RNA Translation Worksheets
Are you a student or educator interested in exploring the fascinating world of RNA translation? Look no further! In this blog post, we will introduce you to a collection of worksheets designed to help you understand this complex biological process. These worksheets provide a structured and practical approach to learning about RNA translation, making it easier for both beginners and advanced learners to grasp the key concepts and engage with the subject matter.
Table of Images 👆
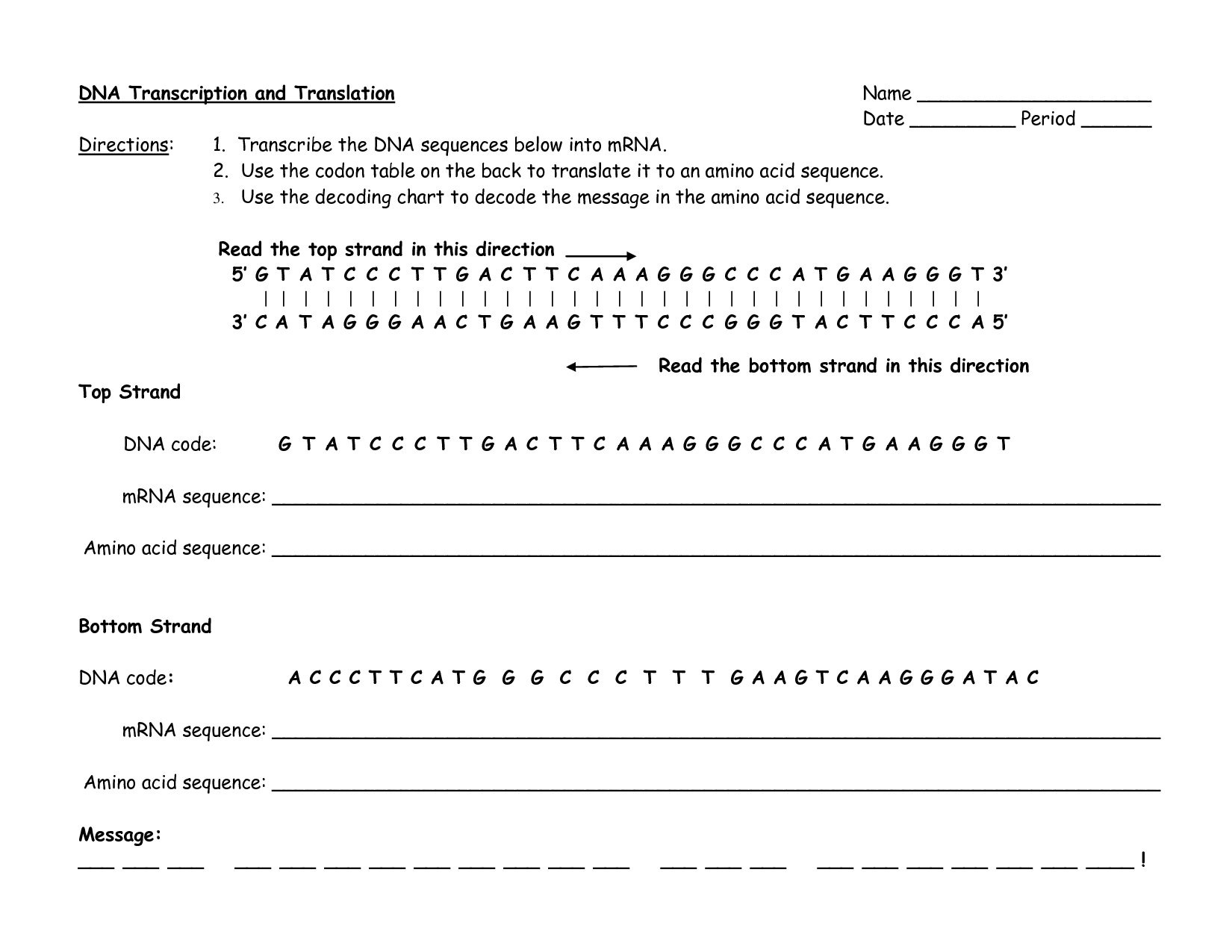
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Transcription Translation Worksheet
- RNA Transcription Worksheet
- DNA Replication Transcription Translation Worksheet
- DNA and RNA Structure Worksheet Answers
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription Translation Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is RNA translation?
RNA translation is the process in which the genetic information encoded in messenger RNA (mRNA) is used to synthesize proteins. It occurs on ribosomes, where transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring specific amino acids to the ribosome based on the mRNA codons, allowing the formation of a polypeptide chain. This process is essential for creating functional proteins that carry out various cellular functions in an organism.
What is the primary function of tRNA in translation?
The primary function of tRNA in translation is to carry amino acids to the ribosome and match them with the appropriate codons on the mRNA during protein synthesis. By recognizing the specific nucleotide sequence on the mRNA, tRNA delivers the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain, allowing for the accurate assembly of proteins.
What are the three stages of translation?
The three stages of translation are initiation, elongation, and termination. In the initiation stage, the ribosome binds to the mRNA and starts matching tRNA molecules to the codons on the mRNA. During elongation, the ribosome reads the mRNA sequence, forms peptide bonds between amino acids, and moves along the mRNA to continue translating the protein. The termination stage occurs when the ribosome reaches a stop codon on the mRNA, leading to the release of the newly synthesized protein and the disassembly of the translation complex.
What is the role of ribosomes in translation?
Ribosomes play a crucial role in translation by serving as the site where messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded and proteins are synthesized. They help bring together transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules and amino acids to form a polypeptide chain based on the sequence of codons on the mRNA. Ribosomes catalyze the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, leading to the production of a functional protein.
What is the start codon in translation?
The start codon in translation is AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine.
What is the significance of the genetic code in translation?
The genetic code is crucial in translation as it determines how the sequence of nucleotides in mRNA is converted into the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Each three-nucleotide codon in mRNA corresponds to a specific amino acid or a stop signal, as dictated by the genetic code. This process ensures the accurate translation of genetic information from DNA to protein, enabling the synthesis of proteins that carry out vital functions in the cell.
How does mRNA determine the amino acid sequence?
mRNA determines the amino acid sequence through a process known as translation. During translation, the mRNA molecule is read by ribosomes, which then match each three-nucleotide sequence (codon) on the mRNA with the corresponding transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule carrying the complementary anticodon and specific amino acid. This process ensures that the amino acids are linked together in the correct order according to the genetic code specified by the mRNA molecule, ultimately determining the sequence of amino acids in the protein being synthesized.
What is the role of initiation factors in translation?
Initiation factors in translation are proteins that play a crucial role in the initiation phase of protein synthesis. They help assemble the ribosome at the start codon of the mRNA to ensure accurate and efficient translation of genetic information. Initiation factors also help recruit the initiator tRNA and facilitate the formation of the first peptide bond between amino acids. Ultimately, initiation factors help kickstart the process of protein synthesis by ensuring that all the necessary components are brought together in the right order at the beginning of mRNA translation.
What is the significance of stop codons in translation?
Stop codons, also known as termination codons, are critical in translation as they signal the end of protein synthesis. When a ribosome encounters a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) on the mRNA, it recognizes that the protein chain is complete and releases the newly synthesized protein. This ensures that the amino acid chain is accurately assembled into the correct protein structure, preventing the addition of unnecessary amino acids. The presence of stop codons is essential for the proper termination of translation and the production of functional proteins.
How is protein synthesis terminated in translation?
Protein synthesis is terminated in translation when a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) enters the A site of the ribosome. This signals the release factor protein to bind to the ribosome, causing the ribosome to release the completed polypeptide chain. The ribosome then dissociates from the mRNA, allowing the newly synthesized protein to fold into its functional conformation.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.




























Comments