Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
Macromolecules are essential components of living organisms, playing crucial roles in various biological processes. Whether you are a student studying biology, a teacher planning interactive lessons, or a curious individual seeking to deepen your understanding of macromolecules, having access to accurate answers to macromolecules worksheets can be invaluable. Here, we provide a comprehensive collection of macromolecules worksheet answers to support your learning journey.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
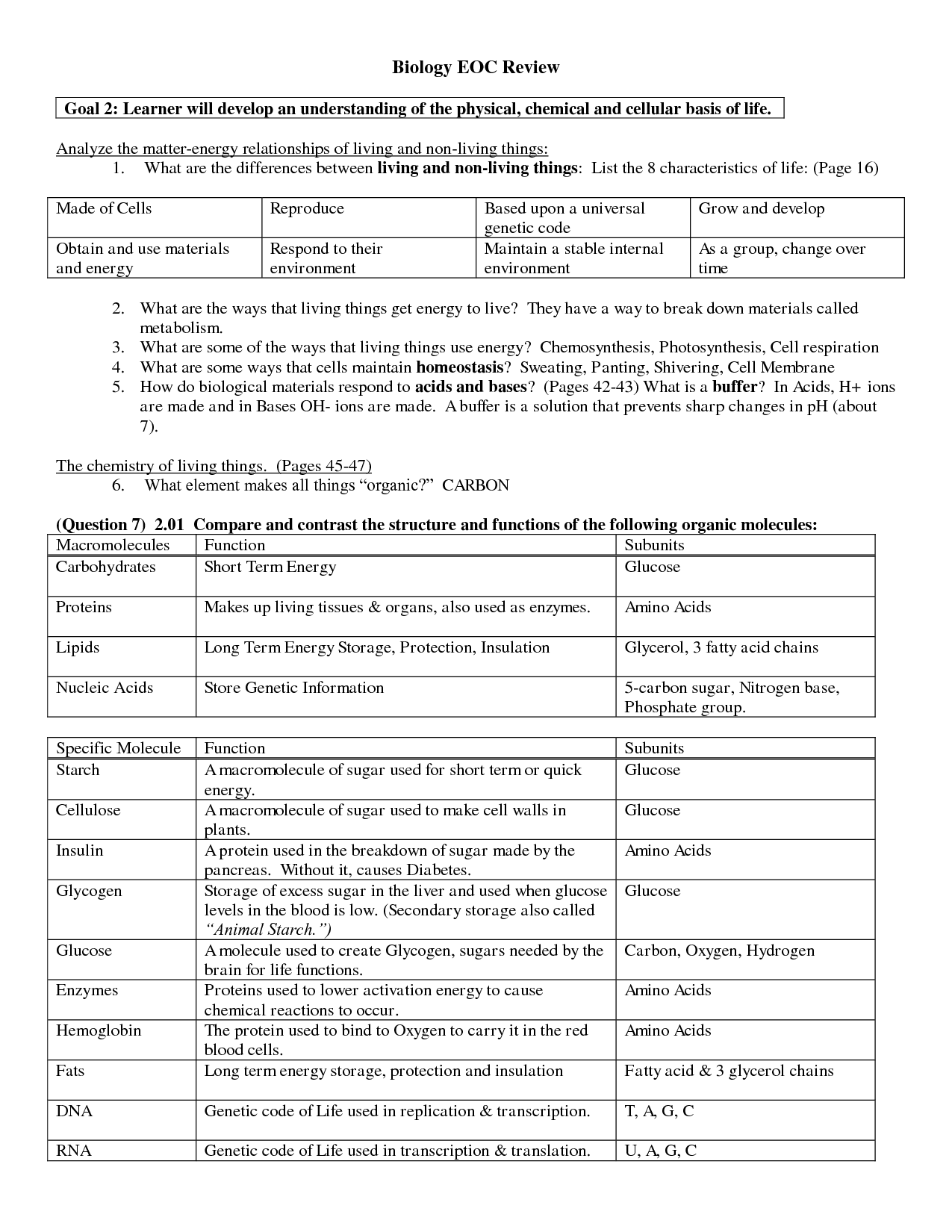
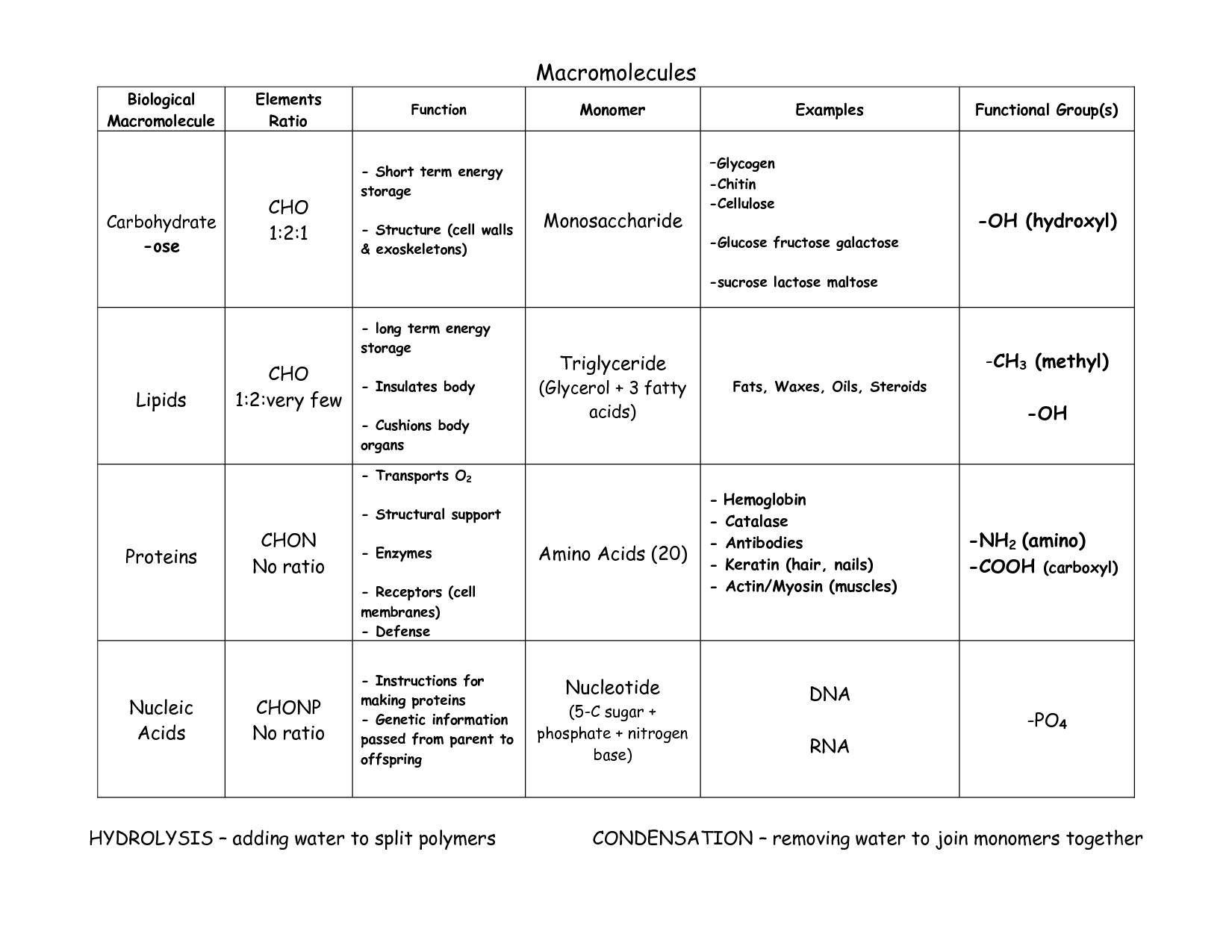
What are macromolecules?
Macromolecules are large molecules that are essential for life, composed of smaller subunits called monomers. There are four main classes of macromolecules found in living organisms: proteins, nucleic acids (DNA and RNA), carbohydrates, and lipids. These macromolecules play vital roles in various biological processes such as energy storage, structural support, and information transfer within cells.
Large molecules made up of smaller units called monomers.
Large molecules are formed by the repeated bonding of smaller units known as monomers. This process of linking monomers together creates polymers, which can vary in size and complexity depending on the type and arrangement of the monomer units. These polymers play crucial roles in various biological processes and materials, contributing to the diverse structures and functions found in living organisms and synthetic materials.
What are the four main types of macromolecules found in living organisms?
The four main types of macromolecules found in living organisms are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Each of these macromolecules plays a distinct and crucial role in various biological processes, such as energy storage and transfer, structural support, enzyme catalysis, and genetic information storage and expression.
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
These are the four main types of biomolecules found in living organisms. Carbohydrates are a source of energy, lipids are important for energy storage and cell membrane structure, proteins are essential for various functions in the body such as enzymes and structural components, and nucleic acids are responsible for storing and transmitting genetic information. Each of these biomolecules plays a crucial role in the functioning and survival of organisms.
Describe the structure of carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are organic molecules composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, arranged in a ratio of 1:2:1, respectively. The basic building block of carbohydrates is a monosaccharide, such as glucose or fructose, which can form linear or ring structures. Monosaccharides can join together through glycosidic bonds to form disaccharides (two monosaccharides) or polysaccharides (multiple monosaccharides). Polysaccharides, like starch and cellulose, can be linear or branched chains of monosaccharide units, serving as energy storage or structural components in living organisms.
Consist of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a ratio of 1:2:1, forming a chain or ring structure.
The compound described is a carbohydrate, a biomolecule made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a ratio of 1:2:1. Carbohydrates can exist in various forms such as monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides, and they play essential roles in providing energy for living organisms and serving as structural components in cells.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates?
The primary function of carbohydrates is to provide energy to the body. Carbohydrates are converted into glucose, which is the main source of fuel for our cells. Additionally, carbohydrates play a role in supporting the structure of cells and tissues, assisting in the proper functioning of organs and muscles, and acting as a storage form of energy in the form of glycogen.
Provide energy for cellular activities and structural support.
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration. They also play a crucial role in maintaining cell structure, as they are involved in processes like cell division and apoptosis, and help regulate cellular energy usage and metabolism. Additionally, mitochondria have their own DNA and can replicate independently within the cell.
Explain the structure of lipids.
Lipids are molecules primarily composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms, with a much higher proportion of carbon and hydrogen compared to oxygen. The basic structure of lipids consists of a glycerol molecule bonded to fatty acids, either in the form of triglycerides, phospholipids, or sterols. Triglycerides contain three fatty acids attached to glycerol, while phospholipids have two fatty acids and a phosphate group connected to glycerol, forming the basis of cell membranes. Sterols, such as cholesterol, have a different structure with multiple carbon rings. Overall, lipids are hydrophobic molecules that play essential roles in energy storage, cell structure, and signaling within the body.
Composed of glycerol and fatty acids, forming long hydrophobic chains.
Lipids are made up of glycerol and fatty acids, which combine to create long hydrophobic chains.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments