mRNA Translation Worksheet
If you're an aspiring biologist or a curious learner seeking a deeper understanding of mRNA translation, then this blog post is for you. In this detailed worksheet, we will dive into the complex process of mRNA translation, breaking it down into manageable steps and explaining the key concepts. Whether you're a student preparing for an exam or simply eager to expand your knowledge, our mRNA translation worksheet will guide you through the intricate world of molecular biology.
Table of Images 👆
- Transcription and Translation Practice Worksheet
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- Transcription and RNA Worksheet Answer Key
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet DNA and RNA
- DNA RNA Transcription Translation Worksheets
- Transcription Worksheet DNA mRNA Amino Acid
- DNA Transcription and Translation Worksheet Answers
- Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answer Key
- Protein Synthesis Transcription and Translation Worksheet
- mRNA and Transcription Worksheet
- DNA Protein Synthesis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
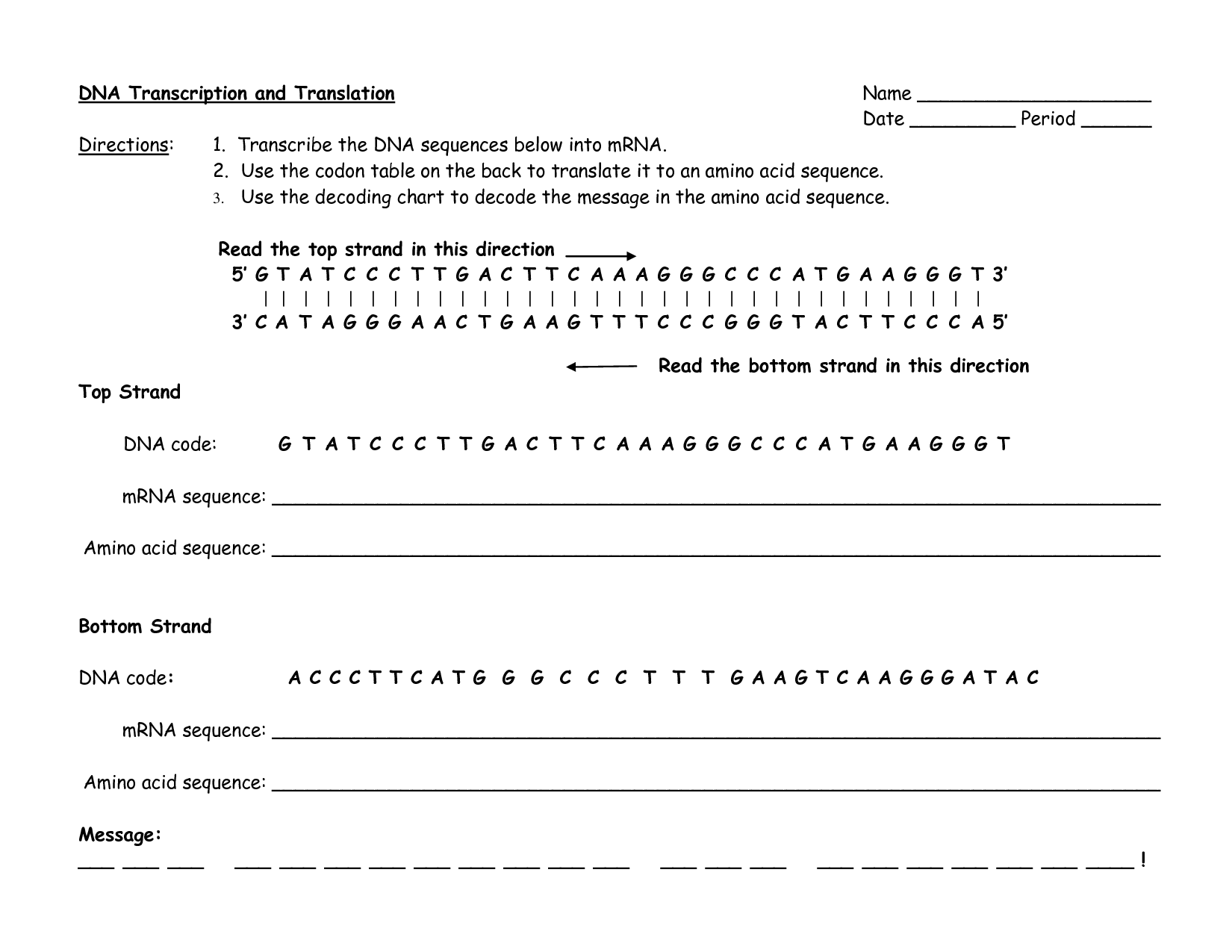
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is mRNA translation?
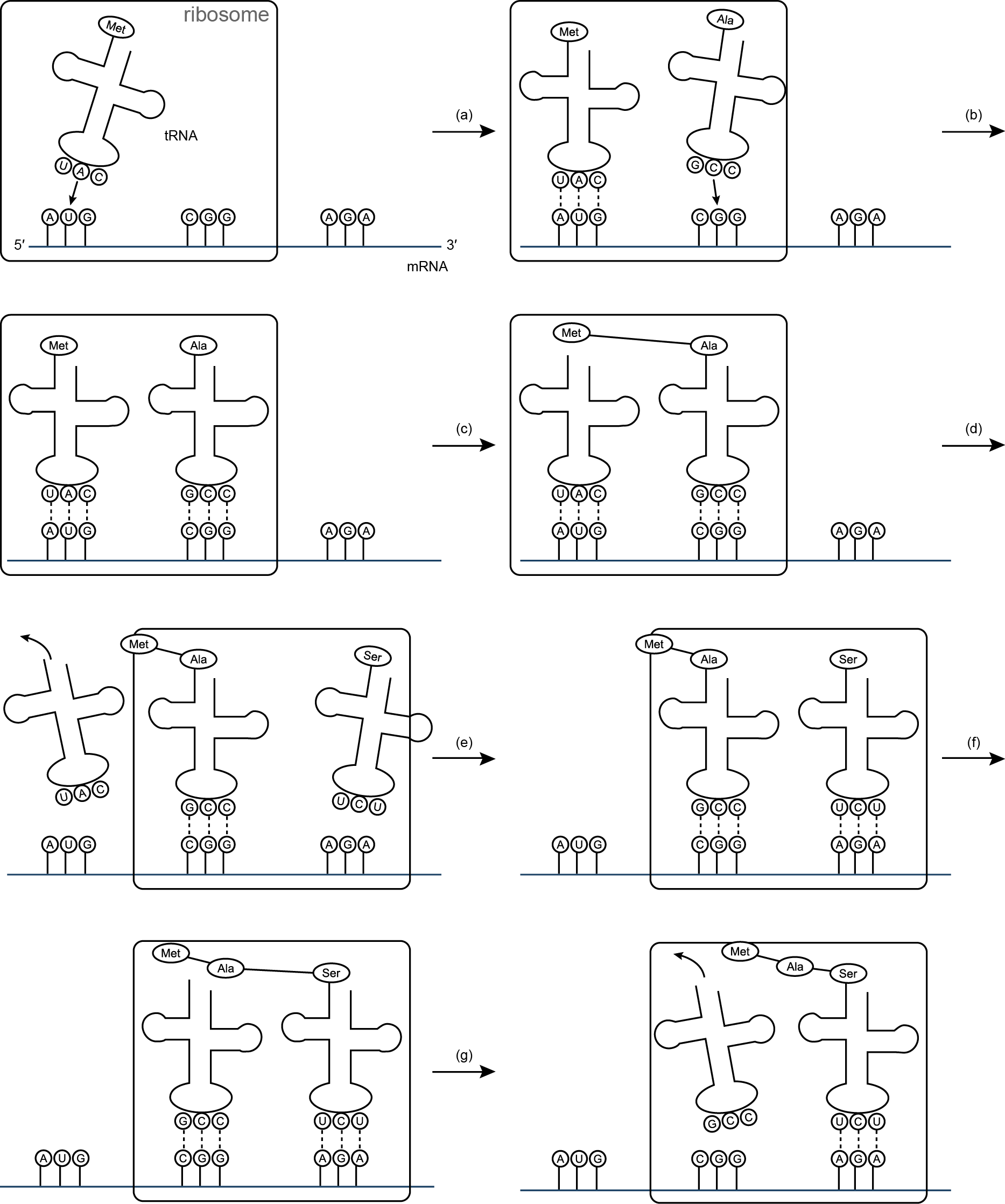
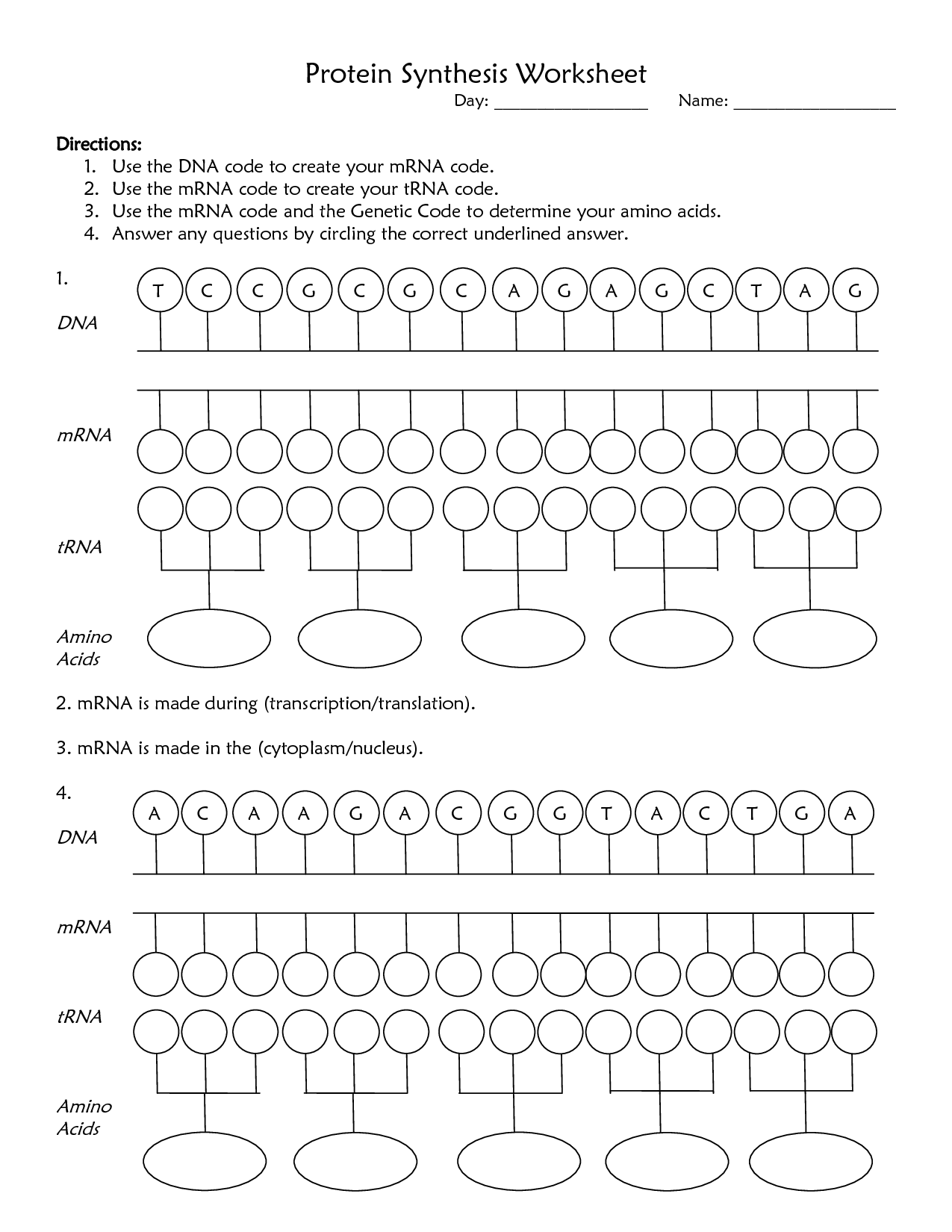
mRNA translation is the process in which the genetic information from messenger RNA (mRNA) is decoded by ribosomes to synthesize proteins. During translation, amino acids are brought to the ribosome by transfer RNAs (tRNAs) based on the codons present on the mRNA. The ribosome reads the mRNA in groups of three nucleotides called codons, and the corresponding amino acids are linked together to form a protein chain according to the instructions encoded in the mRNA.
What is the role of ribosomes in mRNA translation?
Ribosomes play a crucial role in mRNA translation by facilitating the assembly of amino acids into proteins. They read the genetic code carried by the mRNA and use this information to synthesize specific proteins by linking amino acids together in the correct order. This process occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell and is essential for producing the proteins that perform a wide range of functions within the organism.
What is the start codon in mRNA translation?
The start codon in mRNA translation is AUG, which codes for the amino acid methionine and signals the beginning of protein synthesis.
How is the genetic code decoded during mRNA translation?
During mRNA translation, the genetic code is decoded by ribosomes, which are complexes of RNA and proteins. Transfer RNA (tRNA) molecules bring amino acids to the ribosome based on the mRNA sequence. Each tRNA molecule carries a specific amino acid and has an anticodon that is complementary to the codon on the mRNA. The ribosome reads the mRNA sequence three nucleotides at a time (codon) and matches it with the corresponding anticodon on the tRNA. As the ribosome moves along the mRNA strand, it catalyzes the formation of peptide bonds between the amino acids brought by the tRNAs, ultimately leading to the synthesis of a polypeptide chain according to the genetic code.
What are tRNA molecules and what is their role in mRNA translation?
tRNA molecules, or transfer RNA molecules, are a type of RNA that plays a crucial role in mRNA translation. tRNA molecules are responsible for bringing specific amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis. Each tRNA molecule has an anticodon, which is complementary to a specific codon on the mRNA. This matching of the anticodon to the codon allows the tRNA to deliver the correct amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain according to the genetic code, ultimately leading to the production of a functional protein.
Explain the process of initiation in mRNA translation.
Initiation in mRNA translation begins with the binding of the small ribosomal subunit to the mRNA. The initiator tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine also binds to the start codon on the mRNA. This complex then recruits the large ribosomal subunit to form a complete ribosome. Once the ribosome is assembled, translation initiation factors help to ensure that the process is ready to start elongating the polypeptide chain. The initiation process concludes when the ribosome starts moving along the mRNA, reading the codons and adding amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain.
Describe the process of elongation in mRNA translation.
Elongation in mRNA translation involves the addition of amino acids to the growing polypeptide chain. This process begins with the arrival of an aminoacyl-tRNA carrying the appropriate amino acid to the ribosome's A site. The ribosome then catalyzes the formation of a peptide bond between the new amino acid and the previous amino acid in the chain, transferring the growing chain to the tRNA in the A site. Subsequently, the ribosome translocates along the mRNA, moving the tRNAs to the next bonding site (A-to-P site, P-to-E site) and allowing a new aminoacyl-tRNA to enter the A site. This cycle continues until a stop codon is reached, leading to the termination of translation.
What is a stop codon, and what is its significance in mRNA translation?
A stop codon is a nucleotide triplet in mRNA that signals the termination of protein translation. It does not code for any amino acid but instructs the ribosome to release the newly synthesized protein. Stop codons (such as UAG, UAA, and UGA) are essential in mRNA translation as they indicate where the protein synthesis should end, ensuring the creation of a complete and functional protein.
What is the role of release factors in terminating mRNA translation?
Release factors play a crucial role in terminating mRNA translation by recognizing the stop codon on the mRNA and triggering the release of the newly synthesized protein from the ribosome. When a release factor recognizes a stop codon, it promotes the hydrolysis of the bond between the final tRNA and the completed protein, allowing the ribosome to disassemble and the new protein to be released into the cell for further processing and function.
What happens to the polypeptide chain after mRNA translation is complete?
After mRNA translation is complete, the polypeptide chain undergoes folding and post-translational modifications to attain its functional three-dimensional structure. Chaperone proteins assist in the folding process, while enzymes may add chemical groups like sugars or phosphates for functionality. Once correctly folded and modified, the mature protein molecule can then carry out its specific biological functions within the cell.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





























Comments