Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Chart Answers
Are you a student searching for comprehensive and accurate answers to your organic macromolecules worksheet? Look no further! This blog post aims to assist you by providing the entity and subject required for your worksheet.
Table of Images 👆
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Macromolecules Review Worksheet Answer Key
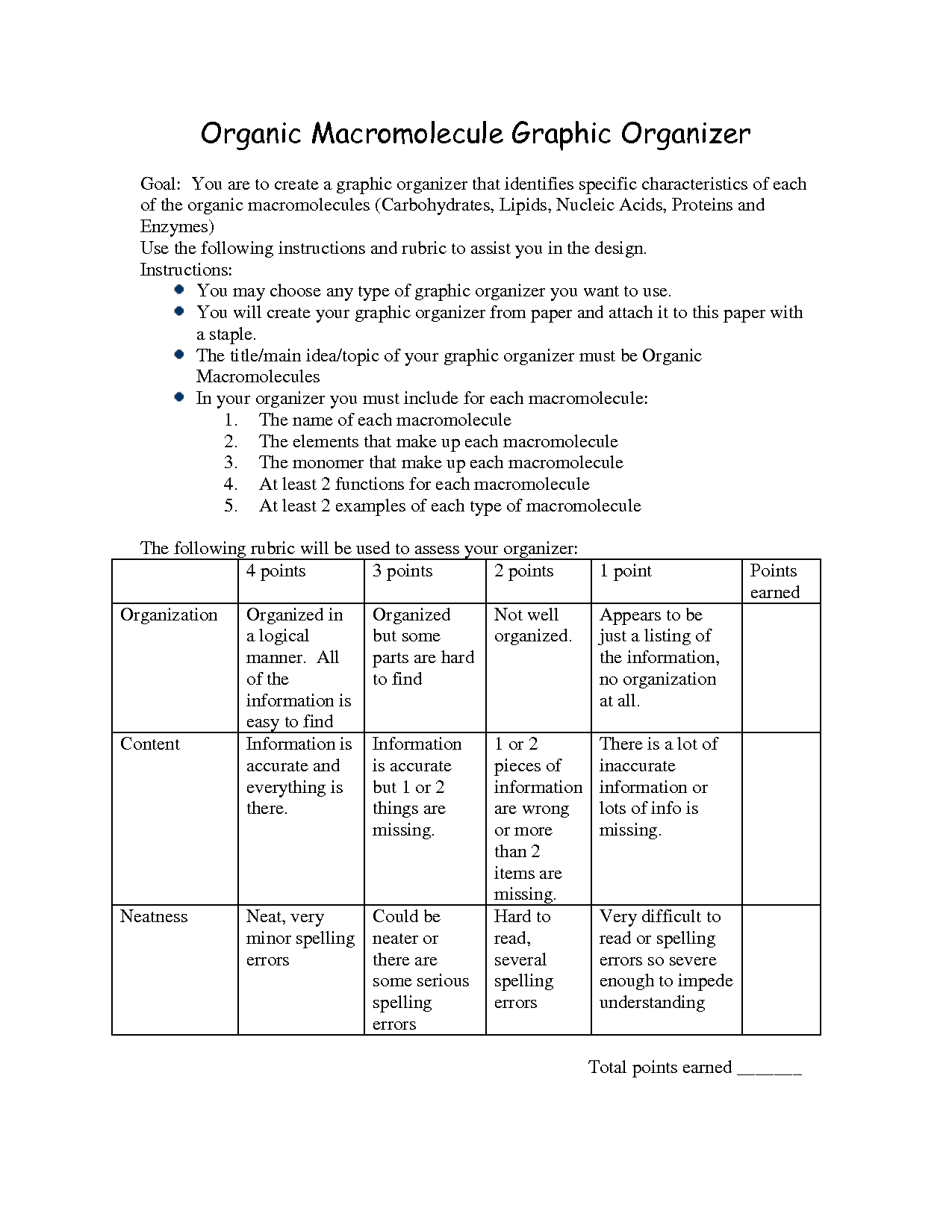
- Organic Macromolecules Graphic Organizer
- Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Molecules of Life Worksheet Answers
- Label and Nutrition Worksheet Macromolecules
- Macromolecules Graphic Organizer Answer Key
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Worksheet Answers
- Organic Macromolecules Chart
- Biological Macromolecules Chart
- Macromolecule Worksheet Answer Key
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
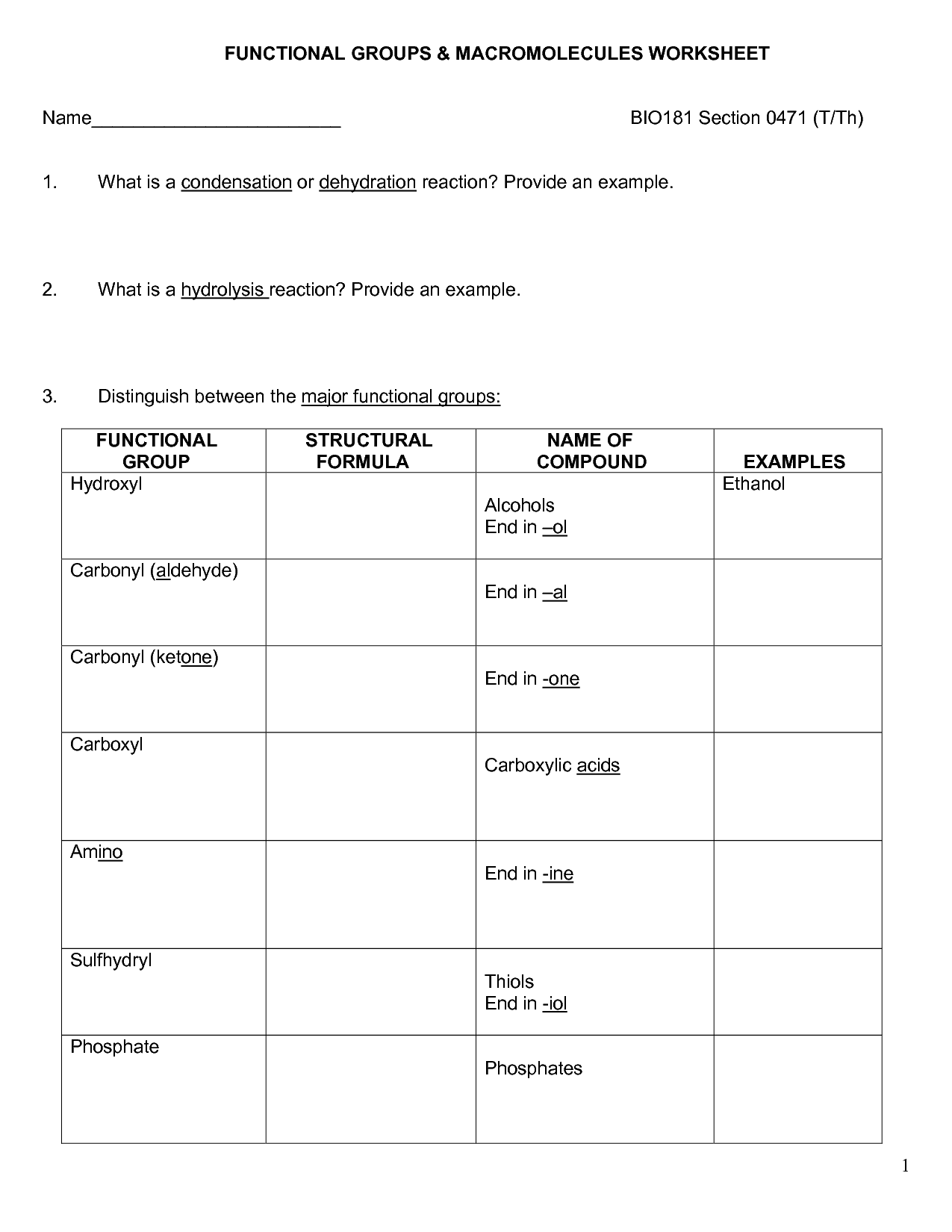
What are organic macromolecules?
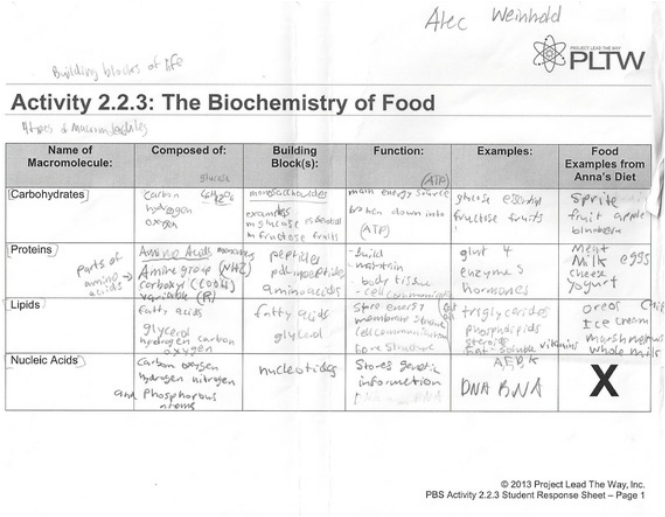
Organic macromolecules are large molecules that are composed of several smaller subunits called monomers. These macromolecules are vital for life and can be found in living organisms. There are four main types of organic macromolecules: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each type of macromolecule plays a crucial role in various biological processes and functions within the body.
Why are organic macromolecules important?
Organic macromolecules, such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids, are critical for life as they serve as the building blocks for cells and tissues. They are essential for various biological processes, including energy storage, structural support, cell signaling, and genetic information transfer. These molecules provide nutrients, carry out metabolic reactions, regulate bodily functions, and even act as enzymes that facilitate biochemical reactions. Overall, organic macromolecules play a fundamental role in maintaining the structure, function, and overall health of living organisms.
What are the four major classes of organic macromolecules?
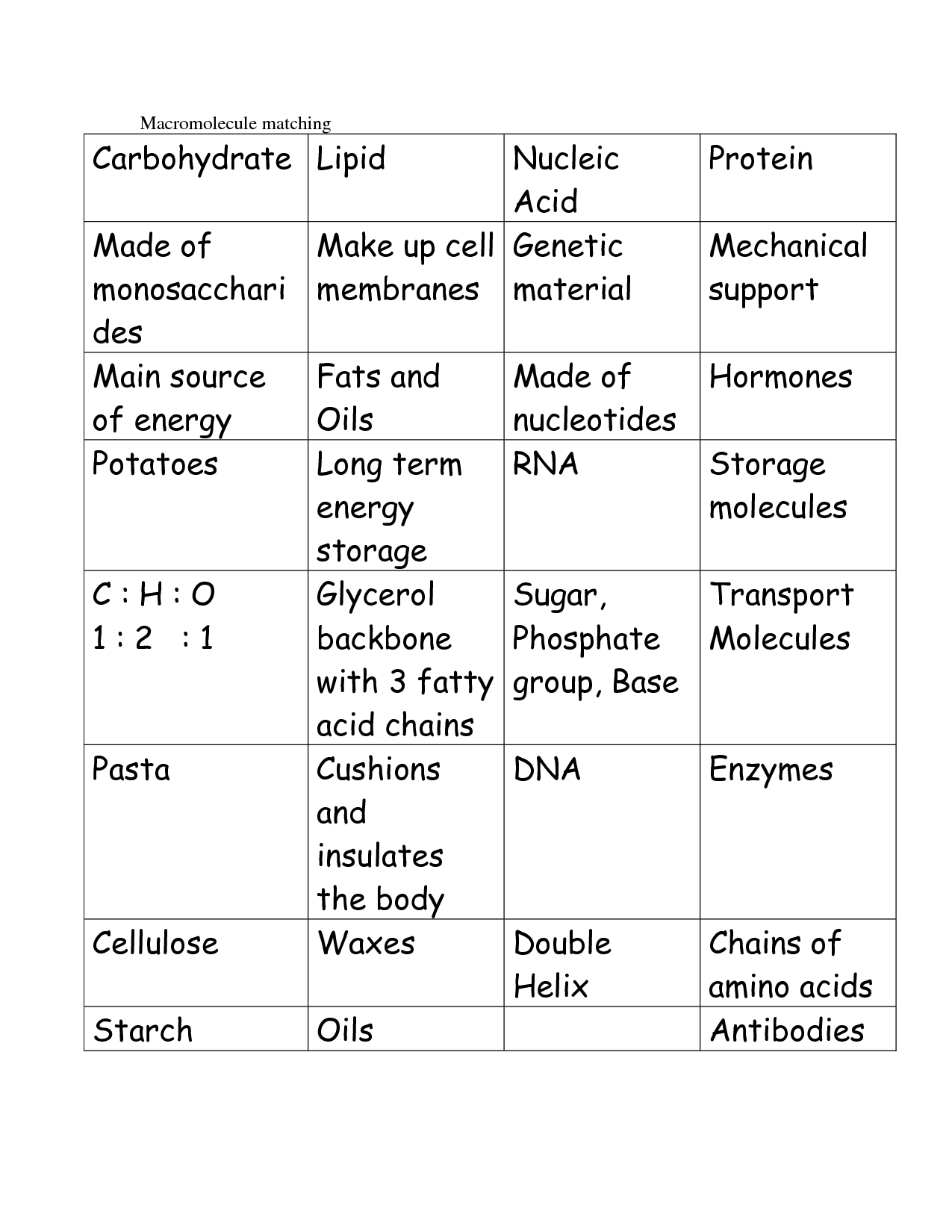
The four major classes of organic macromolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each class plays a crucial role in the structure, function, and regulation of cells and organisms. Carbohydrates are important for energy storage and structural support, lipids are essential for cell membrane structure and signaling molecules, proteins are involved in virtually all cellular functions including enzymatic reactions and structural support, and nucleic acids store and transcribe genetic information crucial for inheritance and cellular function.
What is the monomer of carbohydrates?
The monomer of carbohydrates is a simple sugar molecule, commonly known as a monosaccharide. Examples of monosaccharides include glucose, fructose, and galactose.
What is the function of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Carbohydrates serve as a primary source of energy for living organisms by providing glucose, which is used for cellular respiration to produce ATP for various metabolic processes. Additionally, carbohydrates play a crucial role in cell structure and communication as components of cell membranes and signaling molecules. They also serve as energy storage molecules in the form of glycogen in animals and starch in plants.
What is the monomer of proteins?
The monomer of proteins is amino acids. These building blocks are linked together through peptide bonds to form long chains of polypeptides, which then fold into complex three-dimensional structures to create functional proteins in living organisms.
What is the function of proteins in living organisms?
Proteins serve a variety of critical functions in living organisms, including acting as enzymes to catalyze biochemical reactions, as structural components in cells and tissues, as transport molecules to carry substances within the body, as hormones to regulate body functions, and as antibodies to defend against pathogens. Overall, proteins play a crucial role in maintaining the structure, function, and regulation of all cells and tissues in living organisms.
What is the monomer of nucleic acids?
The monomer of nucleic acids is nucleotide.
What is the function of nucleic acids in living organisms?
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, serve as the genetic material in living organisms, encoding the instructions required for growth, development, and functioning. They play essential roles in processes such as protein synthesis, cell division, and inheritance, making them crucial for the survival and proper functioning of all living organisms.
What is the structure and function of lipids in living organisms?
Lipids are diverse biomolecules that have a hydrophobic nature, allowing them to form cellular membranes that act as barriers to protect and separate the cell from its surroundings. They also serve as long-term storage of energy in the form of triglycerides, insulation to maintain body temperature, and play crucial roles in cell signaling and as precursors to hormones. The structure of lipids typically consists of hydrocarbon chains and a polar head group, enabling them to form lipid bilayers that are integral components of cell membranes, providing structural integrity and allowing for selective permeability to control the flow of molecules in and out of the cell.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments