Volcano Classroom Worksheets
Are you searching for informative and engaging worksheets to enrich your volcano-themed classroom lessons? Look no further! These volcano classroom worksheets are designed to captivate the interest of students who are eager to learn about the fascinating fiery wonders of the Earth. With a focus on developing their understanding of volcano-related concepts and encouraging critical thinking, these worksheets provide valuable resources for educators and parents alike.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
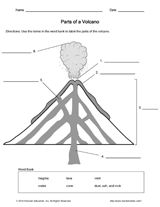
What is a volcano?
A volcano is a natural opening in the Earth's crust through which molten rock, ash, and gases erupt onto the Earth's surface. It is formed when pressure builds up underneath the Earth's surface, leading to a release of magma and volcanic gases.
Where are most volcanoes located?
Most volcanoes are located along tectonic plate boundaries, with the majority found encircling the Pacific Ocean in what is known as the "Ring of Fire." This region, which spans from the west coast of the Americas to Japan and Southeast Asia, is home to about 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes due to the intense tectonic activity in the area.
What are the three main types of volcanoes?
The three main types of volcanoes are shield volcanoes, stratovolcanoes (or composite volcanoes), and cinder cone volcanoes. Shield volcanoes have gently sloping sides and are mainly built from fluid lava flows. Stratovolcanoes are tall, steep-sided volcanoes composed of alternating layers of ash, lava, and rocks. Cinder cone volcanoes are smaller, often symmetrical volcanoes built from pyroclastic material ejected during explosive eruptions.
How are volcanoes formed?
Volcanoes are formed when magma from within the Earth's mantle rises through cracks in the Earth's crust and erupts onto the surface. As this molten rock, known as lava, cools and solidifies, it builds up layers over time, creating a cone-shaped structure we recognize as a volcano. These eruptions can be triggered by tectonic plate movements, pressure buildup, or the presence of water in the magma.
What causes volcanic eruptions?
Volcanic eruptions are caused by the buildup of pressure beneath the Earth's surface due to the movement of magma from deep within the Earth, typically associated with tectonic plate movements or hot spots. When this pressure becomes great enough, it forces magma to the surface through a volcano's vent, resulting in an eruption. The composition of the magma, as well as the type of volcano, can also influence the explosiveness and characteristics of the eruption.
What is the Ring of Fire?
The Ring of Fire is a region in the Pacific Ocean characterized by a high degree of seismic and volcanic activity. It is where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean. The Ring of Fire is located along the edges of the Pacific Plate and is home to about 75% of the world's active and dormant volcanoes. This region spans from the west coast of the Americas, through Alaska and down to the east coast of Asia, including Japan and Indonesia.
How do volcanologists monitor volcanic activity?
Volcanologists monitor volcanic activity through various methods, including seismic monitoring to track earthquakes that could indicate magma movement, gas measurements to assess chemical changes in volcanic gases, satellite imaging to monitor surface deformation, and ground-based observations like thermal imaging and visual inspections of the volcano's activity. Together, these tools help volcanologists to track and analyze volcanic activity, provide early warnings, and inform risk assessments to protect communities living near active volcanoes.
What are some potential dangers associated with volcanoes?
Some potential dangers associated with volcanoes include lava flows, pyroclastic flows, lahars (mudflows), ashfall, volcanic gases, and volcanic avalanches. These hazards can lead to destruction of property, loss of life, respiratory problems, crop failure, disruption of transportation and infrastructure, and long-term environmental impacts. Additionally, volcanic eruptions can trigger tsunamis and earthquakes in nearby areas, further increasing the potential dangers associated with volcanic activity.
How do volcanic eruptions impact the environment?
Volcanic eruptions impact the environment by releasing large amounts of ash, gases, and lava, which can have various consequences such as air pollution, acid rain, destruction of habitats, and changes in climate. The ash can smother plants and animals, while gases like sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide can contribute to global warming. Lava flows can destroy ecosystems and alter landscapes, while volcanic ash can also affect water quality and agricultural productivity. Overall, volcanic eruptions can have both short-term and long-term effects on the environment, influencing the surrounding ecosystem and even global climate patterns.
What are some famous volcanoes around the world?
Some famous volcanoes around the world include Mount Vesuvius in Italy, known for its eruption that buried the Roman city of Pompeii; Mount Fuji in Japan, an iconic symbol of the country; Mauna Loa in Hawaii, one of the largest volcanoes on Earth; Krakatoa in Indonesia, infamous for its catastrophic 1883 eruption; and Mount St. Helens in the United States, which erupted in 1980 causing widespread devastation.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.























Comments