Light Refraction Worksheet Answers
Are you struggling to find the right answers for your light refraction worksheet? Look no further! We have compiled a list of accurate and detailed answers to help you understand this complex topic. Whether you are a student studying physics or a teacher preparing a lesson plan, these answers will provide the necessary guidance to master the subject of light refraction.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
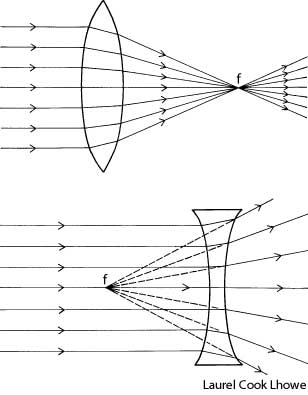
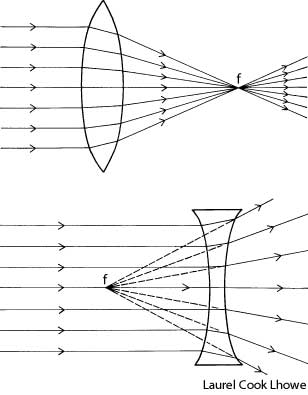
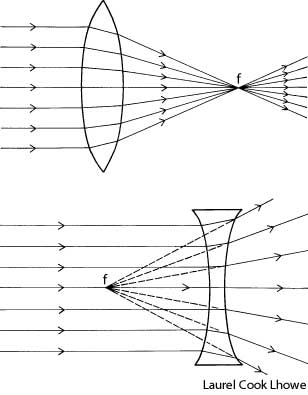
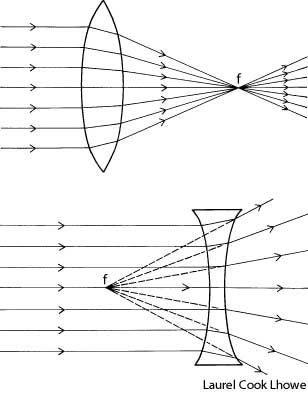
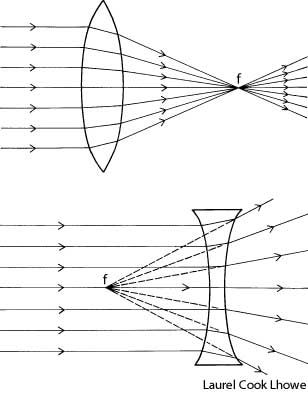
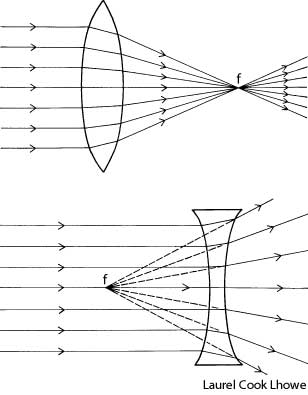
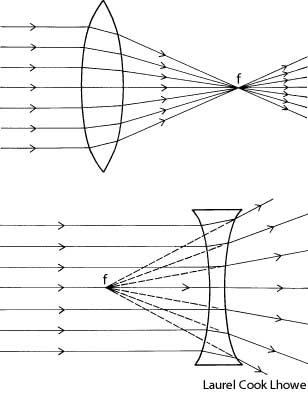
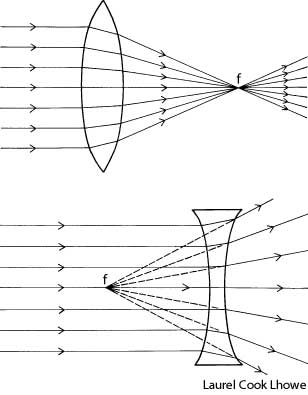
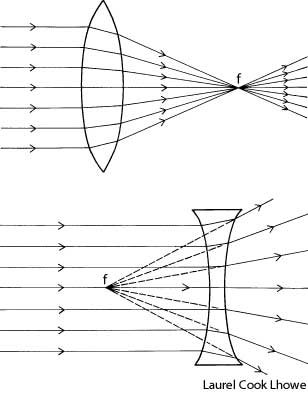
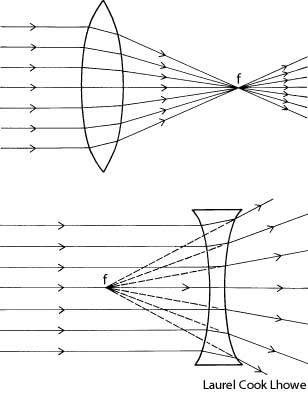
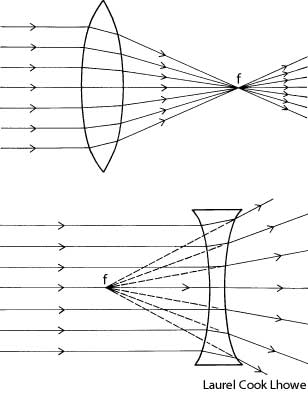
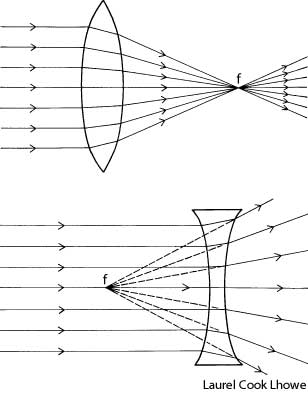
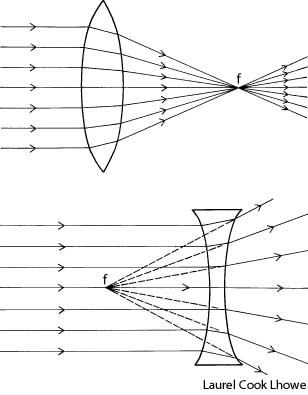
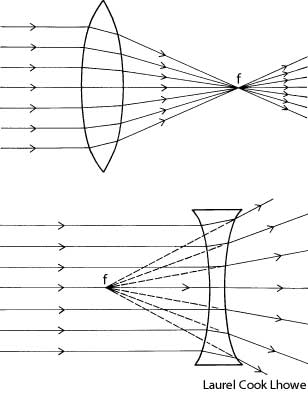
What is refraction?
Refraction is the bending of light as it passes from one medium to another, such as air to water or glass. This bending occurs because light travels at different speeds in different mediums, causing the light ray to change direction at the boundary between the two substances. Refraction is the basis for various optical phenomena, such as the way a pencil appears bent when placed in a glass of water.
The bending of light as it passes from one medium to another.
This phenomenon is known as refraction, where light changes direction as it moves from one medium to another due to the difference in the speed of light in each medium. The change in speed causes the light waves to bend either towards or away from the normal line, resulting in the observed bending of light.
What causes refraction to occur?
Refraction occurs when light travels at an angle from one medium to another with a different optical density, causing a change in its speed. This change in speed results in the bending of the light ray as it enters the new medium, which causes the direction of the light ray to change.
The change in speed of light when it passes through a different medium.
When light passes through a different medium, such as air, glass, or water, its speed changes due to the differing refractive indexes of the materials. The speed of light is fastest in a vacuum and slows down when passing through denser mediums because the photons interact with the particles of the medium, causing them to be absorbed and re-emitted, leading to a decrease in speed. This change in speed is responsible for effects like refraction, where light waves bend as they transition between different mediums, impacting how we perceive and experience light.
What is the refractive index of a medium?
The refractive index of a medium is a measure of how much the speed of light is reduced as it passes through that medium in comparison to its speed in a vacuum. It is a dimensionless quantity that helps determine how light waves propagate in different materials, influencing phenomena such as refraction, reflection, and dispersion.
A measure of how much a medium slows down light compared to its speed in a vacuum.
The measure of how much a medium slows down light compared to its speed in a vacuum is called the refractive index. It indicates how much the velocity of light is reduced as it travels through a particular substance, such as glass or water, compared to its speed in a vacuum.
How does the angle of incidence affect refraction?
The angle of incidence, which is the angle at which a wave strikes a surface, affects refraction by determining the degree to which the wave bends as it enters a new medium. When light or other waves move from one medium to another, such as from air to water, the change in speed causes the wave to bend. The greater the angle of incidence, the greater the degree of bending that occurs during refraction. This bending is described by Snell's Law, which relates the angles of incidence and refraction to the indices of refraction of the two materials involved.
A larger angle of incidence results in a larger angle of refraction.
This statement is not always accurate. The angle of refraction depends on the refractive indexes of the two mediums involved and follows the law of refraction, known as Snell's law. The angle of refraction can be larger, smaller, or equal to the angle of incidence, depending on the refractive indexes of the mediums and the angle of incidence.
What is the relationship between the refractive index and the speed of light?
The relationship between the refractive index and the speed of light is such that the speed of light is inversely proportional to the refractive index of a medium. This is described by the formula v = c/n, where v is the speed of light in a medium, c is the speed of light in a vacuum, and n is the refractive index of the medium. Essentially, the higher the refractive index of a medium, the slower light will travel through it.
The refractive index is inversely proportional to the speed of light in a medium.
Correct. The refractive index of a medium is indeed inversely proportional to the speed of light in that medium. This relationship is described by Snell's Law, which states that the refractive index of a material is equal to the speed of light in a vacuum divided by the speed of light in that material. This means that as the speed of light in a medium decreases, the refractive index of the medium increases.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments