The Eye and Vision Worksheet
The Eye and Vision Worksheet is a valuable resource for students studying biology or anatomy. This comprehensive worksheet provides a detailed overview of the structure and function of the human eye, making it an essential tool for understanding the complex entity that enables us to see.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
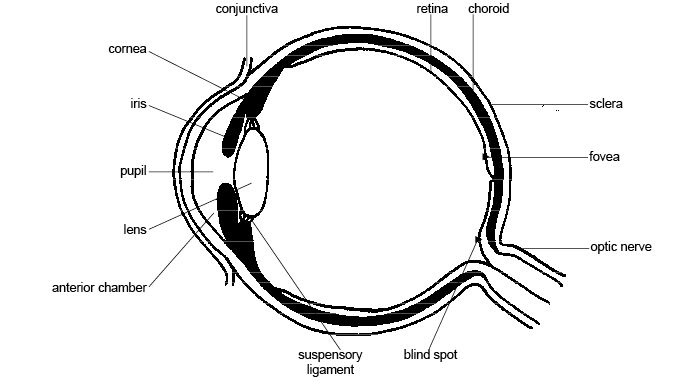
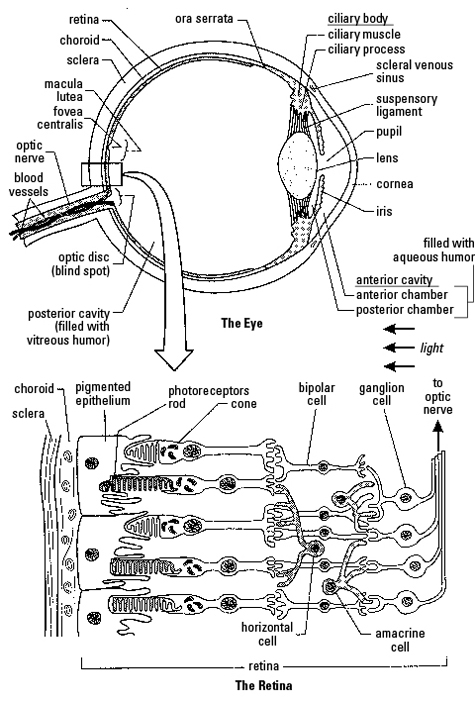
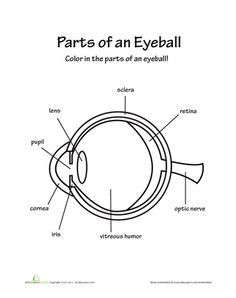
What is the function of the cornea?
The cornea is a transparent, dome-shaped layer at the front of the eye that helps to focus light as it enters the eye. It plays a crucial role in refracting light onto the lens, which then further focuses the light onto the retina at the back of the eye, allowing us to see clearly and sharply.
What is the role of the iris?
The iris is the colored part of the eye that regulates the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil. It contracts in bright light to reduce the amount of light entering the eye and dilates in dim light to allow more light in. This helps to protect the sensitive structures in the eye and ensures proper vision in varying light conditions.
Explain how the lens focuses light onto the retina.
The lens focuses light onto the retina through the process of accommodation, which involves changing its shape to bend the incoming light rays. When the ciliary muscles surrounding the lens contract or relax, it adjusts its curvature to refract light and project a clear image onto the retina at the back of the eye, enabling us to see objects at various distances with clarity.
Define and describe the process of accommodation.
Accommodation is a term used in the field of psychology to describe the process by which existing mental frameworks or schemas are modified or changed to incorporate new information or experiences that do not fit into our current understanding of the world. This process helps individuals adapt to new or novel situations by adjusting their beliefs, perceptions, or behaviors to make sense of the new information. Accommodation allows for cognitive development and enables individuals to better understand and interact with their environment.
What is the purpose of the rods and cones in the retina?
The purpose of rods and cones in the retina is to help detect and process light. Rods are responsible for vision in low light conditions and help with peripheral vision, while cones are responsible for color vision and detail in brighter light. Together, they play a crucial role in enabling us to see and distinguish shapes, colors, and light levels in our surroundings.
What is the blind spot in the eye and why does it occur?
The blind spot in the eye is an area on the retina where there are no light-sensitive cells. This occurs because the optic nerve, which carries visual information from the eye to the brain, passes through this area, blocking the presence of photoreceptor cells. As a result, the brain fills in the missing information from surrounding areas, leading to the perception of a seamless visual field despite the blind spot.
Describe the pathway of visual information from the retina to the brain.
Visual information from the retina is carried through the optic nerve to the optic chiasm, where some fibers cross over to the opposite side. The fibers then continue as the optic tract to the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus. From there, signals are relayed to the visual cortex in the occipital lobe of the brain, where the information is processed and interpreted to form the visual perceptions we experience.
Explain how the brain interprets visual information to create perception.
The brain interprets visual information by processing signals received from the eyes through the optic nerve and transmitting them to the visual cortex at the back of the brain. This information is then analyzed and combined with previous knowledge and experiences to create perception. Various areas of the brain work together to recognize shapes, colors, movement, and depth in order to form a cohesive representation of the visual world. Neural pathways also help to integrate visual information with other senses to provide a complete understanding of the environment.
What is the role of the optic nerve in vision?
The optic nerve is a crucial component in the visual system as it transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. It carries signals generated by the photoreceptor cells of the retina to the visual cortex, where they are interpreted and processed to form the images we see. The optic nerve plays a key role in allowing us to perceive and make sense of the visual world around us.
How does the brain process depth perception in relation to binocular and monocular cues?
Depth perception is processed by the brain through a combination of binocular and monocular cues. Binocular cues, such as retinal disparity and convergence, provide information based on the slightly different perspectives of each eye, enabling the brain to determine depth and distance. On the other hand, monocular cues, such as relative size, interposition, linear perspective, texture gradient, and shading, provide depth information based on a single eye's view of the world. The brain integrates these cues to create a cohesive and accurate perception of depth in our environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




















Comments