Water Cycle Diagram Blank Worksheet
Are you a science teacher searching for a comprehensive and user-friendly worksheet on the water cycle? Look no further, as we have just the resource you need! This water cycle diagram blank worksheet is designed to engage and challenge young learners as they explore the various stages and processes involved in this vital natural phenomenon. From evaporation and condensation to precipitation and collection, this worksheet provides students with an opportunity to showcase their understanding of the water cycle by visually representing its key components.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
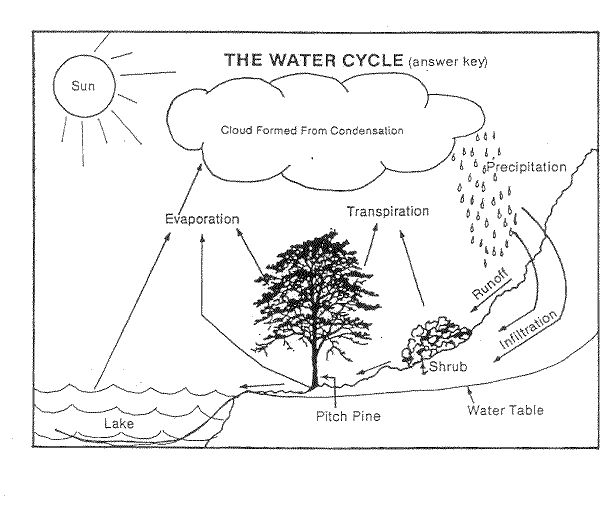
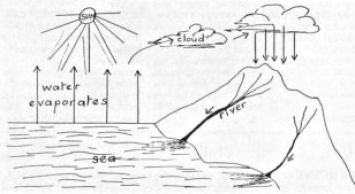
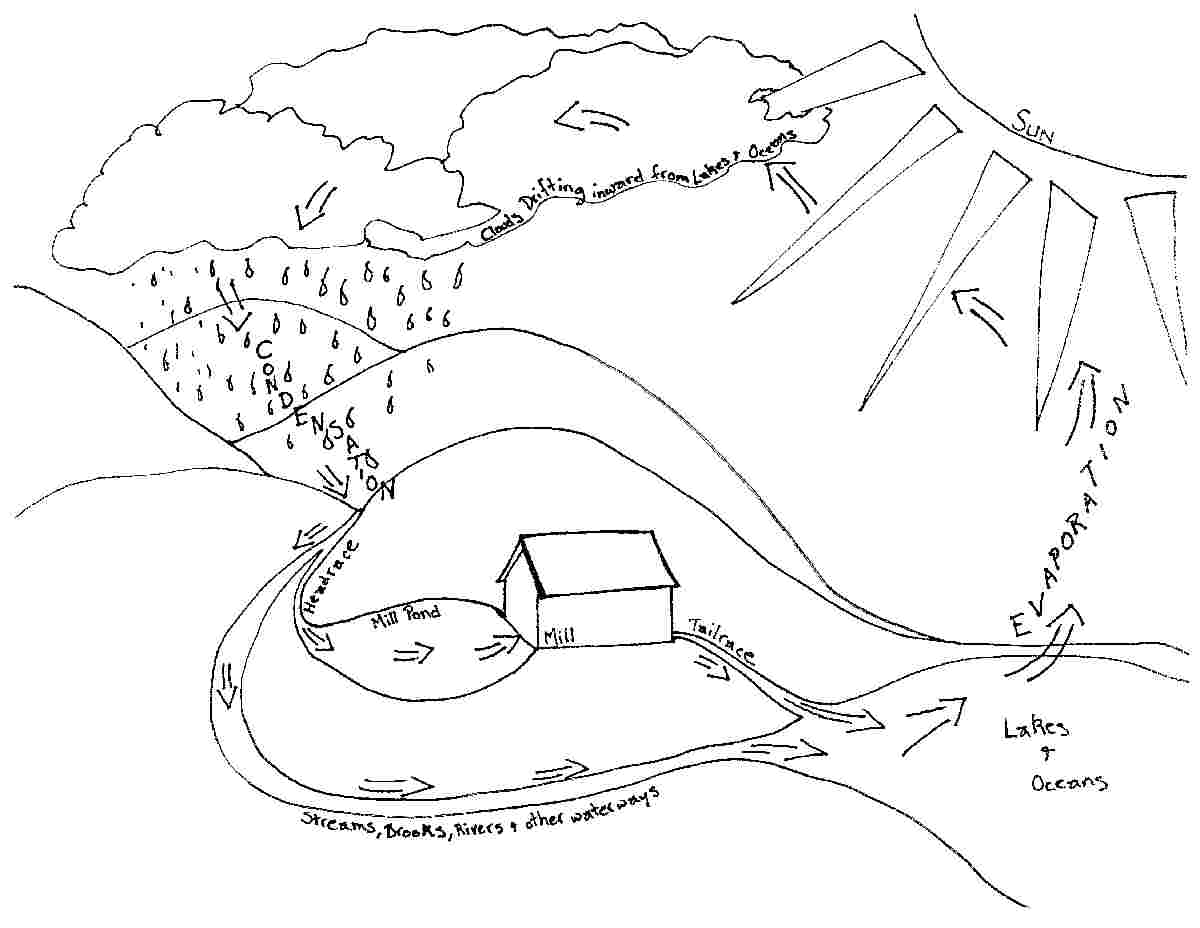
What is the purpose of the water cycle diagram?
The purpose of the water cycle diagram is to illustrate and explain the continuous process of how water moves through the Earth's atmosphere, land, and bodies of water. It shows how water evaporates from the surface, forms clouds, precipitates back to the ground, and then flows back into oceans, rivers, and lakes. By highlighting this cyclical process, the diagram helps in understanding the interconnectedness of the Earth's water systems and the importance of water conservation and management.
What are the main components of the water cycle?
The main components of the water cycle include evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and collection. Evaporation occurs when water from bodies of water, soil, or plants turns into vapor due to heat. Condensation refers to the process of water vapor cooling and transforming back into liquid form to form clouds. Precipitation, such as rain, snow, sleet, or hail, occurs when enough condensation builds up in the clouds. Finally, collection involves the water falling back to the Earth's surface and flowing into bodies of water, completing the cycle.
How does evaporation occur in the water cycle?
Evaporation in the water cycle occurs when heat from the sun causes water from oceans, lakes, rivers, or even the ground surface to change into water vapor and rise into the atmosphere. This process involves the conversion of liquid water into water vapor through the gain of energy, typically from sunlight, and is a crucial step in the water cycle as it leads to the formation of clouds and eventually precipitation.
What happens to the water molecules after they evaporate?
When water molecules evaporate, they transform from their liquid state to a gaseous state and rise into the atmosphere. There, they may undergo various processes such as condensation to form clouds, precipitation as rain or snow, or they may be carried by wind currents around the globe. Ultimately, they contribute to the water cycle by returning to the Earth's surface through precipitation, where they can be absorbed by plants, enter water bodies, or replenish groundwater reserves.
Describe the process of condensation in the water cycle.
Condensation in the water cycle occurs when water vapor in the air cools and transforms into liquid water. This typically happens when warm, moist air rises and encounters cooler temperatures higher in the atmosphere, causing the water vapor to condense into droplets. These droplets then come together to form clouds or fog. As more droplets accumulate, they may grow larger and eventually fall back to the Earth's surface as precipitation in the form of rain, snow, sleet, or hail, continuing the water cycle.
What are some examples of condensation in the natural environment?
Some examples of condensation in the natural environment include the formation of dew on leaves or grass blades in the early morning, the creation of fog as warm, moist air cools down near the ground, and the development of clouds when water vapor in the air reaches its dew point and condenses around tiny particles in the atmosphere. Additionally, the formation of raindrops from water vapor in the atmosphere condensing inside clouds is another common example of condensation in nature.
How does precipitation occur in the water cycle?
Precipitation occurs in the water cycle when water vapor in the atmosphere condenses into liquid droplets or ice crystals and falls to the ground as rain, snow, sleet, or hail. This condensation process is often triggered by cooling of the air, which can be caused by factors such as decreased atmospheric pressure, the lifting of air masses, or contact with cold surfaces. These water droplets or ice crystals eventually accumulate in clouds and grow in size until they become heavy enough to fall as precipitation, completing the cycle of evaporation, condensation, and precipitation in the water cycle.
Explain the role of plants in the water cycle.
Plants play a crucial role in the water cycle as they absorb water from the soil through their roots and release it into the atmosphere through a process called transpiration. This helps in turning liquid water into water vapor that then contributes to cloud formation and precipitation. Additionally, plants help to reduce soil erosion and maintain water quality by absorbing excess nutrients and filtering pollutants from the water. Overall, plants are essential in maintaining the balance of water in the environment and sustaining the water cycle.
What happens to the water after it reaches the ground during precipitation?
After water reaches the ground during precipitation, it can take various paths. It may be absorbed by the soil to nourish plants or flow over the land surface as runoff into rivers, lakes, or oceans. Some precipitation also evaporates back into the atmosphere, continuing the water cycle.
How does the water cycle affect the overall balance of water on Earth?
The water cycle plays a crucial role in maintaining the overall balance of water on Earth by continuously circulating water between the atmosphere, land, and oceans. This cycle involves processes such as evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and runoff, which redistribute water across various reservoirs. Through this constant movement, the water cycle helps regulate the distribution of freshwater and saline water, replenish groundwater supplies, support ecosystems, and sustain life on our planet. Ultimately, the water cycle ensures that there is a balance between the amount of water that evaporates and the amount that falls back to Earth as precipitation, maintaining the delicate equilibrium of water on our planet.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments