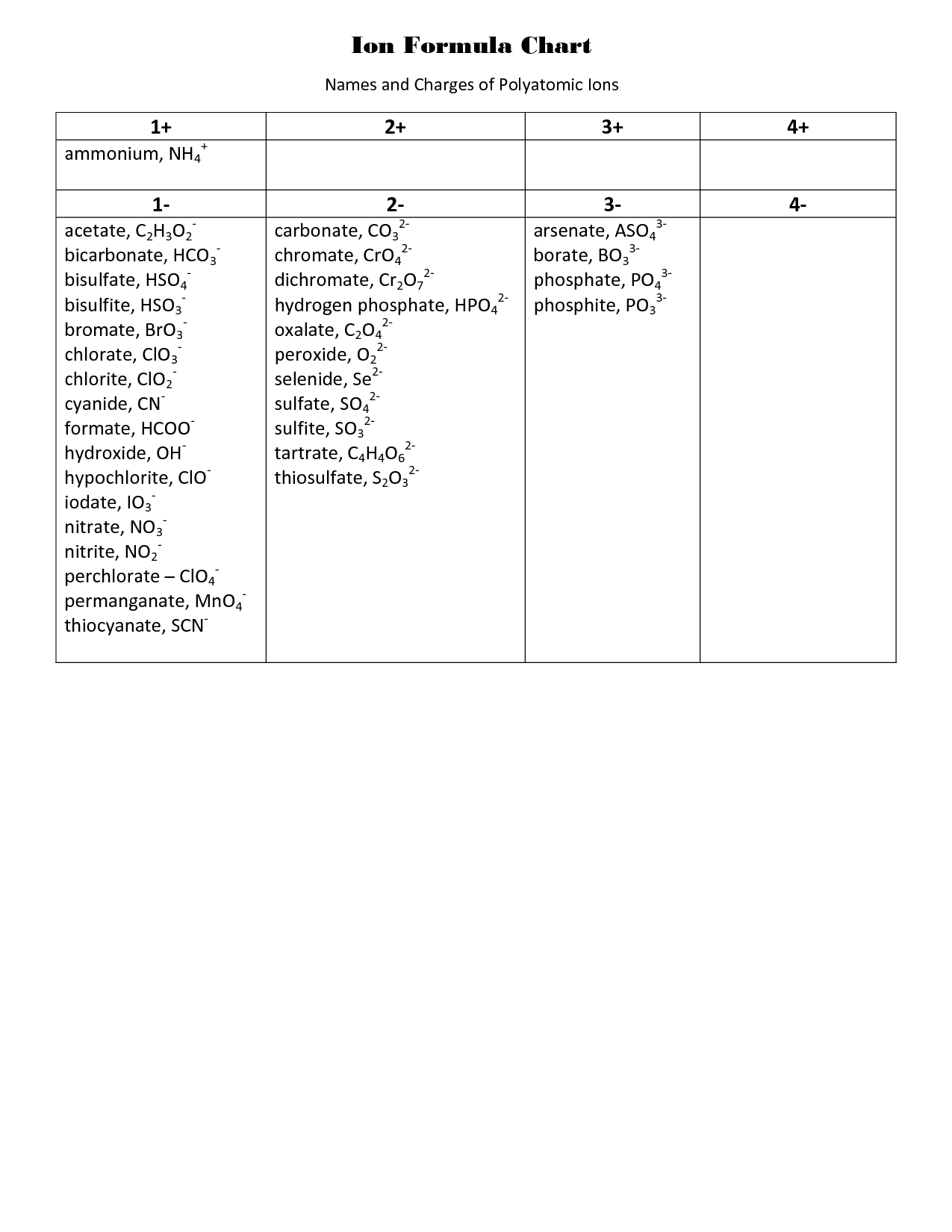
What are polyatomic ions and how do you name them in ionic compounds?
Polyatomic ions are charged species composed of two or more atoms covalently bonded together. These ions have an overall charge and act as single units in ionic compounds. When naming ionic compounds containing polyatomic ions, the name of the polyatomic ion remains unchanged. However, their charge should be considered and used to determine the appropriate ratio of cations to anions in the compound. The overall charge of the compound must be neutral, achieved by balancing the charges of the cations and anions present.
What are the guidelines for writing the formulas of ionic compounds with polyatomic ions?
When writing the formulas of ionic compounds with polyatomic ions, you should first identify the charges of the individual ions involved. Then, crisscross the charges to determine the subscript numbers for each ion to balance the overall charge of the compound to zero. Remember that parentheses are used when there is more than one of a particular polyatomic ion in the formula. Finally, simplify the formula by reducing subscripts to their simplest ratio if necessary.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments