Mitosis in Plant Cells Worksheet Answers
If you're a biology student looking for a helpful resource to test your knowledge of mitosis in plant cells, you've come to the right place. This blog post presents a collection of carefully crafted worksheets that provide comprehensive answers to questions about the processes and stages of mitosis specifically in plant cells.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
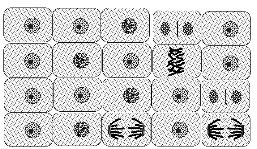
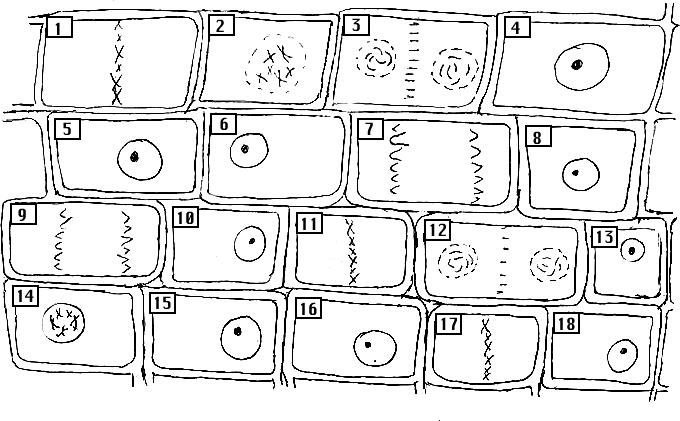
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a process in cell division where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is essential for growth, development, and repair of tissues in multicellular organisms. During mitosis, the cell's genetic material is evenly distributed between the daughter cells to ensure that they have the same genetic information as the parent cell.
Mitosis is the process in which a cell divides to form two identical daughter cells.
Mitosis is a fundamental cellular process where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells, each with the same genetic information as the original cell. During mitosis, the cell's chromosomes are replicated and segregated into two nuclei, ultimately ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of genetic material. This tightly regulated process plays a critical role in growth, development, and tissue repair in multicellular organisms.
What are the main stages of mitosis?
The main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Prophase involves the condensation of chromosomes and the breakdown of the nuclear envelope. Metaphase is characterized by the alignment of chromosomes at the center of the cell. Anaphase sees the separation of sister chromatids towards opposite poles of the cell. Finally, telophase involves the decondensation of chromosomes, the reformation of the nuclear envelope, and the division of the cytoplasm in a process called cytokinesis.
The main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
Correct, the main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, the chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers begin to form. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate. Anaphase is characterized by the separation of sister chromatids towards opposite poles of the cell. Finally, during telophase, the chromosomes decondense, the nuclear envelope reforms, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis, resulting in two daughter cells with identical genetic material.
What happens during prophase?
During prophase, which is the first stage of mitosis, the chromatin in the nucleus condenses into tightly packed chromosomes. The nuclear membrane begins to break down, and spindle fibers start to form. The centrosomes move to opposite poles of the cell, and the chromosomes become visible under a microscope. This process prepares the cell for division by ensuring that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes.
During prophase, the chromatin condenses, the nuclear membrane disintegrates, and the mitotic spindle forms.
During prophase of mitosis, the genetic material inside the nucleus condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and spindle fibers start to form. This process marks the beginning of cell division and prepares the cell for the segregation of chromosomes into the daughter cells.
What happens during metaphase?
During metaphase, the duplicated chromosomes align at the center of the cell along the metaphase plate. The spindle fibers attach to each chromatid at the centromere and help to move the chromosomes into position for separation during anaphase. This alignment ensures that each daughter cell will receive the correct number of chromosomes during cell division.
During metaphase, the chromosomes align at the center of the cell along the metaphase plate.
During metaphase, the chromosomes align at the center of the cell along the metaphase plate.
What happens during anaphase?
During anaphase, the sister chromatids, which are exact copies of each other and are held together by a protein structure called the centromere, are pulled apart toward opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. This results in each daughter cell receiving an identical set of chromosomes.
During anaphase, the sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell.
During anaphase, the sister chromatids, which are exact copies of each other, separate from each other and are pulled towards opposite ends of the cell by the spindle fibers. This movement ensures that each daughter cell receives an identical set of chromosomes during cell division.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments