Types of Waves Worksheet
A types of waves worksheet is a helpful tool for students studying physics or physical science. This worksheet provides an organized and structured way to learn and review the different types of waves and their characteristics. It guides students through identifying and describing the properties of waves, such as wavelength, frequency, and amplitude. By providing clear entity and subject information, this worksheet is an excellent resource for educators and students looking to enhance their understanding of wave behavior.
Table of Images 👆
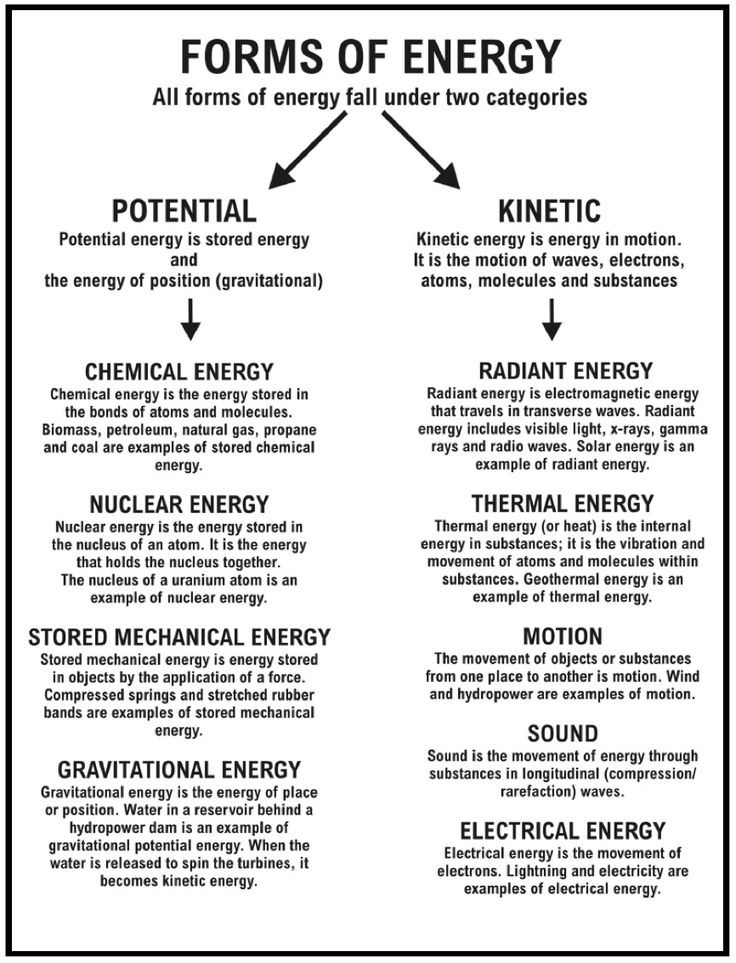
- Different Forms of Energy Worksheets
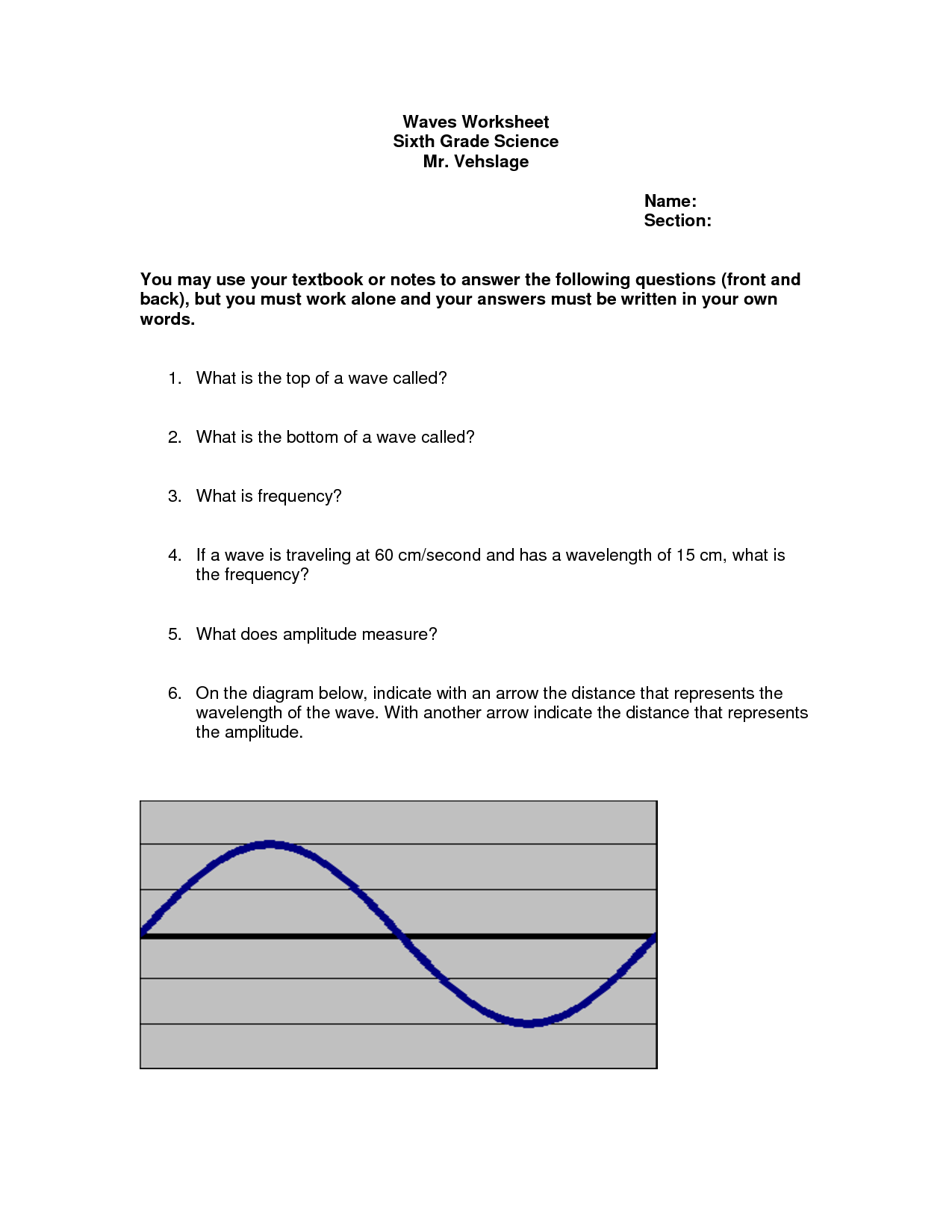
- Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Different Types of Energy Worksheets
- Light Energy Sources Worksheet
- Forms of Energy Worksheet Answers
- Sound Waves Worksheet
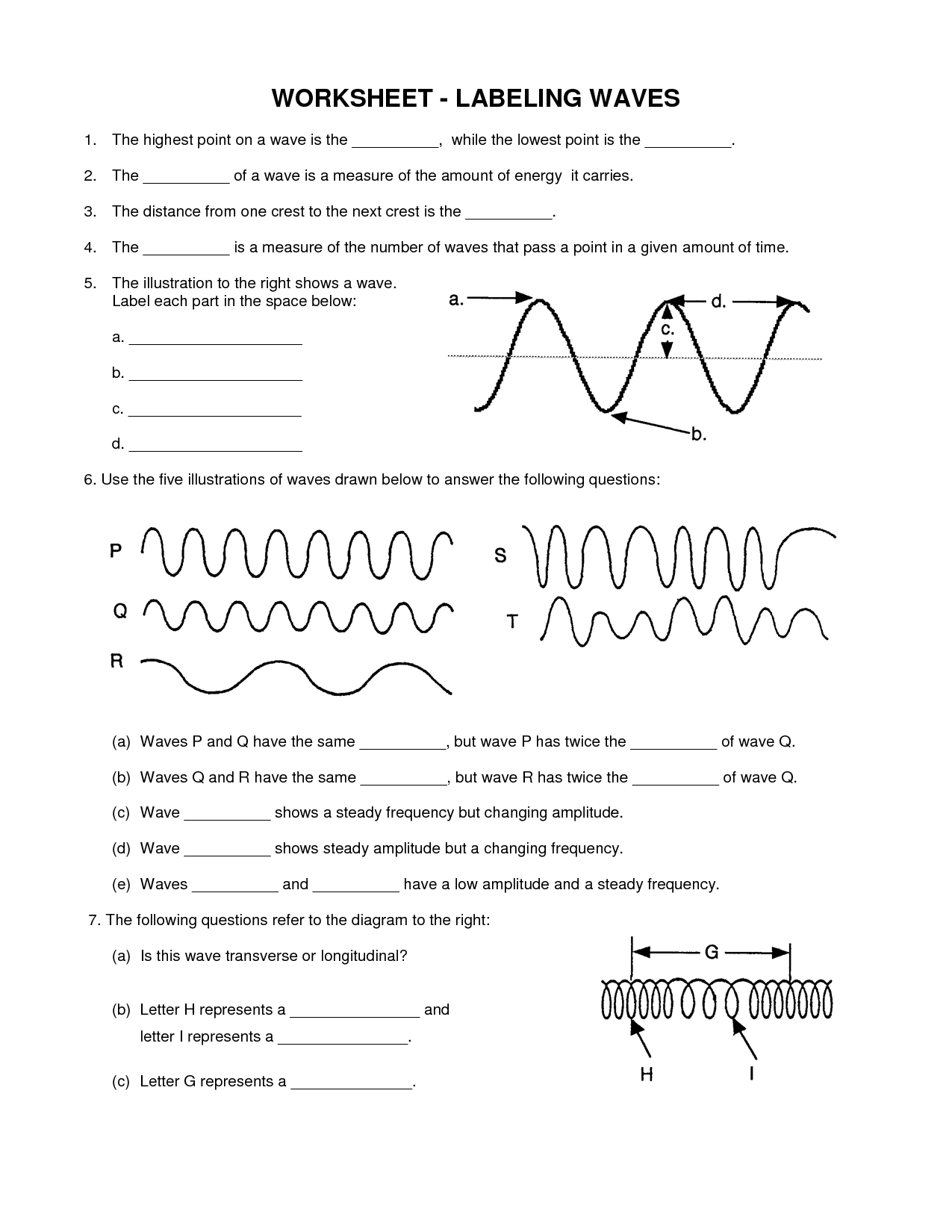
- Labeling Waves Worksheet Answer Key
- Waves and Electromagnetic Spectrum Worksheet Answers
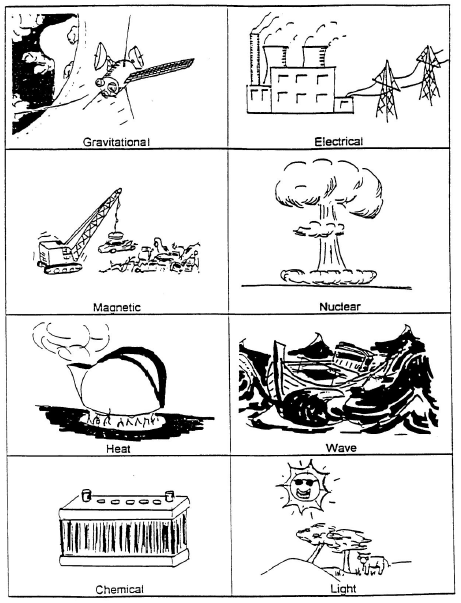
- Science Energy Worksheets
- Heat Energy Transfer Worksheet
- Energy Transformation Worksheets
- Forms of Heat Energy Worksheet
- Energy Word Search Worksheet
- Ocean Floor Worksheet
- Mechanical Waves Worksheet
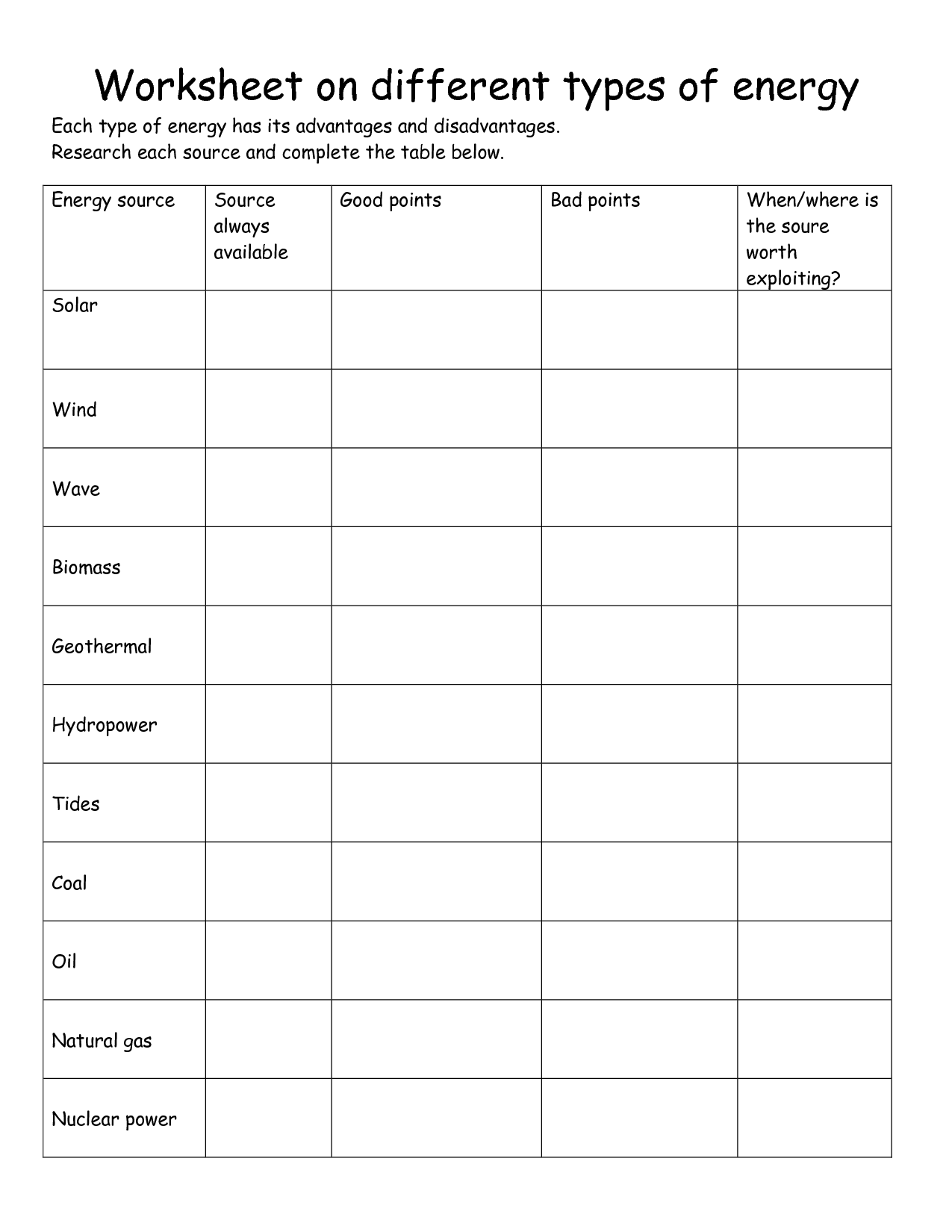
- Energy Sources Worksheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a mechanical wave?
A mechanical wave is a type of wave that propagates through a medium, such as air, water, or a solid material, by transferring energy from one point to another without causing any overall displacement of the medium. Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through and can be classified into two main types: transverse waves, in which the particles of the medium move perpendicular to the direction of the wave, and longitudinal waves, in which the particles move parallel to the direction of the wave.
What is the difference between a transverse wave and a longitudinal wave?
A transverse wave moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave's energy transfer, causing particles in the medium to move up and down or side to side. In contrast, a longitudinal wave moves parallel to the direction of energy transfer, causing particles in the medium to move back and forth along the wave's propagation path.
How are surface waves formed?
Surface waves are formed by the interaction of different factors such as wind, tides, or seismic activity. Wind blowing over the surface of the water generates ripples that can develop into larger waves. Tides and underwater earthquakes can also cause disturbances that create surface waves. The energy from these disturbances is transferred to the water causing it to move in a rolling motion, resulting in the formation of surface waves.
What is a standing wave?
A standing wave is a pattern of oscillation that forms when two waves of the same frequency and amplitude traveling in opposite directions interfere with each other. This interference creates points along the wave that appear to be standing still, while other points experience maximum displacement. Standing waves are characterized by nodes, where there is no movement, and antinodes, where the oscillation is at its maximum.
What is the principle of superposition?
The principle of superposition states that when two or more waves overlap, the resultant displacement at any point is the sum of the displacements that each individual wave would produce at that point. This principle is commonly used in the study of wave phenomena, allowing for the analysis and understanding of complex wave interactions based on the simple addition of individual wave contributions.
What is the relationship between wave speed, wavelength, and frequency?
The relationship between wave speed, wavelength, and frequency is determined by the formula: wave speed = wavelength x frequency. This means that as the wavelength of a wave increases, its frequency decreases, and vice versa, while the wave speed remains constant. Therefore, these three properties of a wave are interconnected and can be calculated using this relationship.
How does the amplitude of a wave affect its energy?
The amplitude of a wave directly affects its energy. A wave with a higher amplitude carries more energy compared to a wave with a lower amplitude. This is because the energy of a wave is proportional to the square of its amplitude. Therefore, increasing the amplitude of a wave results in a corresponding increase in its energy.
What is the difference between constructive interference and destructive interference?
Constructive interference occurs when two waves combine to increase the overall amplitude of the wave, resulting in a wave that is larger in size. In contrast, destructive interference happens when two waves combine to decrease the overall amplitude of the wave, resulting in a wave that is smaller or cancels out entirely.
How does the Doppler effect affect the perceived frequency of a wave?
The Doppler effect affects the perceived frequency of a wave by causing a change in frequency when there is relative motion between the source of the wave and the observer. If the source is moving towards the observer, the perceived frequency is higher than the actual frequency (blueshift), and if the source is moving away from the observer, the perceived frequency is lower than the actual frequency (redshift). This shift in frequency occurs due to the compression or expansion of the wavefronts as they propagate towards or away from the observer.
How are electromagnetic waves different from other types of waves?
Electromagnetic waves differ from other types of waves in that they do not require a medium for propagation, unlike mechanical waves such as sound waves or water waves. Instead, electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum and through various materials. Additionally, electromagnetic waves consist of mutually perpendicular electric and magnetic fields oscillating perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. These waves encompass a wide range of frequencies, from the low-frequency radio waves to the high-frequency gamma rays.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments