Work and Power Calculations Worksheet
Are you a student or teacher searching for a comprehensive worksheet to reinforce work and power calculations? Look no further as we present our specially designed Work and Power Calculations Worksheet. This worksheet is perfect for middle school or high school physics classes and provides an engaging way for students to practice and assess their understanding of the concepts of work and power.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
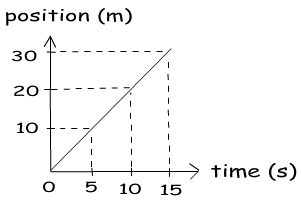
What is work in physics?
In physics, work is defined as the application of a force over a distance, resulting in the movement or displacement of an object. It is calculated as the product of the applied force in the direction of the displacement and the distance over which the force is applied. Work is a scalar quantity and is measured in joules (J) in the International System of Units (SI).
How is work calculated?
Work is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance over which the force is applied. The formula for calculating work is: Work = Force × Distance. The unit of work is joules (J), which represents the amount of energy transferred when a force moves an object over a certain distance.
What are the units of work?
The units of work are typically measured in joules (J) in the International System of Units (SI). Work done is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the distance the object moves in the direction of the force.
What is the relationship between work and energy?
Work and energy are closely related concepts in physics. Work is the transfer of energy and can be defined as the product of the force applied to an object and the distance over which the force is applied. Energy, on the other hand, is the ability to do work. In essence, work done on an object results in a change in its energy, either in the form of potential energy, kinetic energy, or other forms of energy. The principle of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed, reinforcing the interconnection between work and energy in the physical world.
What is power?
Power refers to the ability to influence or control others, resources, or events. It can manifest through authority, strength, knowledge, or other means that allow an individual or group to shape and determine outcomes. Power dynamics are central to social relationships, hierarchies, and structures in various contexts, ranging from politics and economics to relationships and everyday interactions.
How is power calculated?
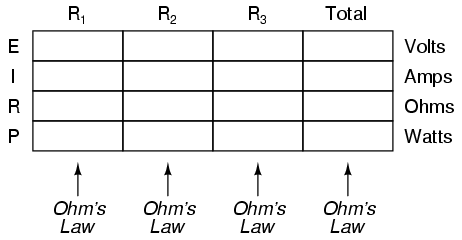
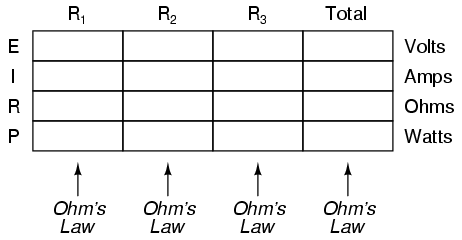
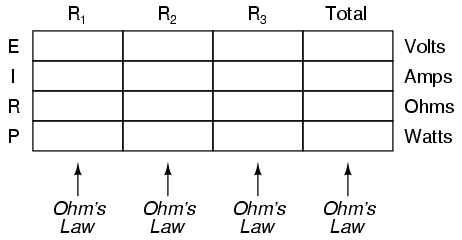
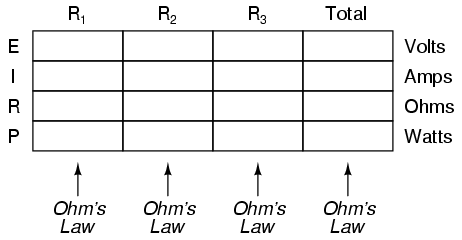
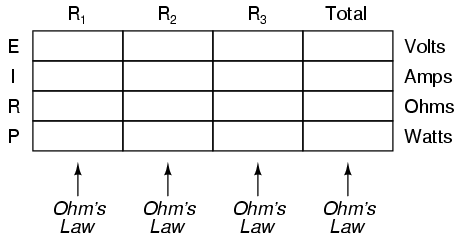
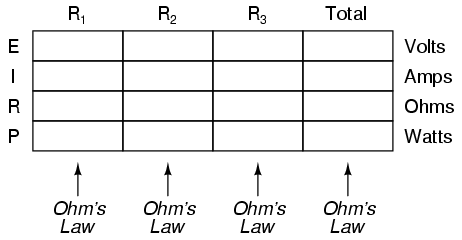
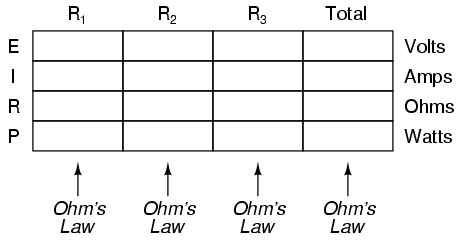
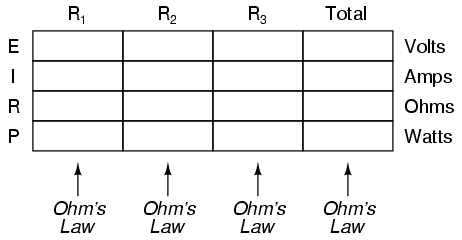
Power is calculated by multiplying force by the distance over which the force is applied per unit of time. In other words, power (P) = work (W) / time (t), where work is the force (F) applied over a distance (d), thus P = F*d/t. There are different units used to measure power, such as watts (W) in the International System of Units (SI) or horsepower (hp) in British Imperial units.
What are the units of power?
The units of power are watts (W), named after the Scottish inventor James Watt.
What is the difference between work and power?
Work is the amount of energy transferred by a force acting through a distance, while power is the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred. In other words, work is a measure of the total energy expended in accomplishing a task, whereas power indicates how quickly that energy is being used or transferred.
How does the concept of time factor into work and power calculations?
Time plays a critical role in work and power calculations as they involve the measurement of how much work is done or how much power is generated over a specific period. In work calculations, the amount of work performed is equal to the force applied multiplied by the distance moved in the direction of the force, where time affects the speed at which the work is done. Similarly, power calculations measure the rate at which work is done or energy is transferred, calculated as work done divided by time taken. Therefore, time is a fundamental component in determining both work and power in various mechanical and physical systems.
Give an example of a real-life application of work and power calculations.
A real-life application of work and power calculations can be seen in the automotive industry, where engineers use these calculations to design and optimize engines. By calculating the work required to move a vehicle a certain distance at a specific speed, engineers can determine the power output needed from the engine to achieve desired performance levels. This helps in improving fuel efficiency, enhancing acceleration and top speed, and ensuring the vehicle operates efficiently under various driving conditions.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments