Water On Earth Worksheet
Water on Earth is a comprehensive worksheet designed for students in middle school who are studying Earth's water cycle and its impact on the planet. This worksheet explores the different entities involved in the water cycle, including the atmosphere, oceans, lakes, and rivers. It also provides a detailed examination of the subject, covering key topics such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is water?
Water is a clear, odorless, tasteless liquid that is essential for all forms of life on Earth. It is composed of two hydrogen atoms bonded to one oxygen atom, forming the chemical formula H2O. Water exists in three states - liquid, solid (ice), and gas (water vapor) - and plays a crucial role in various natural processes, from regulating temperature to aiding in chemical reactions and serving as a solvent for many substances.
How much of the Earth's surface is covered by water?
Roughly 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by water, with about 96.5% found in the oceans, seas, lakes, rivers, and other bodies of water, while the remaining 2.5% is freshwater stored in glaciers, ice caps, and groundwater.
What are the three states of water?
The three states of water are solid (ice), liquid (water), and gas (water vapor).
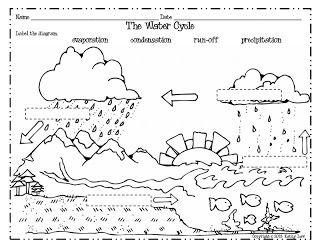
How does water cycle?
The water cycle, also known as the hydrological cycle, involves the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the surface of the Earth. It includes processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. Water evaporates from bodies of water, land, and plants, forms clouds through condensation, and falls back to the Earth as precipitation in the form of rain, snow, or hail. This water then flows into rivers, lakes, and oceans, where the cycle begins again, sustaining life on Earth.
What is the role of water in shaping the Earth's surface?
Water plays a crucial role in shaping the Earth's surface through processes such as erosion, transportation, and deposition. The action of water, in the form of rivers, glaciers, waves, and precipitation, wears down rocks and landforms over time, creating valleys, canyons, and coastlines. Water also transports sediments, minerals, and nutrients from one place to another, contributing to the formation of beaches, deltas, and sedimentary rock layers. Additionally, water is a key element in weathering processes that break down rocks and contribute to the formation of soil. Overall, water is a powerful force that continuously remodels and sculpts the Earth's surface.
What is the importance of water for living organisms?
Water is crucial for living organisms as it is involved in various essential biological processes such as maintaining cell structure and transporting nutrients and waste products. It helps regulate body temperature, acts as a solvent for biochemical reactions, and is a key component of necessary biological fluids. Additionally, water is vital for hydration, aiding digestion, and facilitating the exchange of gases during respiration. Overall, water is indispensable for the survival and functioning of all living organisms.
What is the difference between saltwater and freshwater?
The main difference between saltwater and freshwater is the salt content. Saltwater has a high concentration of dissolved salts, mainly sodium chloride, while freshwater has a very low concentration of salts. Saltwater is typically found in oceans and seas and has a salinity level of about 35 parts per thousand, whereas freshwater is found in rivers, lakes, and streams with a salinity level of less than 0.5 parts per thousand. This difference in salt content has significant implications for the types of organisms that can live in each type of water environment.
How do living organisms obtain water?
Living organisms obtain water through various methods, including drinking it, absorbing it through their skin or other tissues, and obtaining it through the food they consume. In terrestrial environments, plants can absorb water from the soil through their roots, while animals drink water from various sources such as rivers, lakes, or by consuming prey that contains water. In aquatic environments, organisms can directly take in water from their surroundings through processes like osmosis. Overall, the acquisition of water is crucial for the survival and proper functioning of living organisms.
Why is it important to conserve water?
Conserving water is important because it helps to sustain the environment and ensure access to clean water for future generations. By reducing water usage, we can protect ecosystems, wildlife, and biodiversity. It also helps to mitigate the effects of droughts and water scarcity, which are becoming increasingly common due to climate change. Conserving water ultimately contributes to a more sustainable and resilient water supply system, benefiting both the environment and human communities.
What are some human activities that contribute to water pollution?
Human activities that contribute to water pollution include industries discharging chemicals and waste into water bodies, agricultural practices that lead to pesticide and fertilizer runoff, improper disposal of household chemicals and pharmaceuticals, urban runoff carrying pollutants like oil and heavy metals from streets into storm drains, and untreated sewage and wastewater discharges. Additionally, activities such as mining, deforestation, and improper waste management can also contribute to water pollution.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments