Worksheets On DNA Molecule
Are you struggling to understand the intricate details of the DNA molecule? Look no further as we have the perfect solution for you: worksheets on the DNA molecule. These worksheets are designed to help students, researchers, and anyone interested in the subject to grasp the concepts and structure of DNA in a clear and comprehensive manner. With carefully curated questions and exercises, these worksheets serve as an invaluable resource for learning and mastering the entity that holds the key to all life on Earth.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA and RNA Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet High School
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA the Molecule of Heredity Worksheet Answer Key
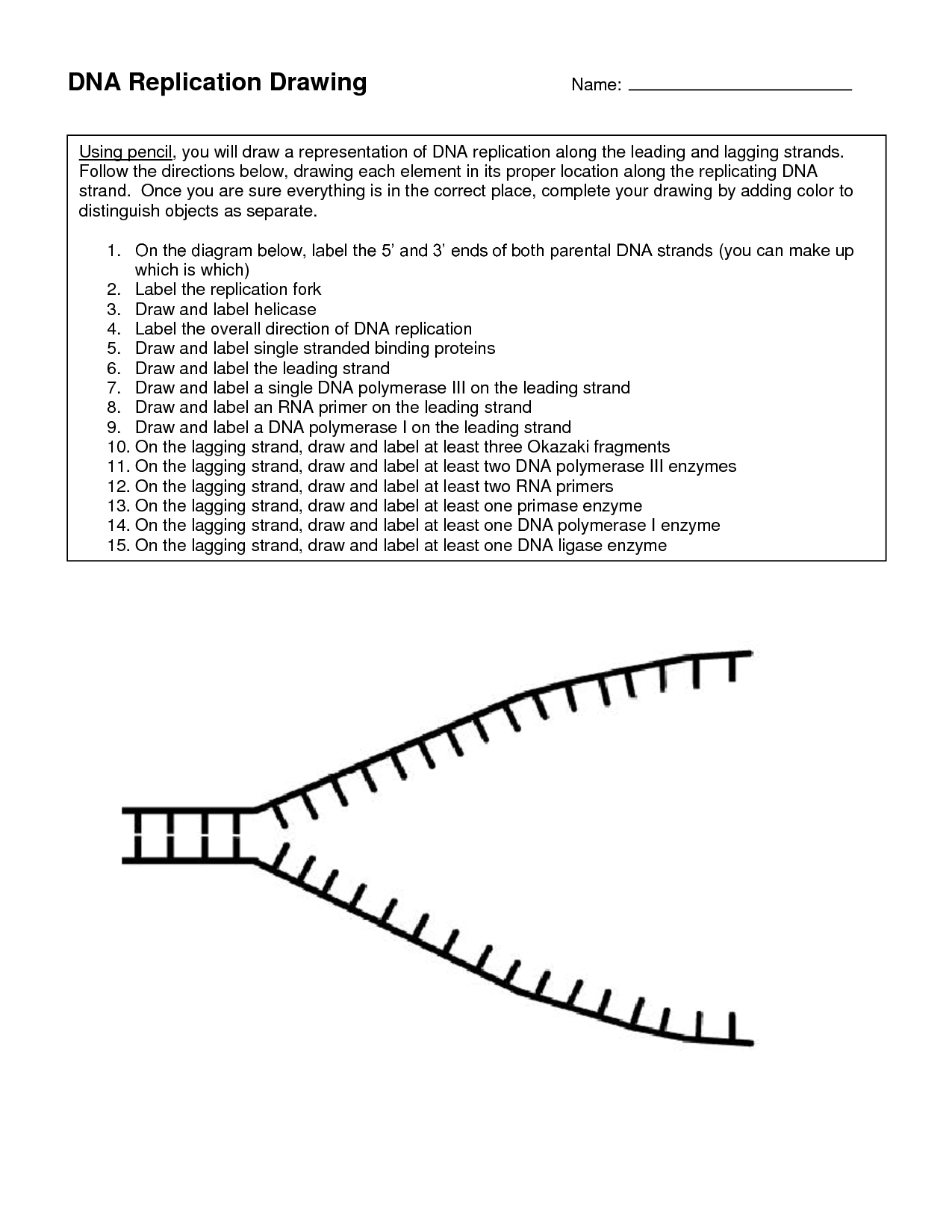
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Molecule of Heredity Worksheet
- DNA Structure and Replication Answer Key POGIL
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- DNA Model Worksheet
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- DNA Fingerprinting Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a DNA molecule composed of?
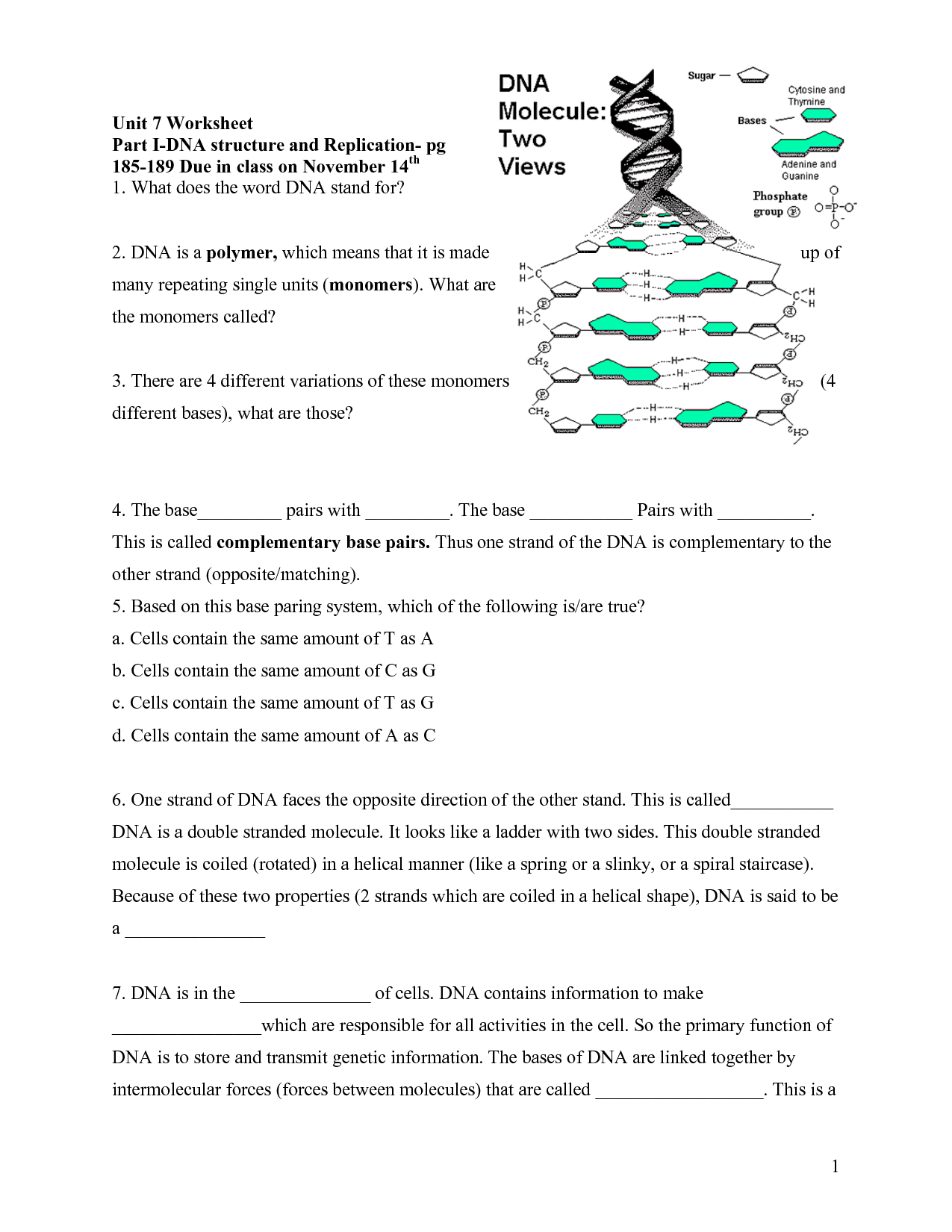
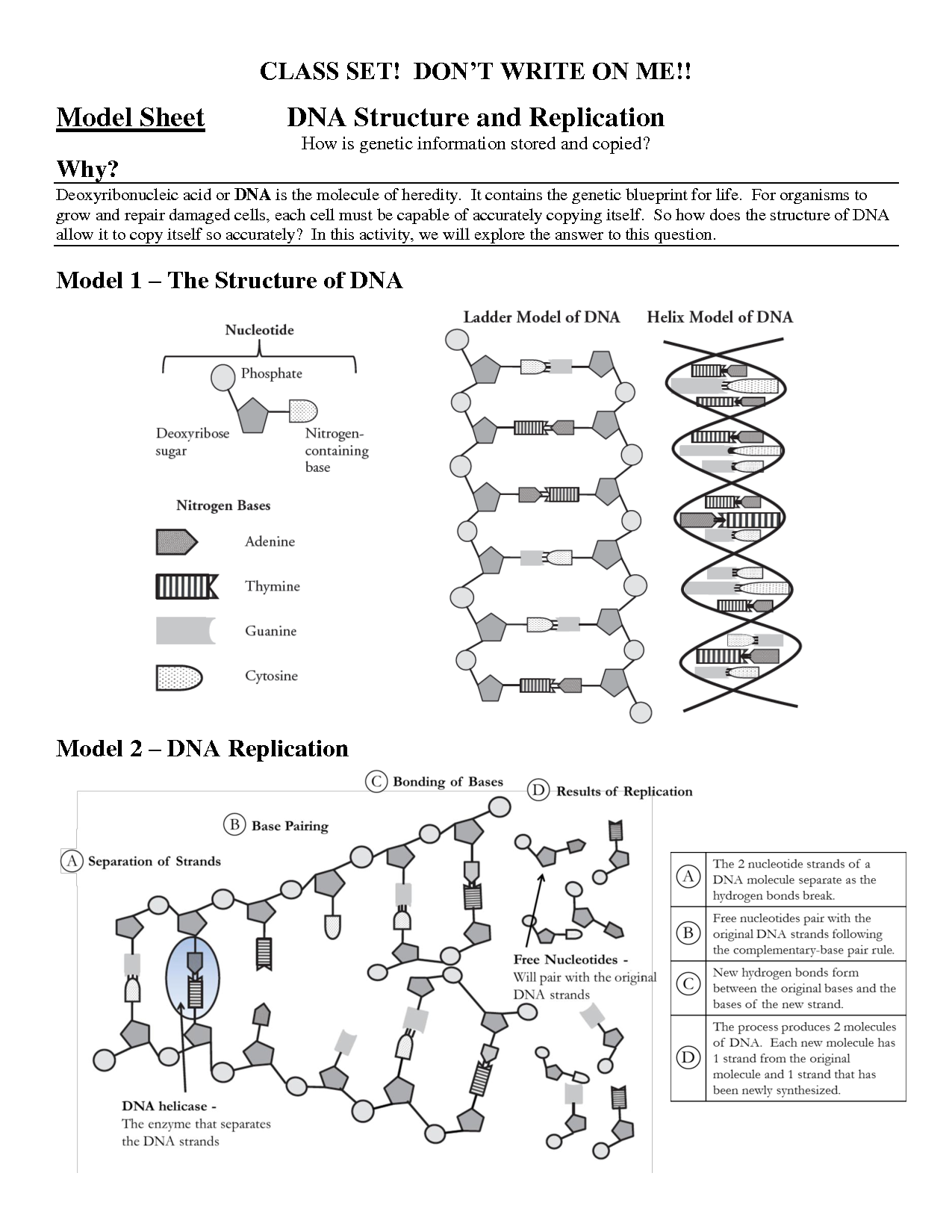
A DNA molecule is composed of two long polymers made up of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). The two polymers are twisted together in a double helix structure, with the nitrogenous bases forming hydrogen bonds between the strands. This arrangement allows DNA to store and transmit genetic information in living organisms.
What is the shape of a DNA molecule?
A DNA molecule has a double helix structure, resembling a twisted ladder. It consists of two strands made up of nucleotides that are connected by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). This iconic shape allows genetic information to be stored and replicated efficiently within the molecule.
What are the four nucleotide bases found in DNA?
The four nucleotide bases found in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
How do the nucleotide bases pair up in a DNA molecule?
In a DNA molecule, the nucleotide bases pair up in a specific way: adenine (A) always pairs with thymine (T), and guanine (G) always pairs with cytosine (C). This pairing forms the double helix structure of DNA, where the two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between the paired bases.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure?
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure of DNA by forming between complementary nitrogenous base pairs on the two strands of the DNA double helix. Specifically, hydrogen bonds form between adenine and thymine (or uracil in RNA) and between guanine and cytosine. These bonds help hold the two strands of the DNA molecule together, contributing to the stability and structure of the double helix. Additionally, hydrogen bonds also facilitate the process of DNA replication and transcription by allowing the strands to separate and re-form in a controlled manner.
How are DNA molecules organized into chromosomes?
DNA molecules are organized into chromosomes through a tightly coiled structure. DNA wraps around proteins called histones, forming nucleosomes. These nucleosomes then coil and condense further to create chromatin fibers. The chromatin fibers then fold and twist into loops and supercoils, eventually forming the condensed structure known as chromosomes. Chromosomes are visible under a microscope during cell division and play a crucial role in organizing and carrying genetic information.
What is meant by the terms "gene" and "genotype" in relation to DNA?
A gene is a specific sequence of DNA that contains instructions for making a particular protein or performing a specific function in an organism. Genotype, on the other hand, refers to the specific genetic makeup of an organism, including all the genes and genetic variations present in its DNA. In summary, genes are the individual units of DNA that contain instructions, while the genotype encompasses the entire genetic information of an organism.
How does DNA replicate itself during cell division?
DNA replication during cell division occurs in the S phase of the cell cycle. The process begins with the unwinding of the DNA double helix by enzymes, followed by the separation of the two strands. Each separated DNA strand serves as a template for the creation of a new complementary strand through the pairing of nucleotides. DNA polymerase enzymes add these nucleotides to the growing strand, ensuring accurate replication. The end result is two identical DNA molecules, each composed of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand. This ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete and accurate copy of the genetic information during cell division.
What is the significance of mutations in DNA?
Mutations in DNA play a crucial role in driving evolution by introducing genetic diversity within populations. They can lead to the creation of new genetic variations that provide advantages in adapting to changing environments, promoting the survival and evolution of species. On the flip side, mutations can also have negative effects, causing genetic disorders and diseases. Overall, mutations are essential for genetic variation and evolutionary processes in all living organisms.
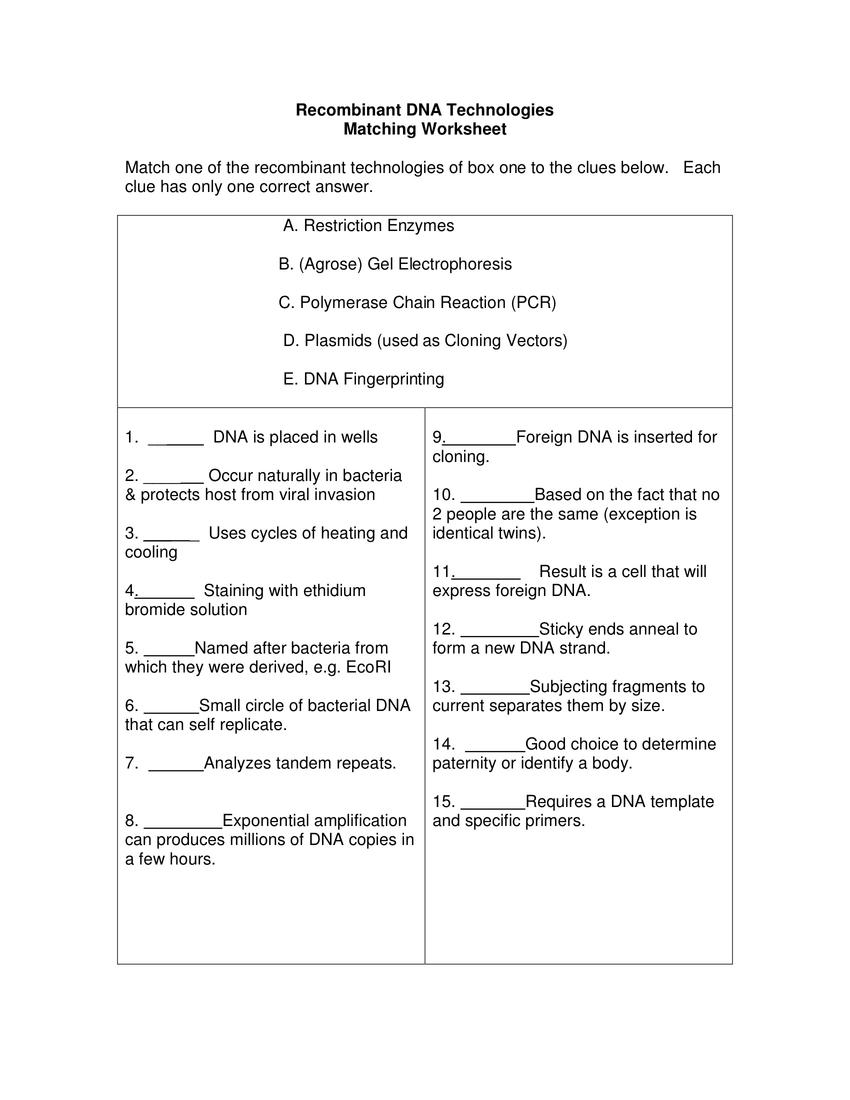
How is DNA used in forensic analysis and paternity testing?
DNA is used in forensic analysis to identify individuals through their unique genetic profiles. By comparing DNA samples found at a crime scene with those of suspects, forensic scientists can determine whether a particular individual was present or not. In paternity testing, DNA analysis is used to establish biological relationships between individuals by comparing their genetic markers. The results of DNA analysis in both forensic and paternity testing are highly accurate and reliable, making them crucial tools for identifying individuals and determining biological relationships.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments