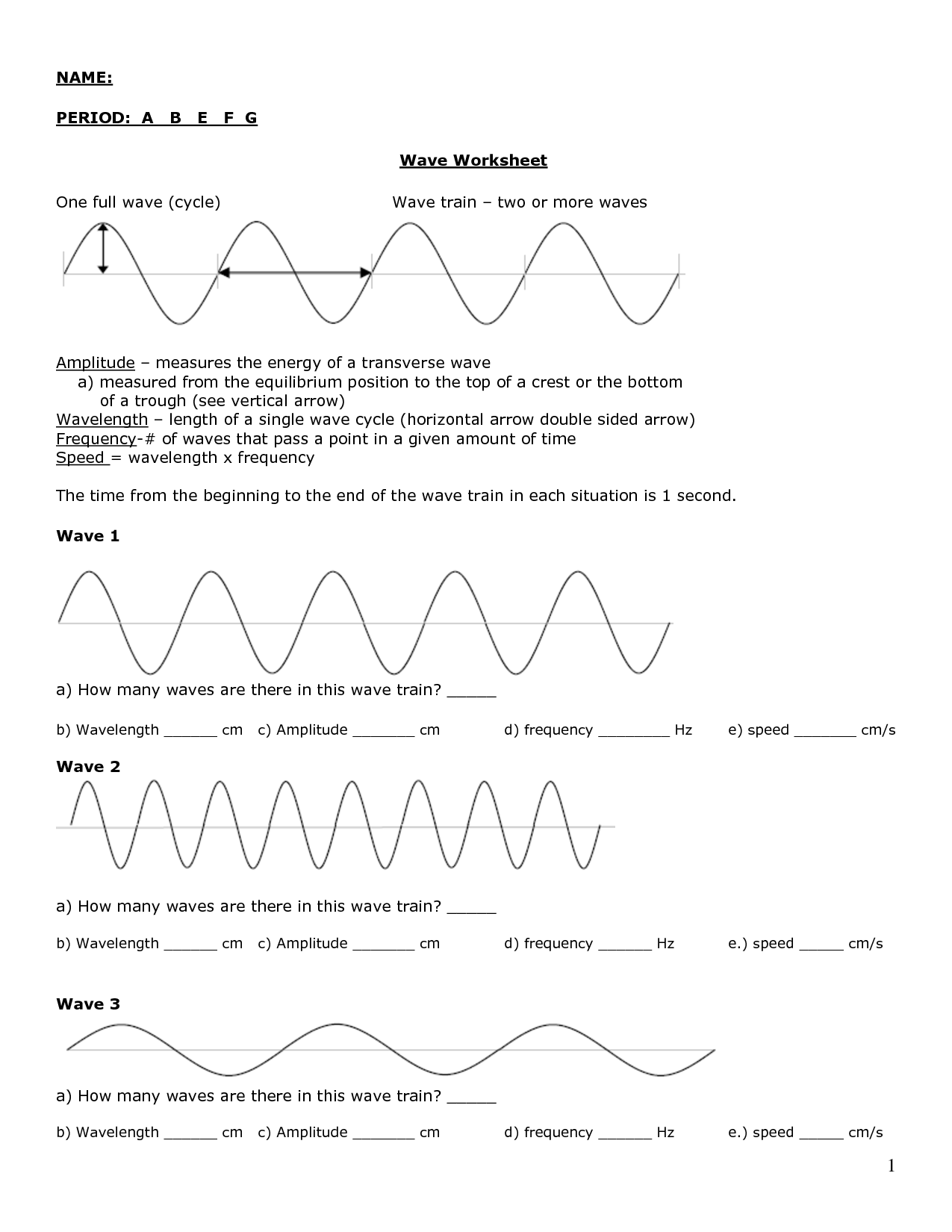
Wave Speed Equation Worksheet
Worksheet exercises are essential for solidifying understanding and mastery of various topics. When it comes to learning about wave speed equations, having a well-designed worksheet can greatly enhance the learning experience. This blog post aims to provide a comprehensive resource for entity and subject (such as students studying physics or individuals interested in understanding wave properties) to practice and apply the wave speed equation in a structured and effective manner.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the wave speed equation?
The wave speed equation is given by: wave speed (v) = frequency (f) × wavelength (?). This equation is used to calculate the speed at which a wave travels through a medium, with the frequency representing the number of wave cycles per second and the wavelength representing the distance between two successive crests or troughs of the wave.
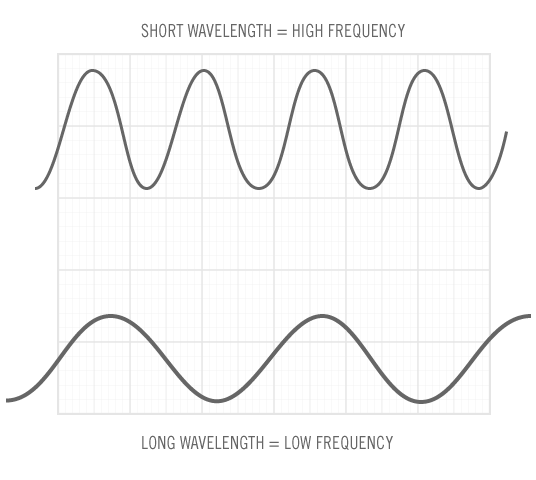
How is wave speed related to frequency and wavelength?
Wave speed is directly proportional to frequency and wavelength. This means that as the frequency of a wave increases, the wave speed also increases, and as the wavelength of a wave increases, the wave speed decreases. This relationship can be described by the formula: wave speed = frequency x wavelength. This means that waves with a higher frequency or shorter wavelength will travel faster than waves with a lower frequency or longer wavelength.
How can the wave speed of a wave be determined?
The wave speed of a wave can be determined by dividing the distance the wave travels by the time it takes for the wave to travel that distance. This formula can be mathematically expressed as: Wave speed = distance/time.
What are the units of wave speed?
The units of wave speed are meters per second (m/s).
How does wave speed change in different mediums?
Wave speed changes in different mediums based on the characteristics of the medium, such as its density and elasticity. In general, wave speed tends to be faster in mediums that are more rigid and have higher density, while slower in mediums that are less rigid and have lower density. This is because the particles in a more rigid and dense medium are closely packed together, allowing the wave to travel more quickly through the medium. On the other hand, in a less rigid and less dense medium, the particles are more spread out, which slows down the wave propagation.
What happens to the speed of a wave when the frequency decreases?
When the frequency of a wave decreases, the speed of the wave remains the same. This is because the speed of a wave is determined by the medium through which it travels, not by its frequency. So, regardless of changes in frequency, the speed of the wave will remain constant as long as it is traveling through the same medium.
How does the speed of a wave affect its energy?
The energy of a wave is directly proportional to its speed. When a wave travels faster, it carries more energy. This means that waves with higher speeds will have greater energy compared to slower waves.
Can the wave speed be greater than the speed of light?
No, according to the theory of relativity, nothing with mass can travel faster than the speed of light in a vacuum, which is approximately 3.00 x 10^8 meters per second. Therefore, the wave speed cannot exceed the speed of light in a vacuum.
Is the wave speed constant for different types of waves?
No, wave speed is not constant for different types of waves. The speed of a wave depends on the medium through which it is traveling. For example, sound waves travel faster in solids than in liquids or gases, while light waves travel at different speeds in different materials. Therefore, the speed of a wave can vary based on the properties of the medium through which it is propagating.
How does the wave speed equation help in understanding wave behavior?
The wave speed equation, v = f?, helps in understanding wave behavior by showing the relationship between wavelength, frequency, and wave speed. It demonstrates that the speed of a wave is directly proportional to its frequency and wavelength. This equation can explain how changes in frequency or wavelength affect the speed of a wave, and how waves can interact with different mediums. By using this equation, we can predict how waves behave in different situations, such as in refraction, reflection, or interference, enabling us to better understand and analyze wave phenomena.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments