Meiosis Review Worksheet
Are you searching for a comprehensive Meiosis review worksheet? Look no further! This blog post is designed to help biology students understand and practice the key concepts of Meiosis. Whether you are preparing for a test or just need extra practice, this worksheet will provide you with the perfect opportunity to strengthen your understanding of this important biological process.
Table of Images 👆
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Review Worksheet Answers
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Study Guide Answers
- 11 4 Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Vocabulary
- Meiosis vs Mitosis Worksheet
- Comparing Meiosis and Mitosis Answer Key
- Mitosis and Meiosis Test
- Mitosis versus Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis 7th Grade Science Worksheet Answers
- Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Test
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
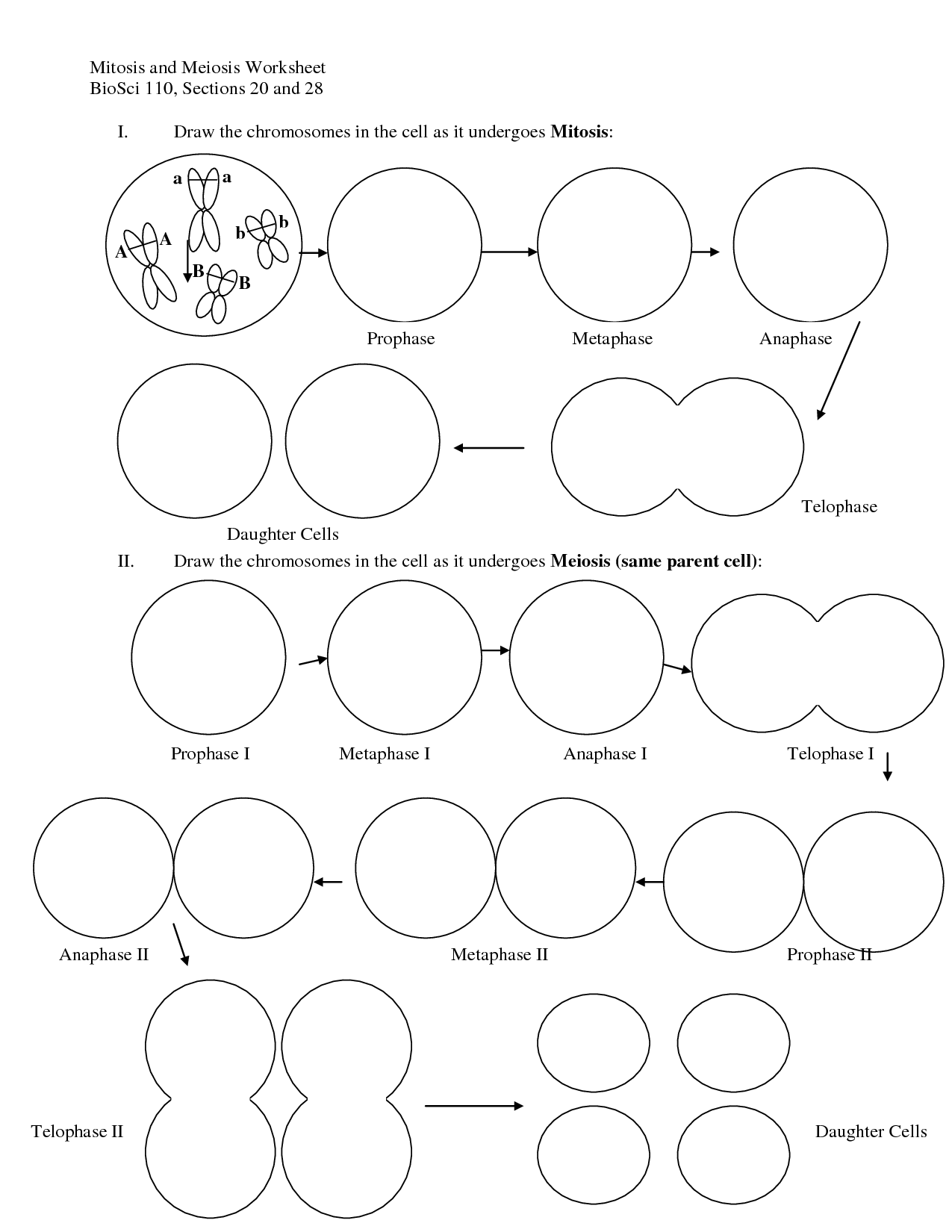
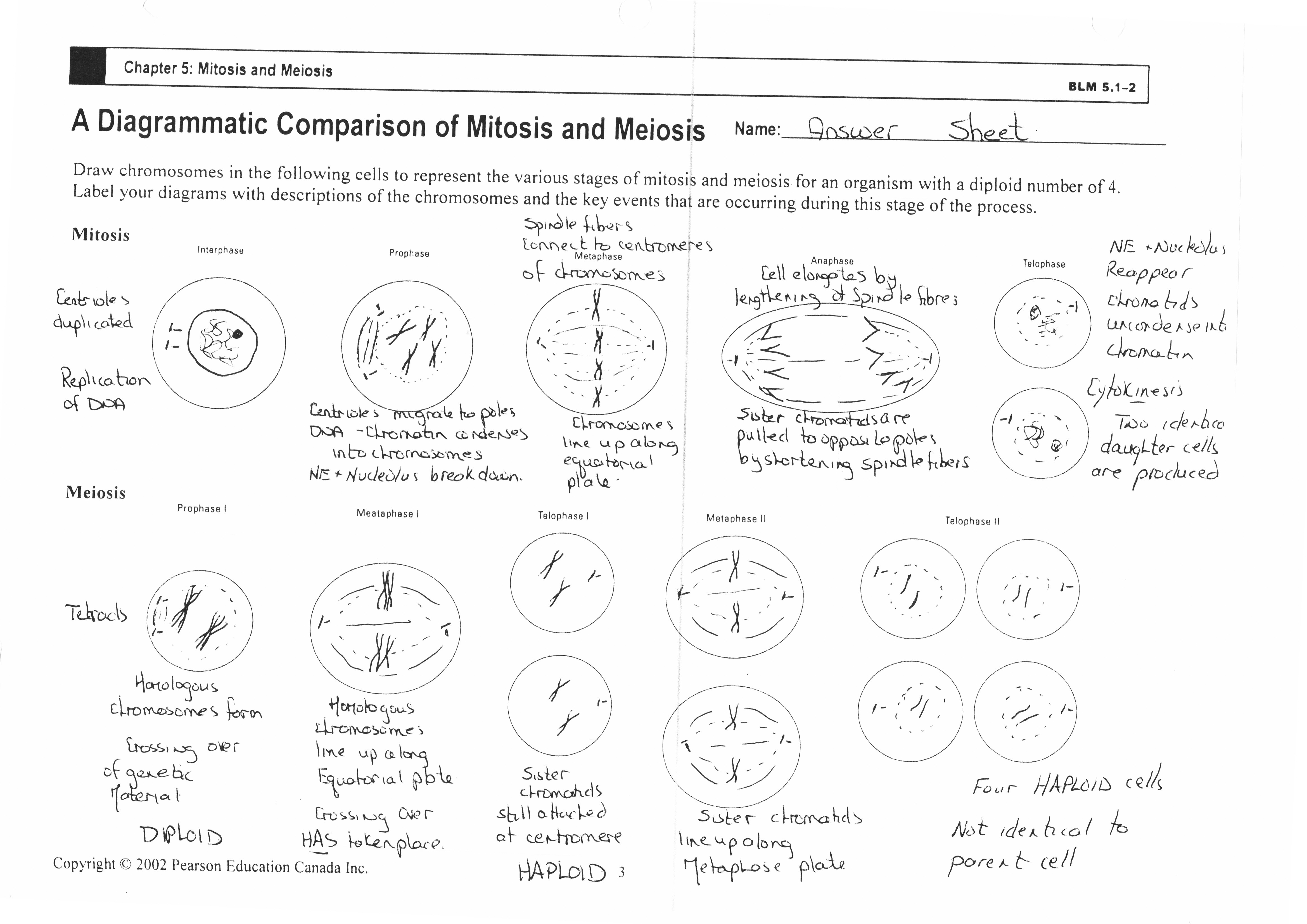
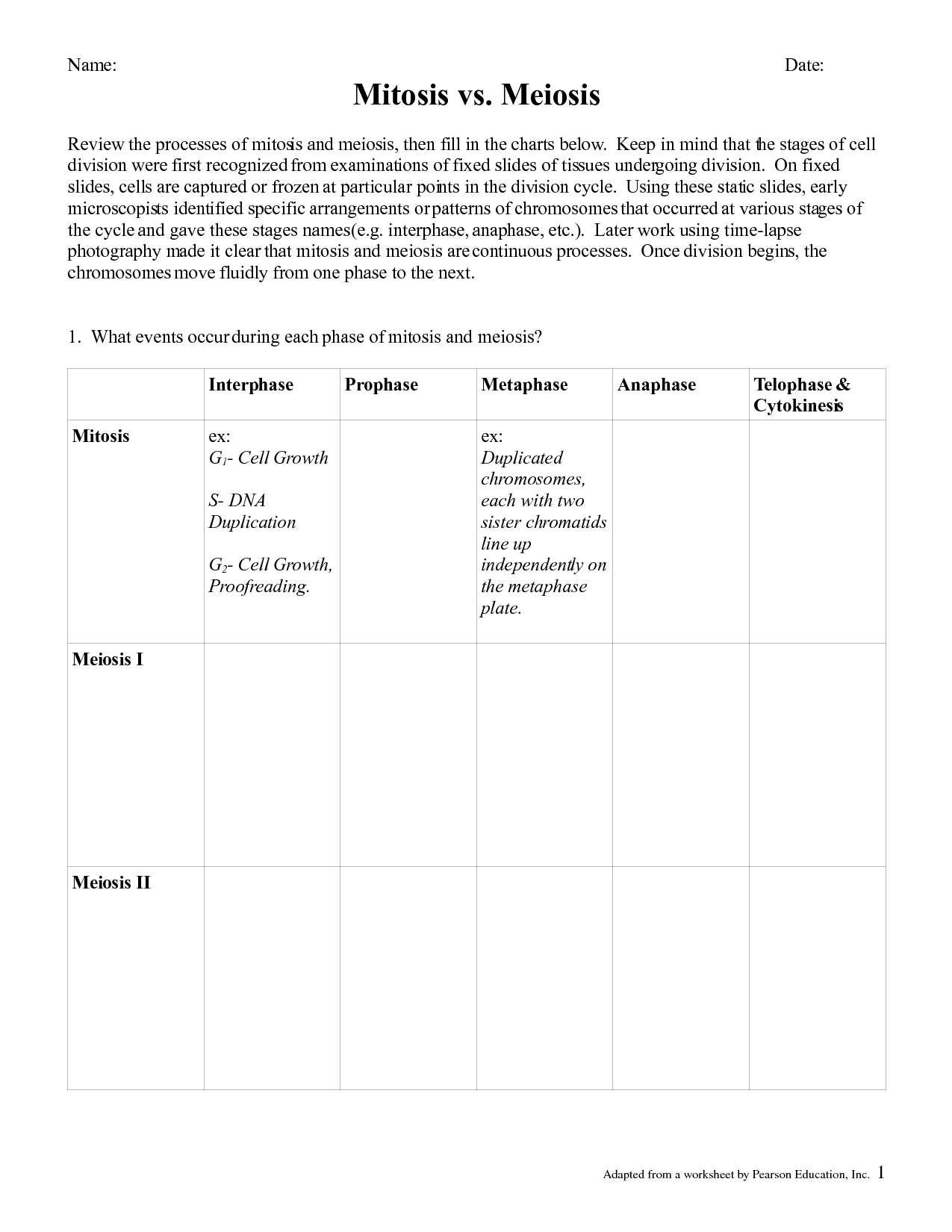
What is meiosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that occurs in sexually-reproducing organisms, resulting in the formation of gametes (eggs and sperm). It involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in four daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis is essential for genetic diversity and the creation of reproductive cells with unique combinations of genetic material.
What is the purpose of meiosis?
The main purpose of meiosis is to produce gametes (sperm and egg cells) that are genetically diverse. This genetic diversity is crucial for sexual reproduction as it ensures the offspring will have a unique combination of genes from the parents, promoting variation and adaptability within a population.
How many divisions occur in meiosis?
Meiosis consists of two divisions: meiosis I and meiosis II. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate, resulting in two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell. In meiosis II, the sister chromatids from the first division separate, creating four daughter cells with the haploid number of chromosomes.
How many cells are produced at the end of meiosis?
At the end of meiosis, four cells are produced. Each of these cells is haploid, meaning they contain half the number of chromosomes as a normal body cell.
What is the difference between meiosis I and meiosis II?
Meiosis I involves the separation of homologous chromosomes, resulting in two haploid cells with duplicated chromosomes. Meiosis II, on the other hand, involves the separation of sister chromatids, resulting in four haploid cells with unduplicated chromosomes. Both processes are necessary for the production of gametes in sexual reproduction.
Where does meiosis occur in the body?
Meiosis occurs in the gonads, specifically in the testes of males and the ovaries of females.
What is the significance of crossing over in meiosis?
Crossing over in meiosis is significant because it promotes genetic diversity by allowing for the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process creates new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes, increasing variability in offspring. It also helps in the repair of damaged DNA and ensures proper alignment of chromosomes during meiosis, ultimately leading to the formation of genetically unique gametes.
How does meiosis contribute to genetic diversity?
Meiosis contributes to genetic diversity through two main mechanisms: independent assortment and crossing over. Independent assortment occurs during metaphase I when homologous chromosomes align randomly on the metaphase plate, leading to different combinations of maternal and paternal chromosomes in the resulting daughter cells. Crossing over occurs during prophase I when homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material, creating new combinations of alleles. These processes result in a high degree of genetic variation among offspring, promoting diversity within a population.
What are the main phases of meiosis?
Meiosis consists of two main phases: Meiosis I and Meiosis II. In Meiosis I, homologous chromosomes pair up and exchange genetic material during crossing over in prophase I, followed by the separation of homologous chromosomes in anaphase I. This is followed by cytokinesis, resulting in two daughter cells with half the number of chromosomes as the original cell. Meiosis II is similar to mitosis, where sister chromatids separate in anaphase II, followed by cytokinesis, resulting in four haploid daughter cells each with a unique combination of genetic material.
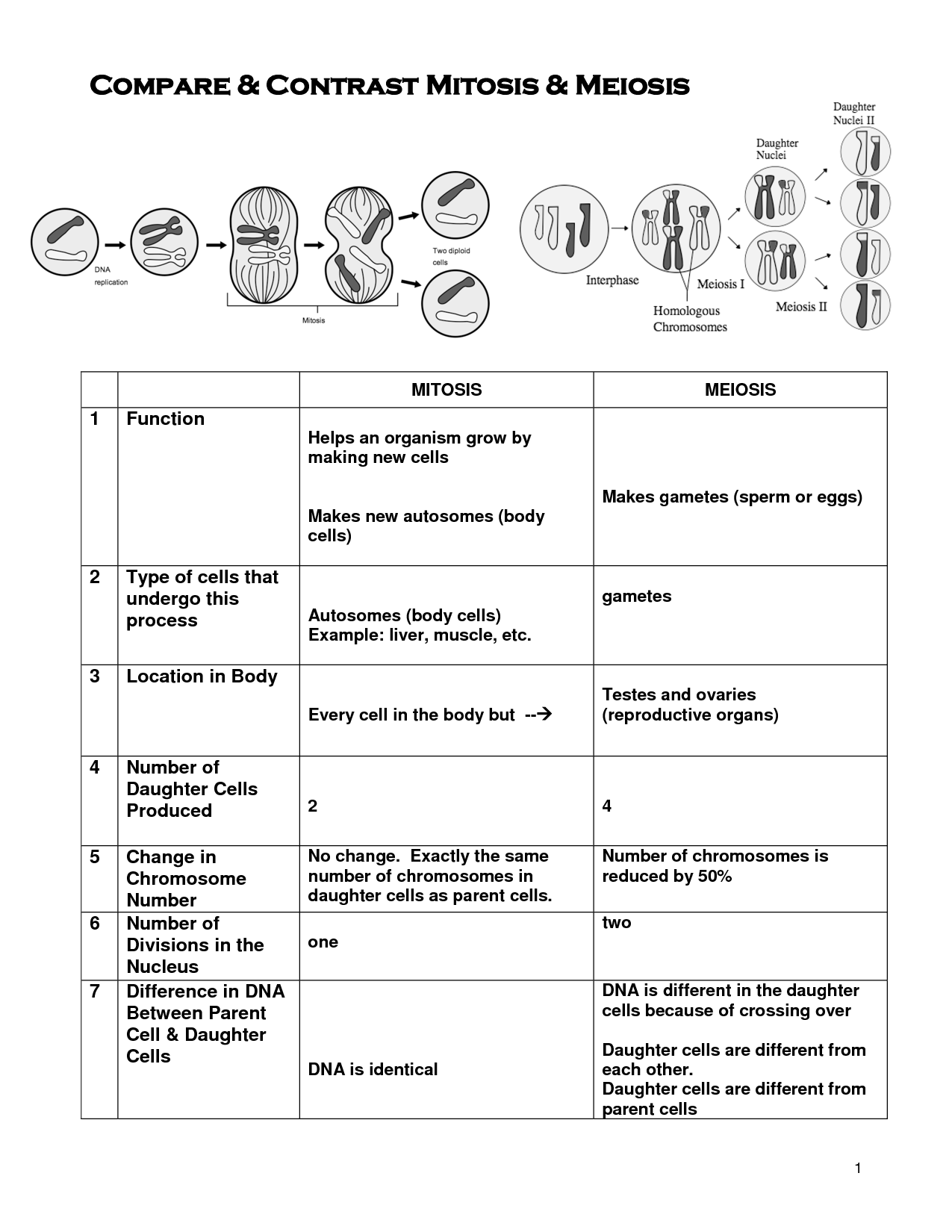
How is meiosis different from mitosis?
Meiosis is a type of cell division that results in the formation of gametes with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell, while mitosis is a cell division process that produces two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Meiosis involves two rounds of cell division, resulting in four genetically unique haploid cells, whereas mitosis involves one round of cell division, resulting in two genetically identical diploid cells. Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction and genetic diversity, while mitosis is important for growth, repair, and asexual reproduction.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.



























Comments