Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
Worksheets are an invaluable tool for students and educators alike, providing a structured way to practice and learn new concepts. When it comes to the topic of mutations, a well-designed worksheet can serve as an essential resource to reinforce understanding. Whether you are a biology teacher seeking a comprehensive answer key or a student looking for a helpful study guide, the mutations worksheet answer key presents a clear and concise solution to explore this complex subject.
Table of Images 👆
- DNA Mutations Practice Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
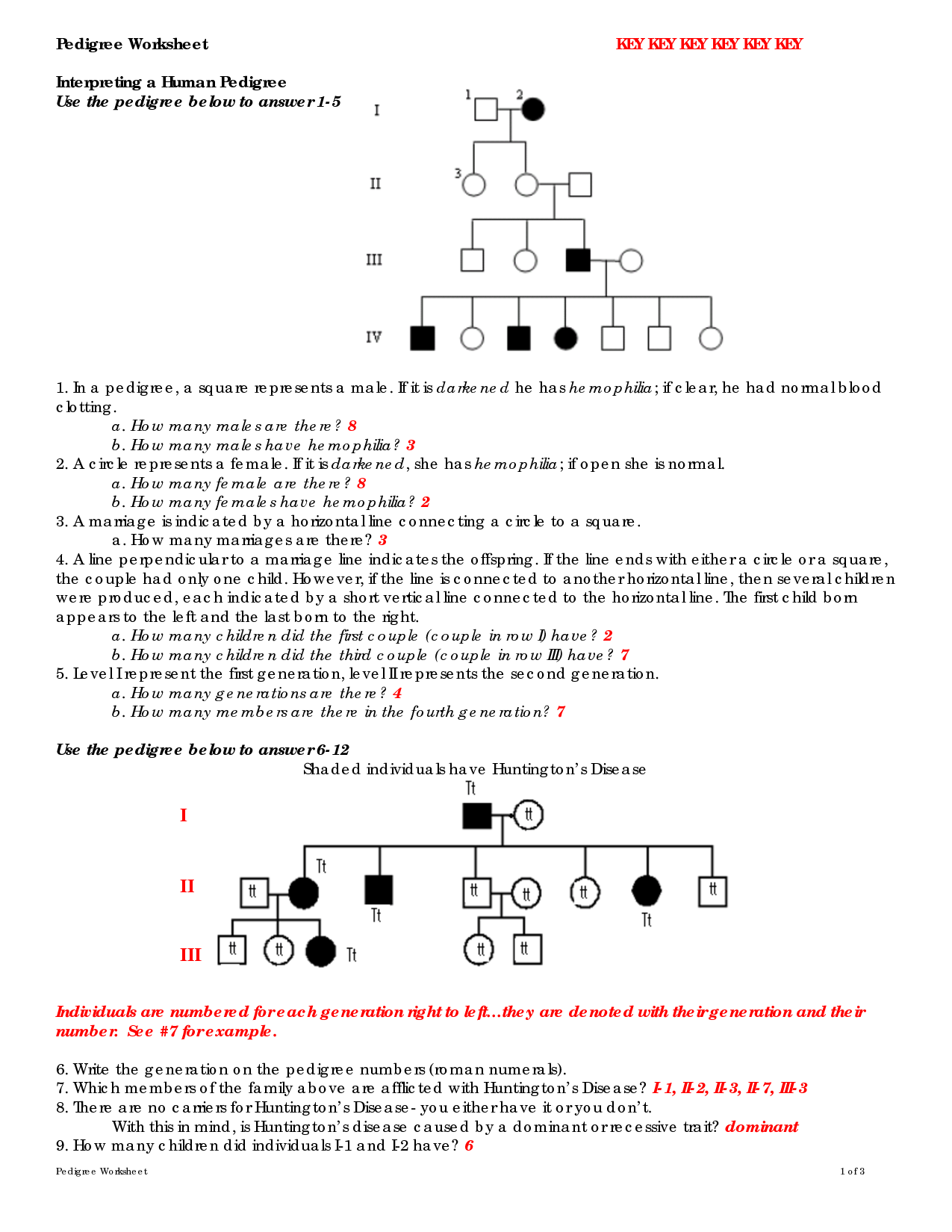
- Genetics Pedigree Worksheet Answer Key
- Gene Mutation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Replication Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Chemistry Unit 5 Worksheet 2 Answer Key
- Monohybrid Cross Worksheet Answer Key
- Genetic Mutation Worksheet Answers
- DNA Mutation Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are mutations?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can result in genetic variation. These changes can be caused by a variety of factors, such as errors during DNA replication, exposure to environmental factors like radiation or chemicals, or genetic predisposition. Mutations can have a range of effects, from being harmless to causing genetic disorders or increasing an organism's chance of survival in changing environments.
How do mutations occur?
Mutations occur when there are changes in the genetic material, such as alterations in the DNA sequence. These changes can be caused by errors in DNA replication, exposure to mutagenic chemicals or radiation, or even spontaneous alterations. Mutations can also be inherited from parents or occur randomly.
What are the different types of mutations?
There are several types of mutations, including point mutations (substitutions, insertions, deletions), frameshift mutations, silent mutations, missense mutations, nonsense mutations, inversion mutations, duplication mutations, and translocation mutations. These mutations can occur in different parts of the DNA sequence and can have various effects on the resulting proteins or organisms.
What is the role of DNA repair mechanisms in preventing mutations?
DNA repair mechanisms are essential in preventing mutations by detecting and fixing errors that occur during DNA replication or as a result of environmental factors such as UV radiation or chemicals. These mechanisms ensure that any damages or mutations in the DNA sequence are properly corrected, maintaining the integrity of the genetic information and preventing the accumulation of mutations that could lead to diseases such as cancer. Failure of DNA repair mechanisms can result in the proliferation of mutations, increasing the risk of genetic disorders and other detrimental effects on the organism.
How do mutations contribute to genetic diversity?
Mutations contribute to genetic diversity by introducing changes in the DNA sequence of an organism, leading to different alleles and variations within a population. These mutations can alter gene function, create new traits, and provide the raw material for evolution through natural selection, enabling species to adapt and survive in changing environments. By generating diversity at the molecular level, mutations play a crucial role in the inheritance and evolution of traits within species.
What are the potential consequences of mutations?
Mutations can have a range of consequences, including causing genetic disorders, changing an organism's physical traits or behaviors, and potentially leading to diseases like cancer. Some mutations may have no effect at all, while others could be harmful or beneficial to an organism's survival and reproduction. The impact of a mutation depends on where it occurs in the genome, how it alters the genetic information, and how it interacts with other genetic and environmental factors.
How do mutations affect protein function?
Mutations can alter the structure and sequence of proteins, affecting their function by changing the amino acid composition, disrupting protein folding, or modifying protein stability. This can lead to loss of function, reduced activity, or gain of new functions, resulting in possible changes in protein interactions, cellular processes, and overall biological functions.
What is the difference between somatic and germ-line mutations?
Somatic mutations occur in non-reproductive cells and are not passed on to offspring, affecting only the individual in whom they occur. Germ-line mutations, on the other hand, occur in reproductive cells (sperm or egg cells) and can be passed on to offspring, potentially affecting future generations.
How can mutations lead to the development of diseases?
Mutations can lead to the development of diseases by disrupting the normal functioning of genes and proteins in the body. This can result in the production of faulty or non-functional proteins, altered cellular processes, and improper regulation of cell growth and division. Such abnormalities can lead to various health conditions, including genetic disorders, cancer, and other diseases.
What are some examples of beneficial mutations?
Some examples of beneficial mutations include the ability to digest lactose in adulthood, resistance to specific diseases such as malaria or HIV, increased bone density for improved strength, and adaptations for high-altitude living. These mutations provide advantages to individuals in their specific environments, contributing to their survival and reproductive success.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.































Comments