Food Web Worksheet
A food web worksheet is a valuable learning tool that helps students understand the intricate relationships between organisms in an ecosystem. Designed for students studying ecology or biology, this worksheet provides a visual representation of a complex network of interconnected food chains within a given habitat. By identifying organisms as entities and exploring their roles as subjects in the food web, students gain a deeper understanding of the delicate balance and interdependence that exists in nature.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
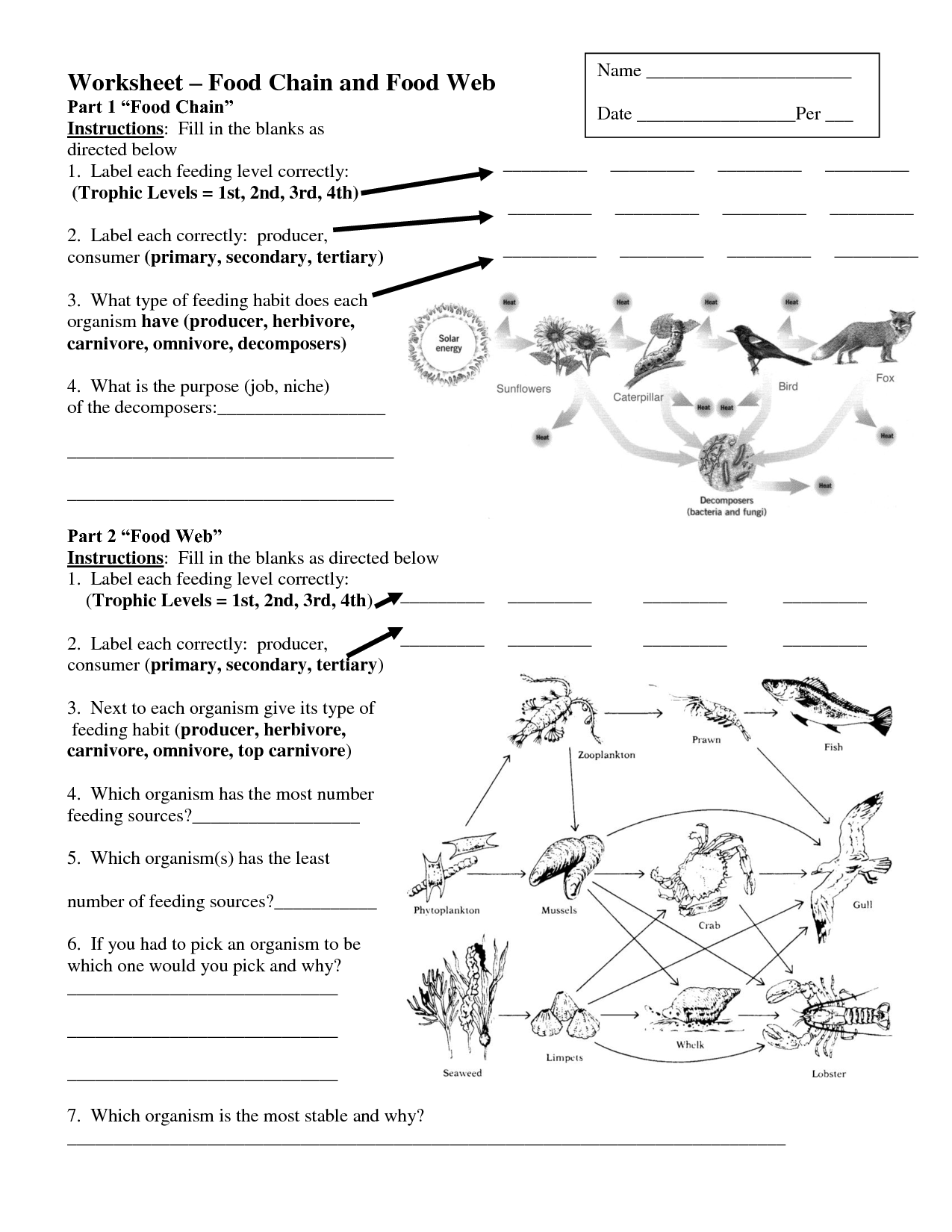
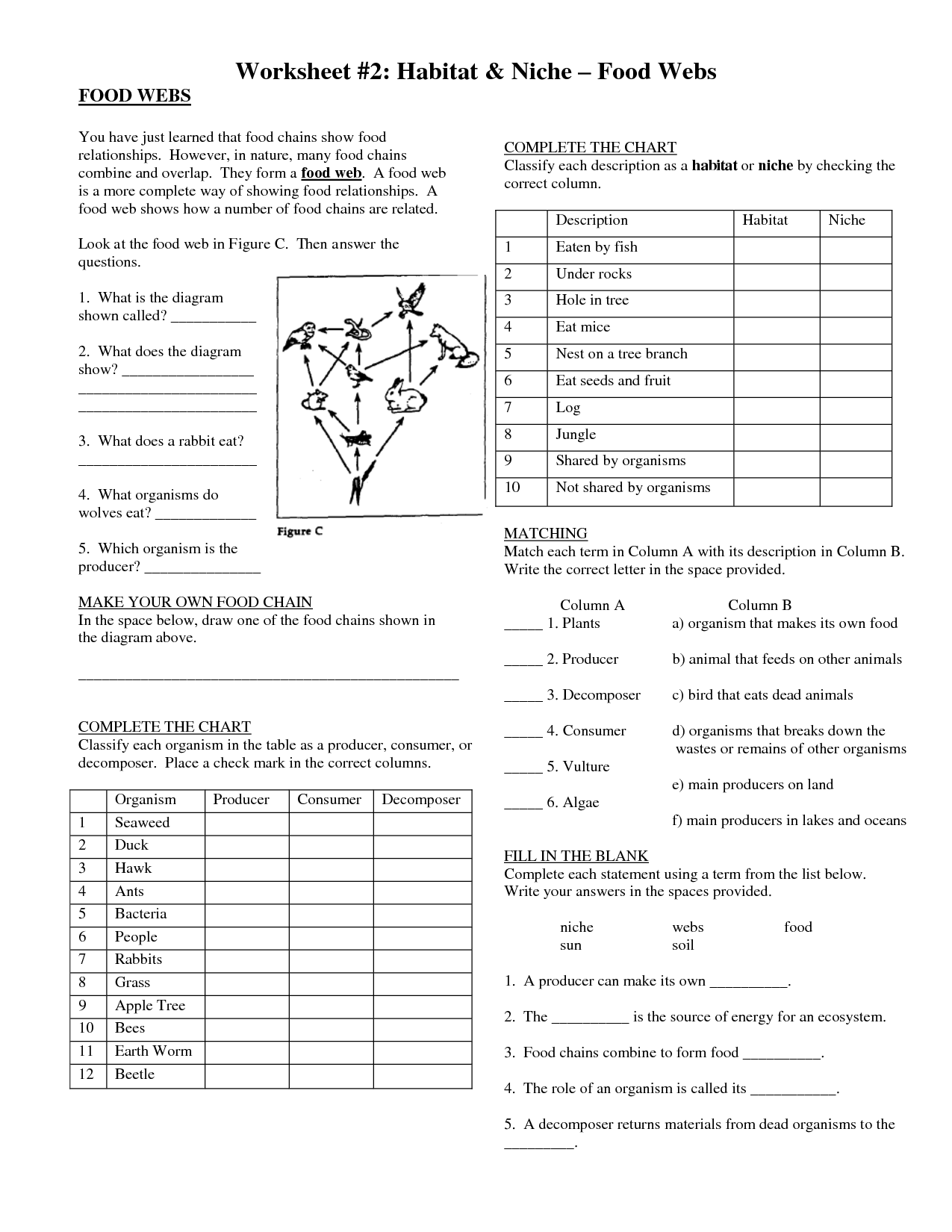
What is a food web?
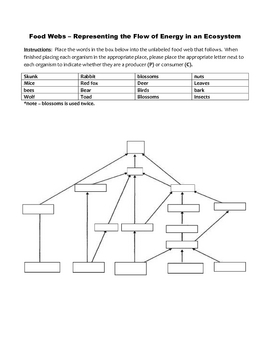
A food web is a complex network of interrelated food chains in an ecosystem that shows the flow of energy and nutrients through various organisms. It consists of producers, consumers, and decomposers, illustrating how different organisms are connected through their feeding relationships.
How are food webs different from food chains?
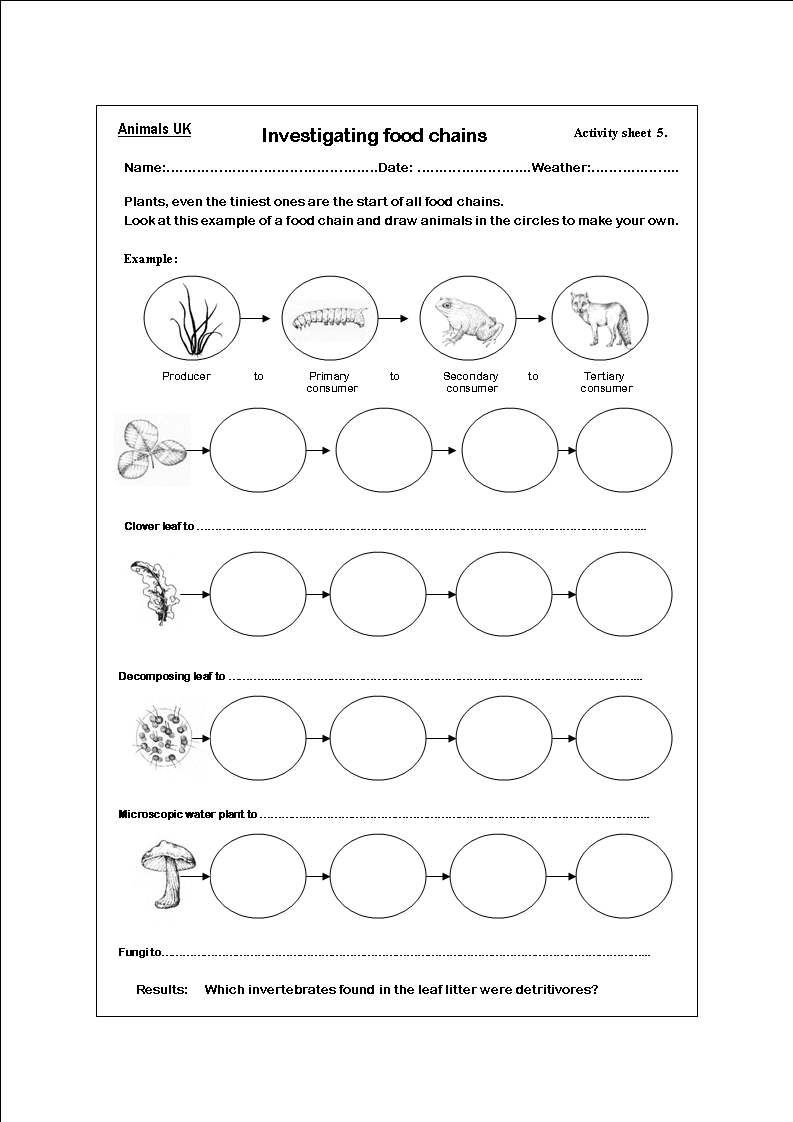
Food webs are more complex than food chains because they show multiple interconnected food chains within an ecosystem, demonstrating how different organisms are interconnected and depend on each other for energy transfer. In contrast, food chains are simple linear representations of energy flow from one organism to another in a specific sequence. Food webs provide a more accurate and holistic view of the flow of energy and nutrients in an ecosystem, showing the interdependence of various species and the multiple pathways through which energy can flow.
What is a producer in a food web?
A producer in a food web is an organism, typically a plant or algae, that is capable of photosynthesis to convert sunlight into energy. Producers are the foundation of the food chain as they produce their food from sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide, providing energy for other organisms in the ecosystem.
What are primary consumers?
Primary consumers are organisms that consume autotrophic organisms (plants) as their main food source. These organisms are herbivores that obtain energy by feeding on plants and other producers in the ecosystem. They play a critical role in energy transfer through the food chain by converting the energy from plants into nutrients that can be consumed by higher-level consumers. Examples of primary consumers include rabbits, cows, and insects.
Give an example of a secondary consumer.
A coyote is an example of a secondary consumer, as it feeds on primary consumers like rabbits and rodents.
What is a decomposer and what role do they play in a food web?
Decomposers are organisms that break down dead plants and animals into simpler substances, such as nutrients, by decomposing them. They play a crucial role in a food web by recycling nutrients back into the ecosystem, allowing them to be reused by plants for growth. Decomposers help maintain the balance of nutrients in an ecosystem and are essential for the continuation of life processes.
Explain how energy flows through a food web.
Energy flows through a food web in a linear fashion starting with producers that convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis. This energy is then transferred to primary consumers, such as herbivores, that eat the producers. Secondary consumers, like carnivores, further consume the primary consumers. As each organism feeds on another, energy is transferred along the food chain. However, energy is lost at each trophic level as heat during metabolism, making the higher trophic levels less energetically efficient. This process continues until decomposers break down the dead organisms, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem to be used by producers, thus completing the energy flow cycle in the food web.
How do predators affect the balance of a food web?
Predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of a food web by regulating the population of prey species. By controlling the numbers of herbivores, predators prevent overgrazing and help to maintain the health and diversity of plant populations. This in turn can impact the abundance of other species within the ecosystem, creating a complex web of interdependent relationships that contribute to overall ecosystem stability.
Describe the impact of human activities on food webs.
Human activities can disrupt food webs in various ways, such as overexploitation of specific species, habitat destruction, pollution, and introducing invasive species. These actions can lead to imbalances in predator-prey relationships, loss of biodiversity, and ultimately destabilization of entire ecosystems. As human activities continue to alter natural environments, the health and functioning of food webs are at risk, which can have far-reaching consequences on both plant and animal populations.
How does biodiversity contribute to the stability of a food web?
Biodiversity contributes to the stability of a food web by increasing the resilience of the ecosystem. A diverse array of species within an ecosystem provides various sources of energy and nutrients, creating multiple interconnected pathways for the transfer of energy and maintenance of food webs. This prevents a single species from dominating the ecosystem and allows for the adaptation of different species to changes in their environment, ultimately leading to a more stable and balanced ecosystem. Additionally, a diverse range of species can buffer against disturbances, such as disease outbreaks or changes in climate, as some species may be more resistant or resilient than others, thus helping to maintain the overall health and functionality of the ecosystem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments