Sound Waves Worksheet Label
Are you looking for a helpful resource to teach your students about sound waves? Look no further! Our Sound Waves Worksheet is designed to engage and educate students on the topic of sound waves. This worksheet provides clear labeling exercises to help students identify the different components and characteristics of sound waves. Whether you're a teacher looking for a classroom activity or a parent wanting to supplement your child's learning at home, this worksheet is perfect for anyone seeking a comprehensive understanding of sound waves and their properties.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
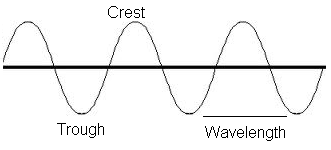
What is a sound wave?
A sound wave is a type of pressure wave that transmits energy through a medium, such as air or water, by vibrating particles in the medium in a back-and-forth motion. These vibrations create changes in pressure that our ears can detect as sound. Sound waves travel at different speeds depending on the medium they are passing through, and they can have varying frequencies and amplitudes, which determine the pitch and volume of the sound we hear.
How does sound travel through different mediums?
Sound travels through different mediums by creating vibrations that are transmitted through the molecules of the medium. In solids, such as metals, sound travels fastest because the molecules are closely packed together, allowing for efficient transfer of energy. In liquids, such as water, sound travels at a moderate speed as the molecules are more spread out. In gases, like air, sound travels slowest because the molecules are farther apart, causing the vibrations to move less efficiently. The speed of sound in a medium depends on factors such as temperature and density, with sound waves moving faster in denser materials.
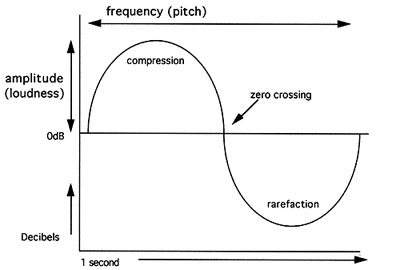
What is the frequency of a sound wave?
The frequency of a sound wave is the number of complete cycles of a wave that occur in a certain amount of time, typically measured in hertz (Hz), which represents cycles per second. It determines the pitch of the sound, with higher frequencies corresponding to higher pitches and lower frequencies to lower pitches.
What is the relationship between frequency and pitch?
Frequency and pitch are directly related, as frequency determines the pitch of a sound. The higher the frequency of a sound wave, the higher the pitch perceived by the human ear. Conversely, lower frequencies result in lower pitches. This relationship is a fundamental aspect of how we perceive and differentiate various sounds in our environment.
How is the amplitude of a sound wave related to its volume?
The amplitude of a sound wave is directly related to its volume – a sound wave with a higher amplitude will have a greater volume, while a sound wave with a lower amplitude will have a lower volume. Essentially, the larger the amplitude of a sound wave, the louder the sound will be perceived by our ears. This relationship is fundamental to understanding how loud or soft sounds are perceived by humans.
How is a sound wave produced?
A sound wave is produced when a vibrating object causes the surrounding air particles to compress and rarefy, creating a series of alternating regions of high and low pressure. This pattern of compressions and rarefactions travels through the air as a sound wave, eventually reaching our ears where it is detected and interpreted as sound.
What is the speed of sound in air?
The speed of sound in air is approximately 343 meters per second at room temperature (20 degrees Celsius).
How is the wavelength of a sound wave determined?
The wavelength of a sound wave is determined by the speed of sound in a medium and the frequency of the wave. The wavelength can be calculated using the formula wavelength = speed of sound / frequency. This means that as the frequency of a sound wave increases, the wavelength decreases, and vice versa.
How does the shape of a sound wave affect its quality or timbre?
The shape of a sound wave affects its quality or timbre by determining the presence and relative strength of harmonics and overtones. Different shapes of sound waves create different harmonic content, which gives each sound its unique timbre. For example, a sine wave produces a pure tone without any harmonics, while complex waveforms like sawtooth or square waves contain rich harmonic content, resulting in a more complex and colorful timbre.
How are sound waves detected by the human ear?
Sound waves are detected by the human ear through a process where the waves enter the ear canal and cause the eardrum to vibrate. These vibrations are then transmitted through the middle ear bones to the cochlea in the inner ear. Within the cochlea, hair cells convert the vibrations into electrical signals that are then sent to the brain via the auditory nerve for processing, allowing us to perceive and interpret the sound.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
































Comments