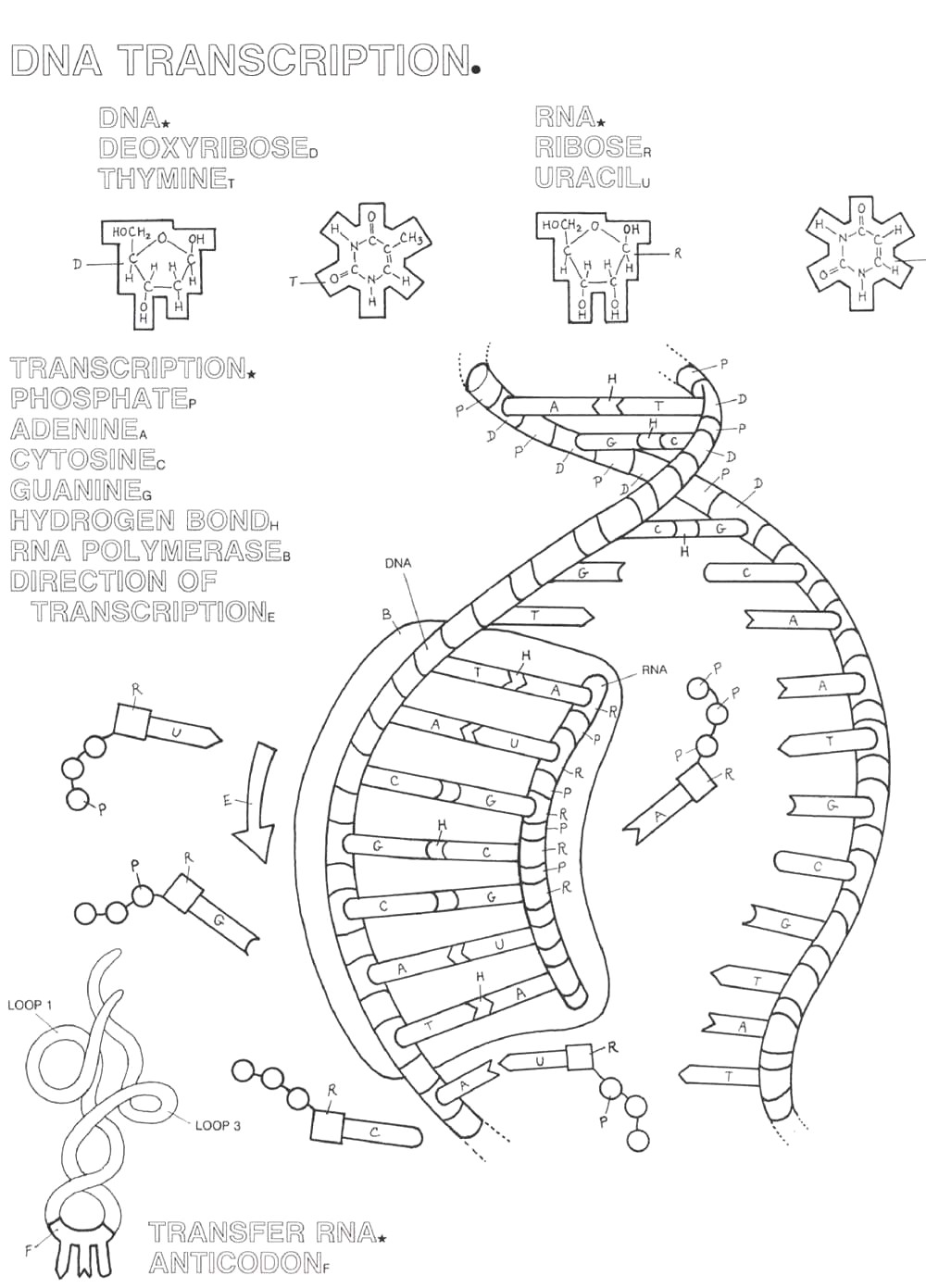
Double Helix Coloring Worksheet
The Double Helix Coloring Worksheet is an engaging and educational activity perfect for budding scientists and biology enthusiasts. This worksheet allows students to explore the structure of DNA, focusing on the fascinating double helix shape. By providing a visual representation and key terms, this worksheet facilitates a deeper understanding of this essential biological entity and its significance in the world of science.
Table of Images 👆
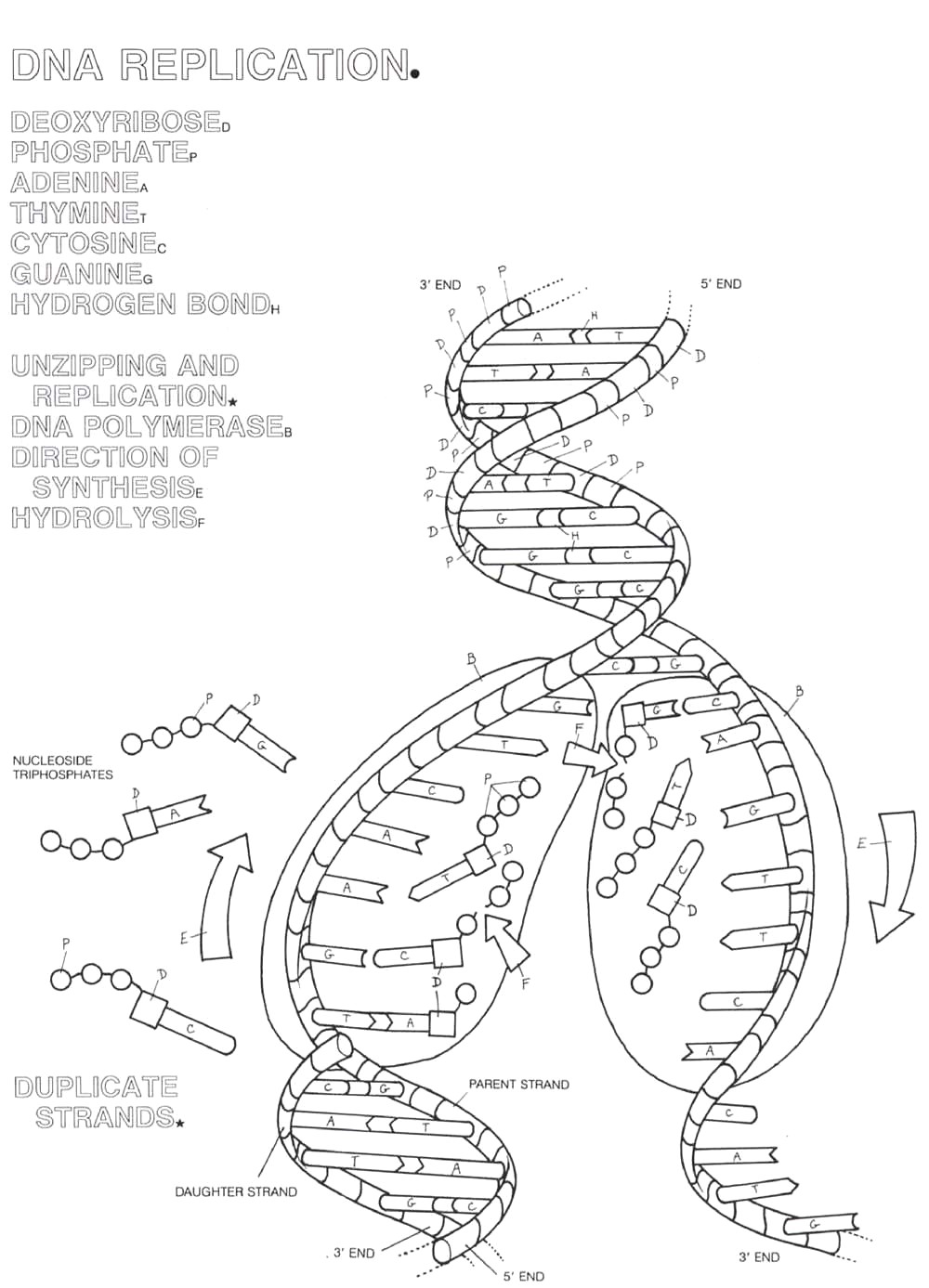
- The Double Helix DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
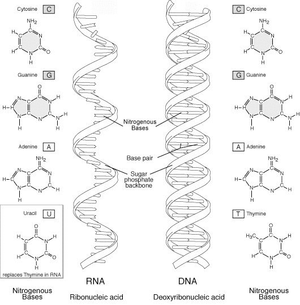
- DNA and RNA Molecules
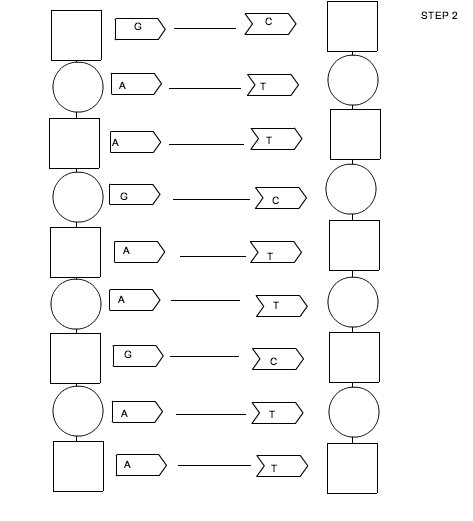
- DNA Replication Coloring Worksheet
- DNA Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- The DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
- DNA Structure Worksheet Coloring Page
- DNA Replication Coloring Sheet
- Pearson Education Biology Worksheet Answers
- DNA Double Helix Coloring Worksheet Answers
- DNA Coloring Transcription and Translation
- Worksheets DNA Coloring Page
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of the Double Helix Coloring Worksheet?
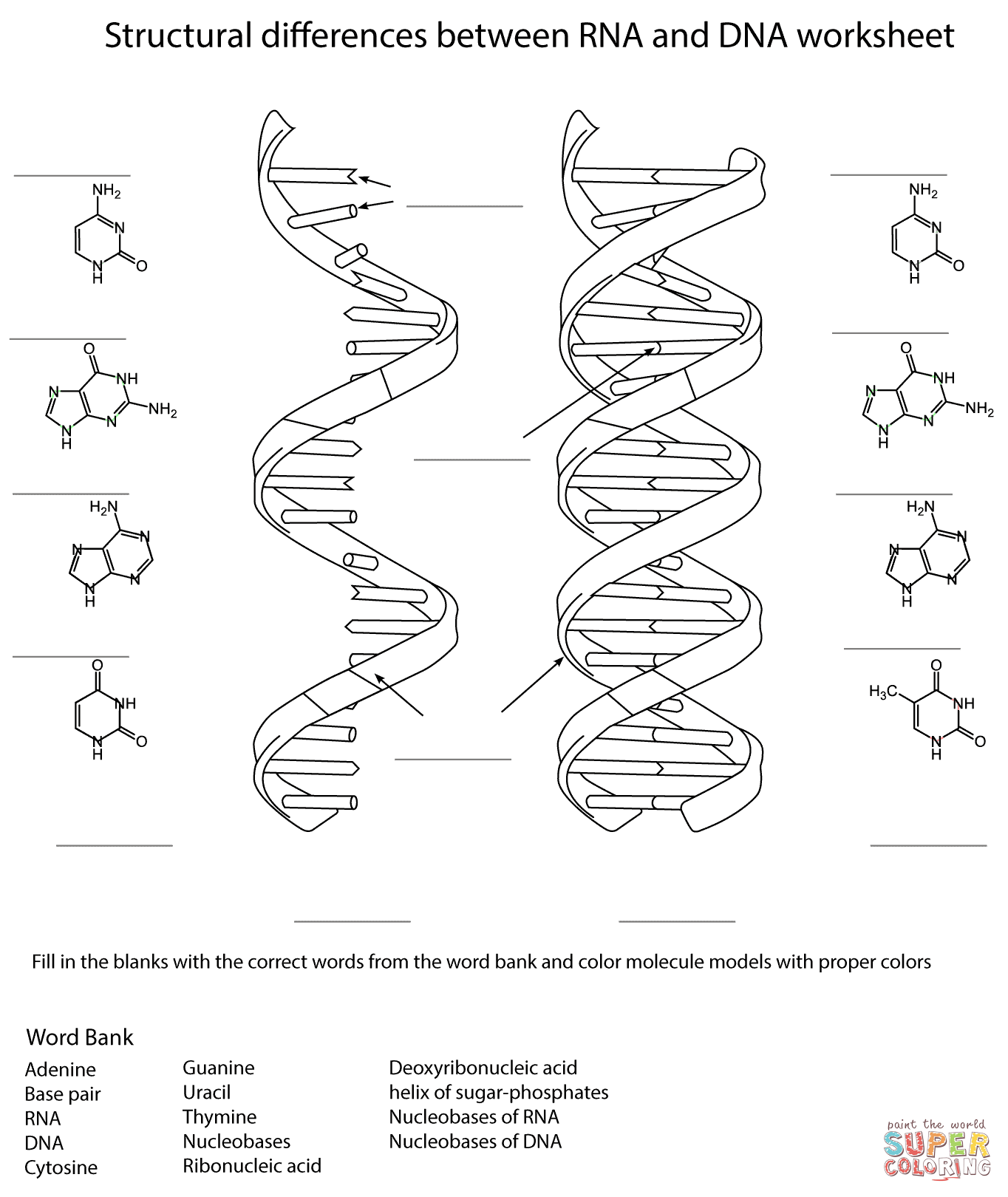
The purpose of the Double Helix Coloring Worksheet is to help students visually understand the structure of DNA by coloring and labeling the components of the double helix, such as nucleotides, base pairs, sugar-phosphate backbones, and hydrogen bonds. This activity can enhance students' knowledge and comprehension of DNA's structure and function through a hands-on and interactive approach.
What are the main components of the double helix structure?
The main components of the double helix structure of DNA are nucleotides, which consist of a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar molecule, and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). These nucleotides form complementary base pairs within the double helix structure, with adenine pairing with thymine and cytosine pairing with guanine. The two strands of nucleotides are held together by hydrogen bonds between the nitrogenous bases, giving DNA its characteristic twisted ladder-like shape.
How many nitrogenous bases are found in DNA?
There are four nitrogenous bases found in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
What are the four types of nitrogenous bases present in DNA?
The four types of nitrogenous bases present in DNA are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G). These bases pair up in specific combinations (A with T and C with G) to form the double helix structure of DNA.
What allows DNA to carry genetic information?
The unique sequence of nucleotides in DNA allows it to store and transmit genetic information. The four different types of nucleotides (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) can be arranged in various combinations to encode the instructions for making proteins and determining the traits of an organism. This genetic code is read and interpreted by the cell's machinery to carry out essential biological processes and pass on hereditary traits to offspring.
How are the two strands of DNA held together?
The two strands of DNA are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. Adenine pairs with thymine (A-T) and guanine pairs with cytosine (G-C), forming stable base pairs that connect the two strands of the DNA double helix.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in the double helix structure?
Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in stabilizing the double helix structure of DNA. They form between complementary base pairs (adenine with thymine, and cytosine with guanine) on opposite DNA strands, holding the two strands together. Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak individually but collectively they provide the necessary stability for the double helix structure, allowing DNA to store genetic information and undergo processes like replication and transcription accurately.
How does DNA replication occur in the double helix structure?
DNA replication in the double helix structure occurs through a process called semi-conservative replication, where the two strands of the double helix separate and act as templates for the synthesis of new complementary strands. Enzymes such as helicase unwind and separate the two strands, forming a replication fork where DNA polymerase synthesizes new strands by adding complementary nucleotides to the exposed bases on each template strand. The result is two identical copies of the original DNA molecule, each consisting of one old strand and one newly synthesized strand.
How does the double helix structure protect DNA from damage?
The double helix structure of DNA helps protect it from damage in several ways. Firstly, the helical shape wraps the genetic information inside, shielding it from external factors that could cause damage. Secondly, the bases in the helix are paired in a specific way, forming hydrogen bonds that help maintain the stability of the structure. Additionally, the helix structure allows for efficient repair mechanisms to recognize and fix any damage that may occur, ensuring the integrity and functionality of the DNA molecule.
Can variations in the double helix structure of DNA lead to genetic mutations?
Yes, variations in the double helix structure of DNA can lead to genetic mutations. These variations, such as substitutions, deletions, or insertions of nucleotides, can disrupt the genetic code and lead to changes in the protein that is produced, potentially resulting in genetic mutations that can impact an individual's traits or health.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments