Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answers
Worksheet activities can be an invaluable tool for learners of all ages, providing a structured and organized way to reinforce and assess knowledge on a particular subject. When it comes to understanding nucleic acids, having access to a well-designed worksheet with accurate and comprehensive answers can make all the difference. Whether you are a biology student diving into the complexities of DNA and RNA or a teacher searching for a reliable resource to enhance your lesson plans, having a set of nucleic acids worksheet answers can provide clarity and support in this specialized area of study.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets and Answers
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
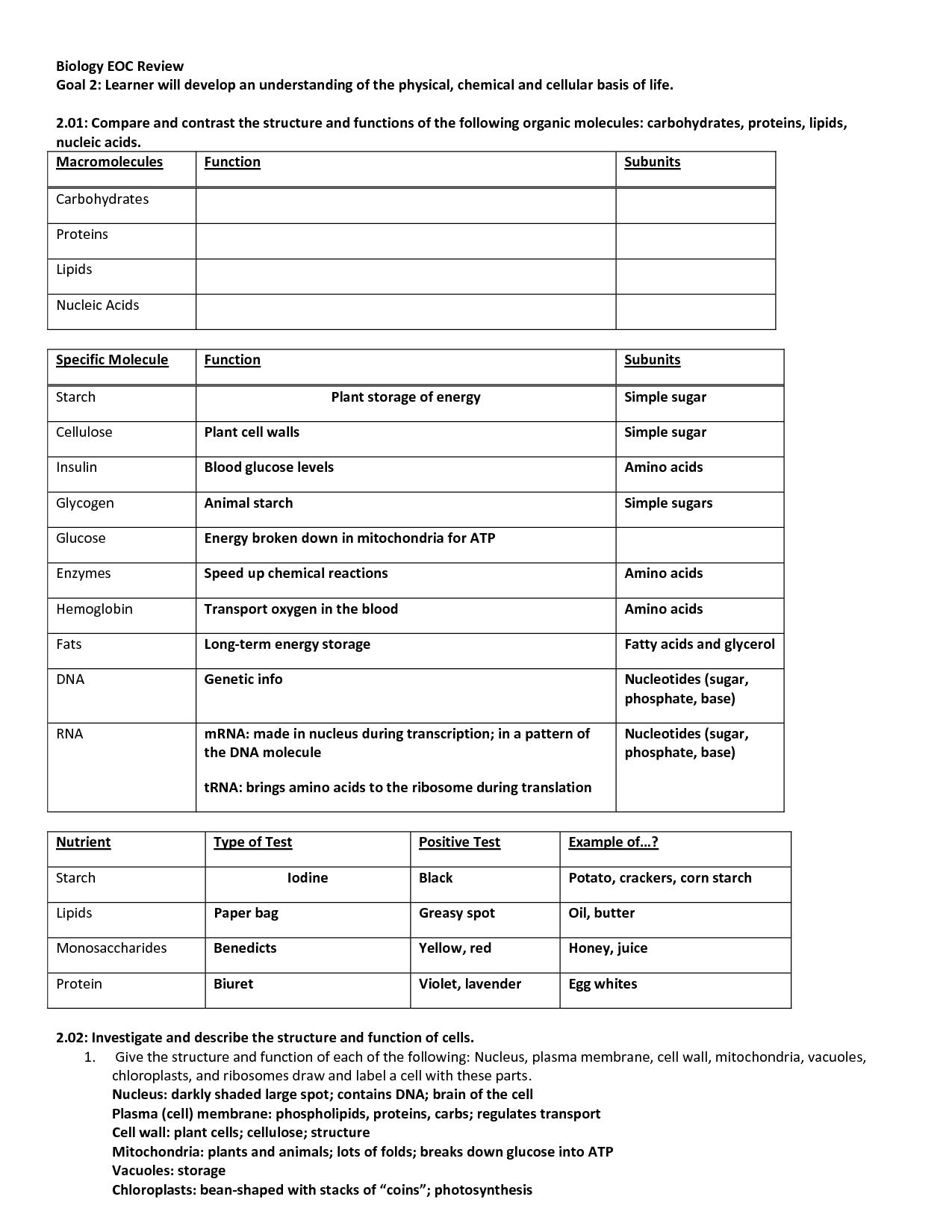
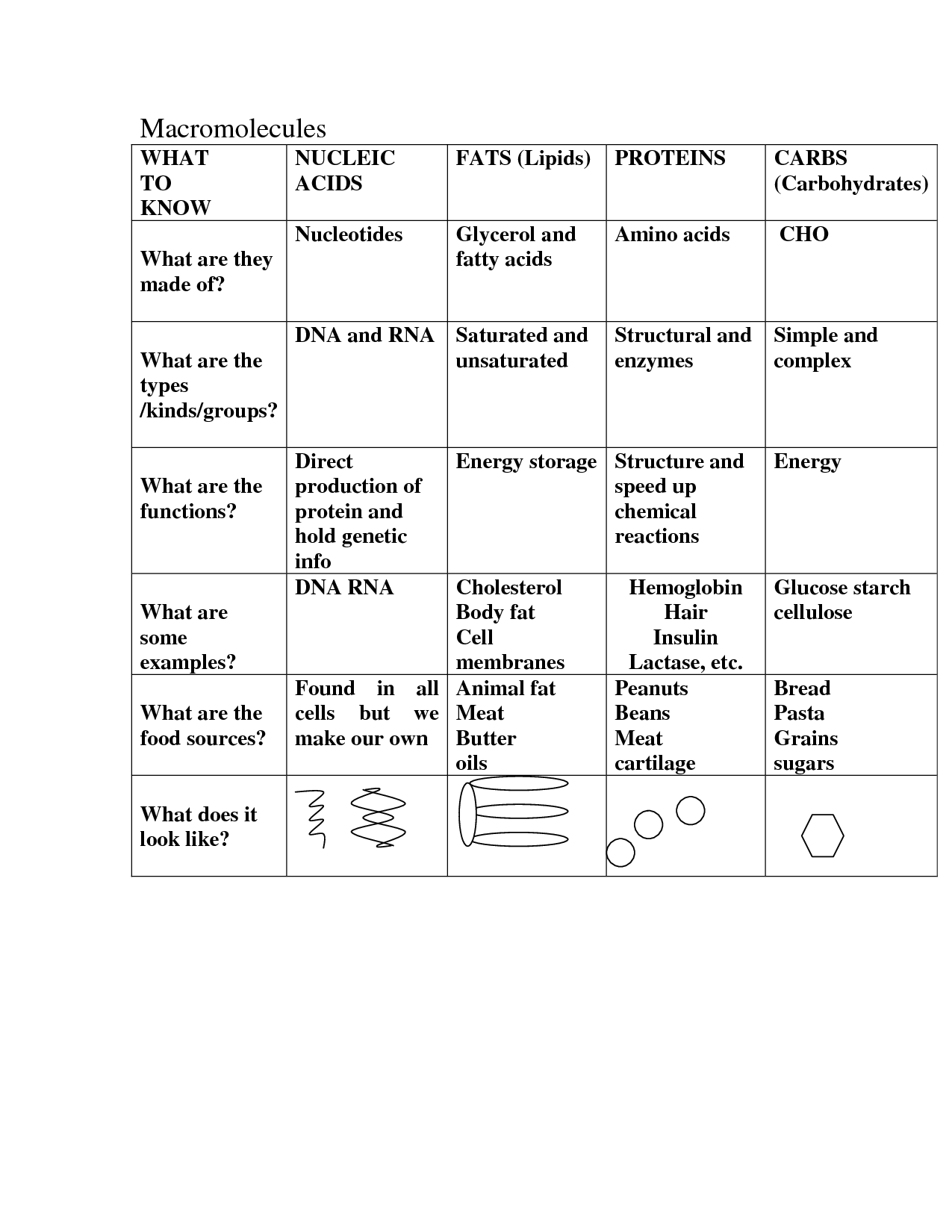
- Macromolecules Chart Worksheet
- Nucleic Acids Worksheet Answer Key
- Acids Bases and Salts Worksheet Answers
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Elements and Macromolecules in Organisms Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are nucleic acids?
Nucleic acids are biopolymers made up of nucleotides, which are molecules composed of a sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base. They serve as the building blocks of DNA and RNA, the molecules responsible for genetic information storage, transmission, and expression in living organisms. Nucleic acids play a crucial role in the functioning and regulation of cells, as well as in the inheritance of genetic traits from one generation to the next.
What is the structure of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of three parts: a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (either ribose in RNA or deoxyribose in DNA), and a nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous base can be adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, or uracil, depending on whether the nucleotide is part of DNA or RNA. These three components form the basic building blocks of nucleic acids, which are essential for genetic information storage and transfer in living organisms.
What are the two types of nucleic acids?
The two types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). DNA carries genetic information in the form of genes, while RNA plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and other cellular processes.
What is the role of nucleic acids in the body?
Nucleic acids play a crucial role in the body as they are the building blocks of DNA and RNA, which are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. DNA contains the instructions for making proteins, while RNA helps in the process of protein synthesis. Additionally, nucleic acids are involved in various cellular functions such as cell division, growth, and repair, making them essential for overall health and proper functioning of the body.
What is the process of DNA replication?
DNA replication is a complex biological process where a DNA molecule is duplicated to produce two identical copies. The process begins with the separation of the two strands of the DNA double helix by enzymes called helicases. Primase then adds short RNA primers to each strand, which serve as templates for DNA polymerases to synthesize new DNA strands. The leading strand is synthesized continuously in the 5' to 3' direction, while the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously in fragments called Okazaki fragments, which are later joined by DNA ligase. The end result is two identical DNA molecules, each consisting of one original strand and one newly synthesized strand.
What is transcription and why is it important?
Transcription is the process of copying genetic information from DNA to RNA. It is important because it is the first step in gene expression, where specific segments of DNA are transcribed into RNA molecules that serve as templates for protein synthesis. This process is essential for the production of proteins that carry out various cellular functions and processes, making transcription a fundamental mechanism for translating genetic information into functional molecules within living organisms.
How does RNA differ from DNA?
RNA differs from DNA in several key ways. RNA is single-stranded, whereas DNA is double-stranded. RNA contains ribose sugar, while DNA contains deoxyribose sugar. RNA contains uracil as a base instead of thymine found in DNA. Additionally, RNA is mainly involved in protein synthesis and carries out various functions in the cell, such as translating genetic information from DNA into proteins, while DNA carries genetic information and is responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information.
What is translation and how is it related to nucleic acids?
Translation is the process by which a ribosome decodes mRNA to produce a specific amino acid sequence, forming a protein. This process is closely related to nucleic acids as mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to the ribosome. During translation, transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules deliver amino acids to the ribosome based on the codons on the mRNA, ultimately leading to the synthesis of proteins. Thus, translation is a fundamental process that converts the genetic information coded in nucleic acids into functional proteins essential for various cellular processes.
What is the role of mRNA, tRNA, and rRNA in protein synthesis?
mRNA (messenger RNA) carries genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs. tRNA (transfer RNA) brings amino acids to the ribosomes based on the mRNA sequence, ensuring the correct sequence of amino acids is incorporated into the growing protein chain. rRNA (ribosomal RNA) is a component of the ribosomes where the actual protein synthesis takes place, providing the site for the assembly of amino acids into a functional protein. Together, these three types of RNA play essential roles in the process of protein synthesis within cells.
How do mutations in nucleic acids contribute to genetic disorders?
Mutations in nucleic acids, such as DNA or RNA, can lead to genetic disorders by altering the normal sequence of genetic information. These changes can disrupt the production of functional proteins, affect gene regulation, or impair essential cellular processes. As a result, mutations can cause abnormalities in an individual's development, metabolism, or overall health, leading to the manifestation of genetic disorders.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments