Food Web Worksheets for Middle School
Food web worksheets are a valuable tool for middle school students to deepen their understanding of the intricate relationships between different organisms within an ecosystem. By exploring the concepts of producers, consumers, and decomposers, students can grasp the complex interconnectedness of these entities and their roles as subjects within a food web. These worksheets provide an engaging way for students to visualize and analyze the flow of energy and matter through various organisms, enhancing their ecological knowledge and critical thinking skills.
Table of Images 👆
- Food Web Pyramid Worksheet
- Food Web Worksheet
- Food Chain Worksheets
- Food Web Worksheets High School
- Food Chain Worksheets Free
- Health and Nutrition Worksheets
- Energy Pyramid Worksheet Middle School
- High School Ecosystem Food Chain Worksheet
- Food Web Energy Pyramid Worksheet
- Wetland Food Web Activity
- Antonym Worksheets Middle School
- Nutrition Label Worksheet
- High School Food Chain Worksheet
- Nutrition Worksheets for High School Students
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
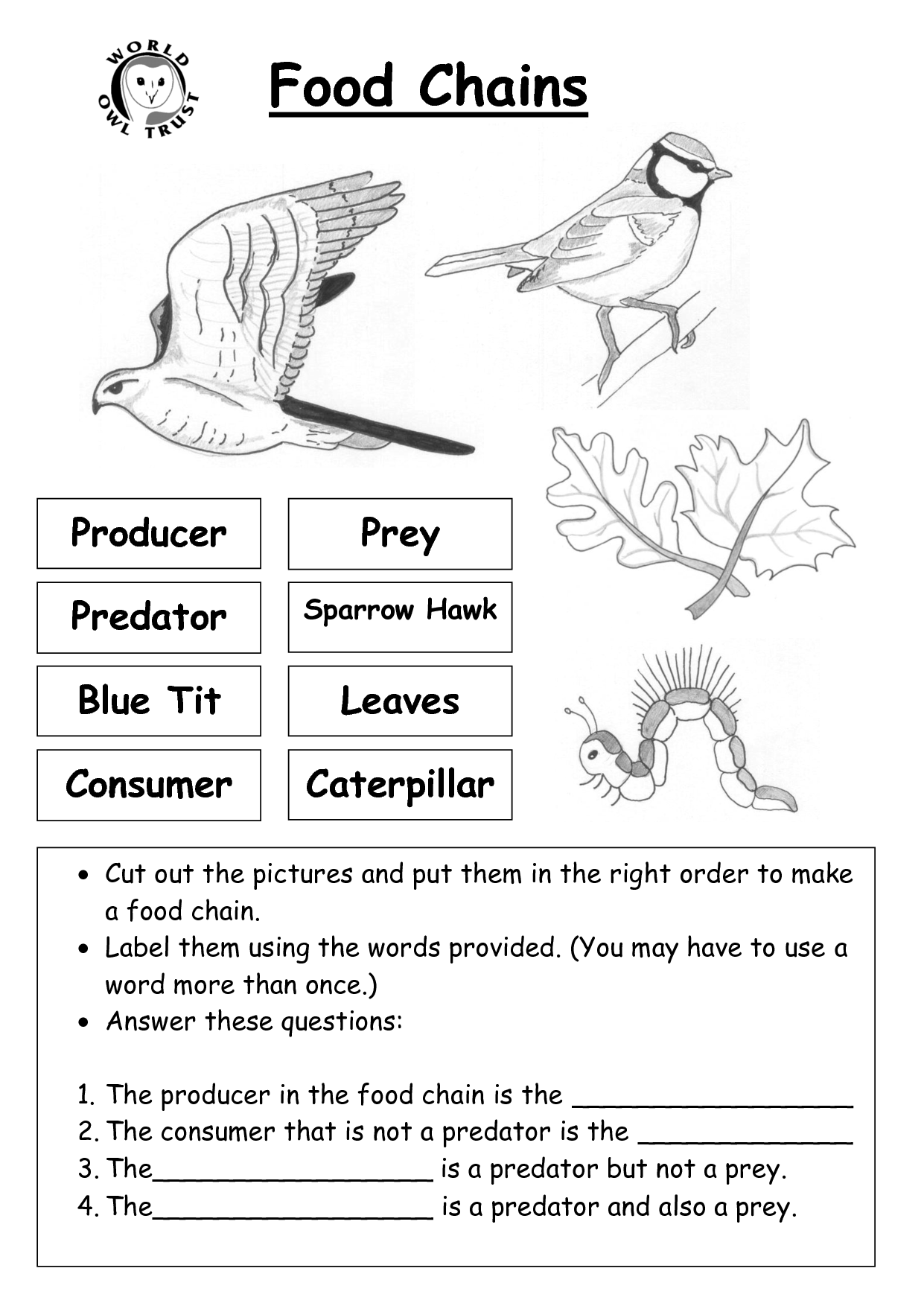
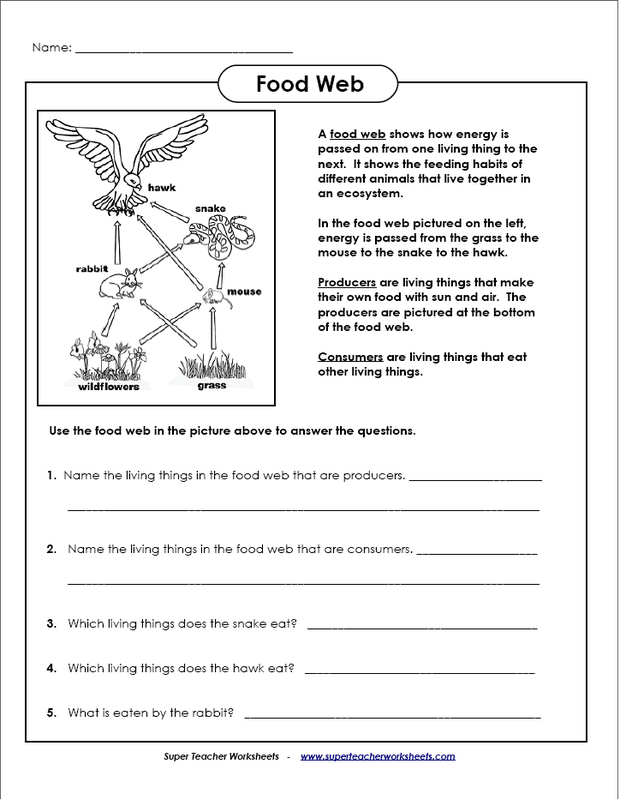
What is a food web?
A food web is a network of interconnected food chains that illustrates the flow of energy and nutrients within an ecosystem. It consists of various organisms, from producers like plants to consumers like herbivores, carnivores, and omnivores, showing how they are all linked through their feeding interactions. Each organism in a food web plays a specific role in transferring energy and maintaining the balance of the ecosystem.
How are food chains and food webs related?
Food chains and food webs are related in that they both represent the flow of energy and nutrients through an ecosystem. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms showing who eats whom, while a food web is a more complex network of interconnected food chains. Essentially, a food web is made up of multiple food chains that are interlinked, showing the complexity and diversity of interactions between different organisms in an ecosystem. Both food chains and food webs help illustrate the transfer of energy from one organism to another and highlight the interconnectedness of different species within an ecosystem.
What is the role of producers in a food web?
Producers in a food web play a crucial role as they are the foundation of the ecosystem by converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. They provide food and energy for all other organisms in the ecosystem, serving as the primary source of nutrients that sustain all levels of the food chain. Without producers, the energy flow and stability of the entire ecosystem would be disrupted.
Give an example of a primary consumer in a food web.
An example of a primary consumer in a food web is a rabbit that feeds on plants and vegetation.
Explain the difference between a herbivore and a carnivore in a food web.
In a food web, herbivores are organisms that primarily feed on plants and algae, while carnivores are organisms that primarily feed on other animals. Herbivores rely on the energy and nutrients obtained from consuming plant material, while carnivores obtain their energy and nutrients by hunting and consuming other animals. This differentiation in diet preferences and feeding habits plays a crucial role in shaping the dynamics and balance of energy flow within the ecosystem.
What happens if a species is removed from a food web?
If a species is removed from a food web, it can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. This can disrupt the balance of the ecosystem, leading to population fluctuations and potentially affecting the survival of other species in the food web. For example, if a predator is removed, it can result in an increase in the population of its prey, which can then lead to overgrazing of plants and a decline in plant species diversity. Ultimately, the removal of a species can have far-reaching consequences on the stability and health of the ecosystem.
Describe the role of decomposers in a food web.
Decomposers play a vital role in a food web by breaking down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, into simpler nutrients like carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus. This process releases these essential nutrients back into the ecosystem, where they can be taken up by producers like plants to kickstart the food chain again. Essentially, decomposers help recycle nutrients, maintain soil fertility, and ensure that energy flows through the ecosystem efficiently.
How do energy and nutrients flow in a food web?
Energy flows through a food web as it is transferred from one organism to another when they consume each other. Nutrients, on the other hand, move through a food web as organisms break down and decompose, releasing these nutrients back into the environment for other organisms to use. Ultimately, energy and nutrients in a food web are constantly being recycled and redistributed among different organisms within an ecosystem.
What are the different trophic levels in a food web?
Trophic levels in a food web include producers (plants and algae), primary consumers (herbivores that eat producers), secondary consumers (carnivores that eat herbivores), and tertiary consumers (carnivores that eat other carnivores). Some food webs may also have quaternary consumers, which are carnivores that feed on tertiary consumers. Each trophic level represents a different position in the energy transfer and nutrient flow within an ecosystem.
Explain the concept of interdependence in a food web.
Interdependence in a food web refers to the relationships between different organisms where they rely on each other for survival. It signifies that any change in one species within the web can have cascading effects on other species. For example, if a predator population increases, it can lead to a decrease in its prey species, causing a ripple effect through the ecosystem. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of maintaining a balance within ecosystems to ensure the survival of all species in the food web.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.


























Comments