Diagram Mitosis Worksheet Answers
If you're a biology student in need of a tool to help you understand and practice the concept of mitosis, you've come to the right place. In this blog post, we will introduce you to the power of worksheets as a valuable learning resource. Specifically, we will explore a helpful worksheet that provides diagrammatic explanations and answers for the process of mitosis. Whether you're studying for an upcoming exam or simply aiming to deepen your understanding, this worksheet will guide you through the stages of mitosis, ensuring clarity and comprehension along the way.
Table of Images 👆
- Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis Worksheet Answers
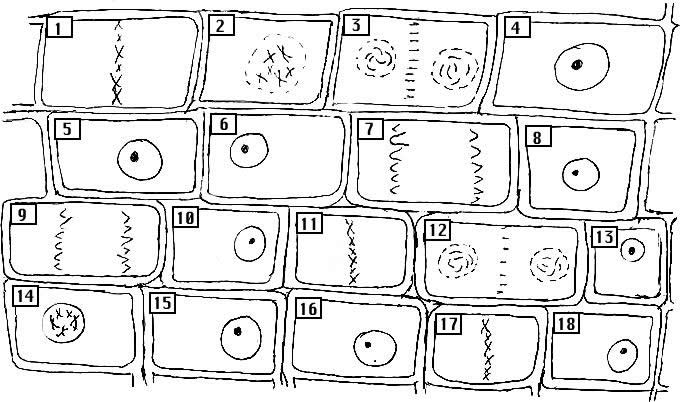
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
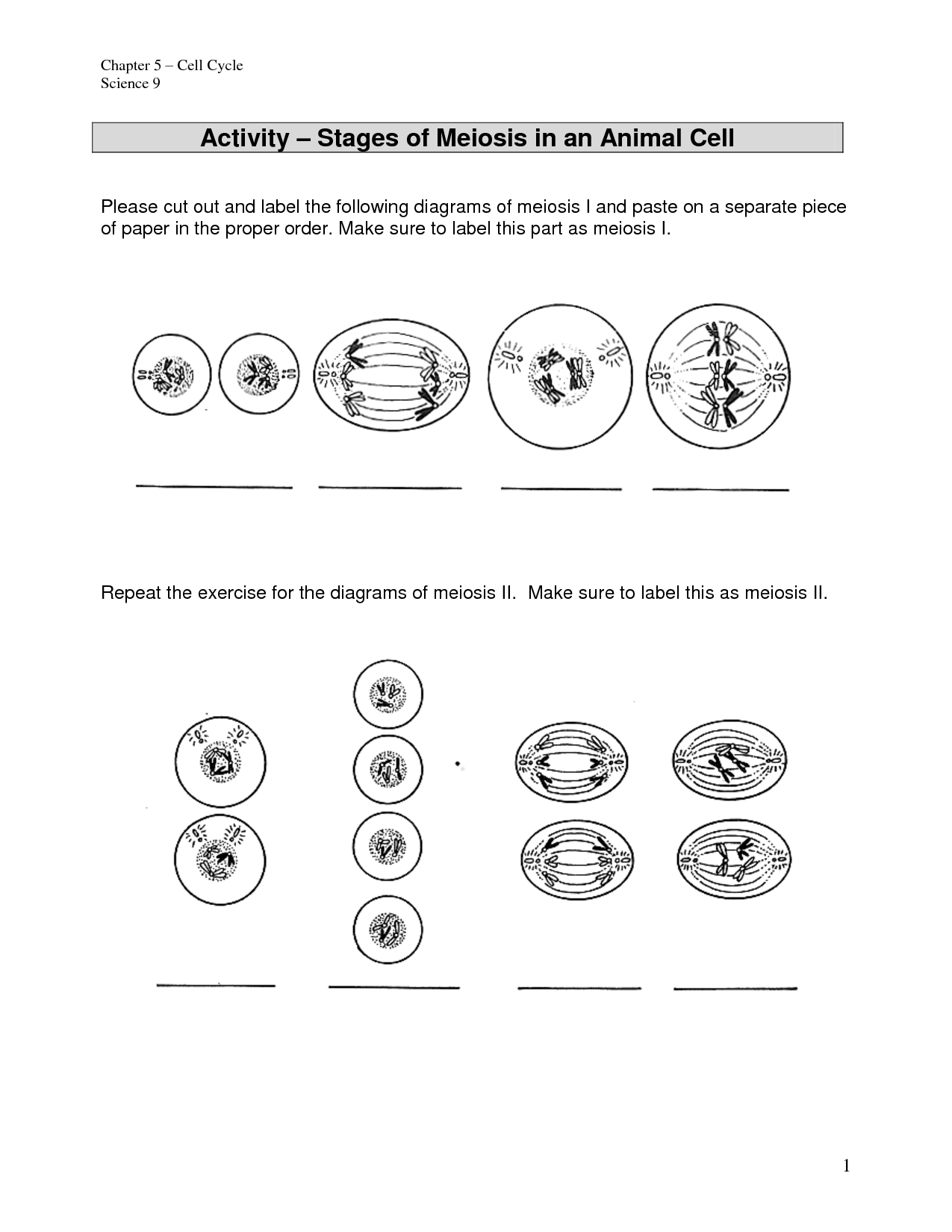
- Cut and Paste Meiosis Worksheet Answers
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Sequencing Worksheet
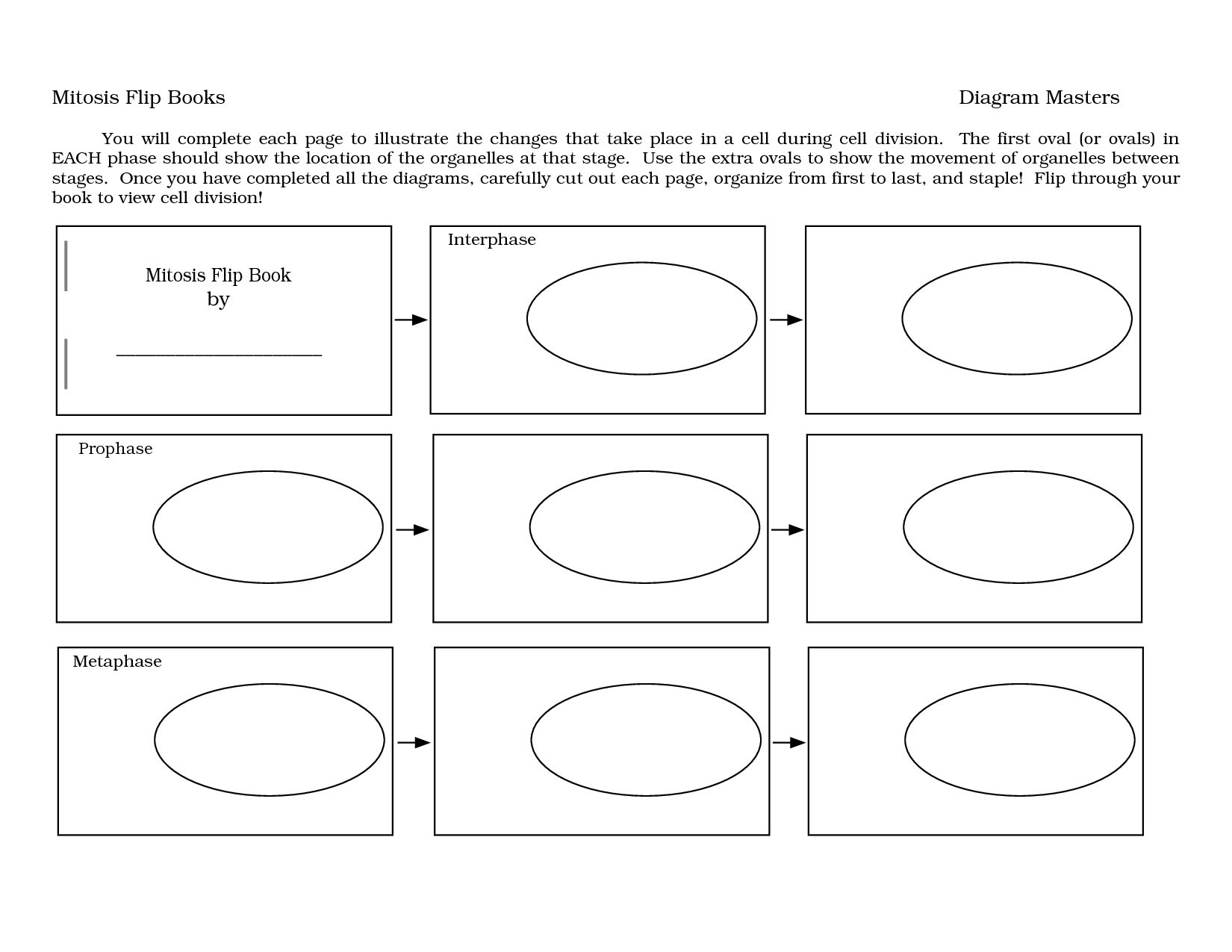
- Mitosis Flip Book
- Meiosis and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
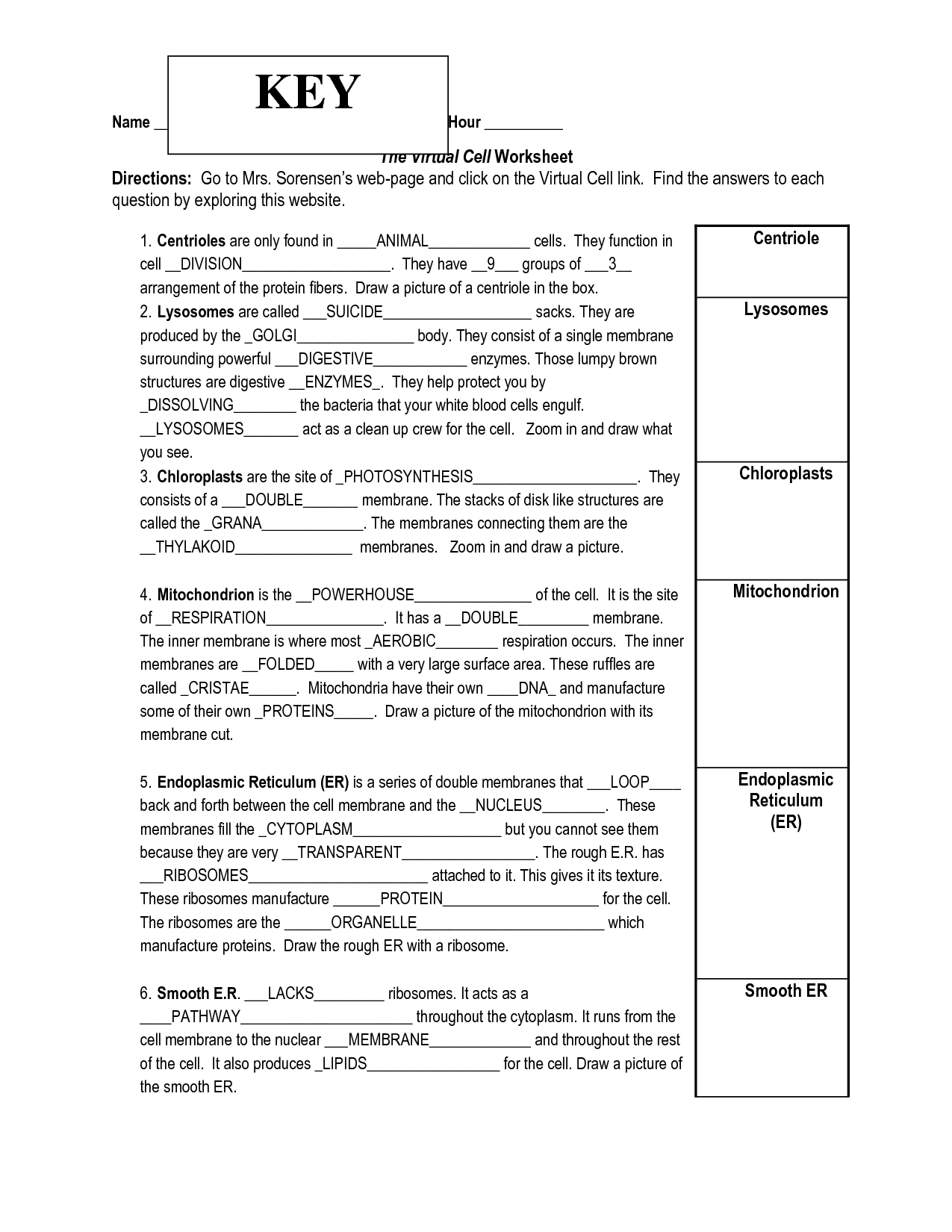
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Onion Cell Mitosis Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
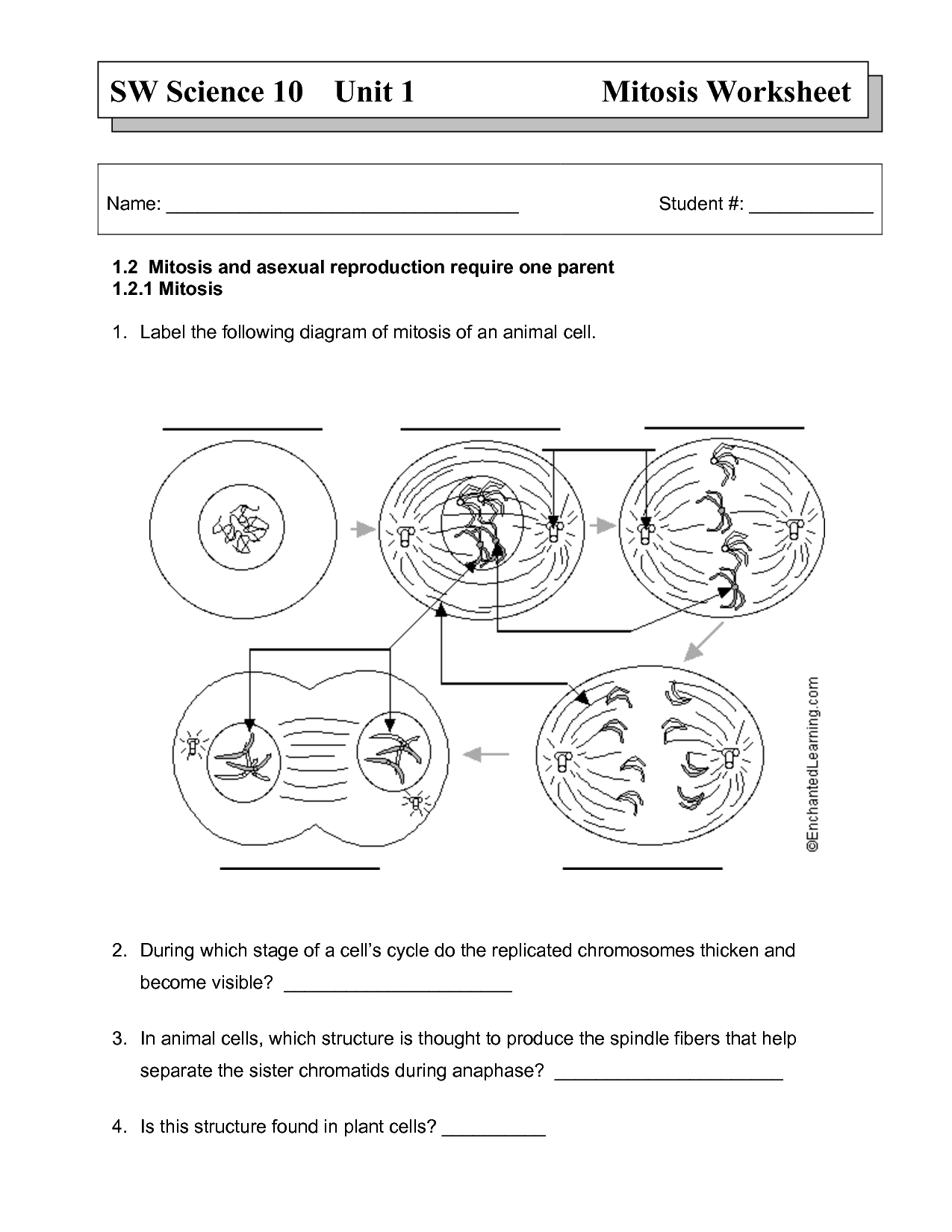
What is mitosis?
Mitosis is a type of cell division where a single cell divides into two identical daughter cells. This process is crucial for growth, repair, and maintenance of multicellular organisms, as it ensures the distribution of genetic material evenly between the daughter cells. During mitosis, the cell goes through several stages, including prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, ultimately leading to the formation of two identical cells with the same number of chromosomes as the original cell.
What are the stages of mitosis?
The stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In prophase, the nuclear membrane breaks down, chromosomes condense, and spindle fibers form. During metaphase, the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell. Anaphase is when the sister chromatids are pulled apart towards opposite poles of the cell. Finally, in telophase, new nuclear membranes form around the separated chromosomes, and the cell prepares to divide into two daughter cells during cytokinesis.
How is chromatin organized during mitosis?
During mitosis, chromatin condenses to form tightly coiled structures called chromosomes. This condensation is necessary to ensure accurate segregation of genetic material into daughter cells. The chromatin is organized into distinct chromosomes with two sister chromatids joined at the centromere. This organization helps maintain the integrity of genetic material and allows for efficient distribution of chromosomes during cell division.
What is the purpose of mitosis?
The purpose of mitosis is to produce two identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, allowing for growth, development, and repair of tissues in multicellular organisms.
What happens to the nuclear membrane during mitosis?
During mitosis, the nuclear membrane breaks down and disintegrates. This allows the chromosomes, which have condensed and become tightly packed, to be separated and organized into two distinct daughter cells. Once the chromosomes have been separated and the process of cell division is complete, the nuclear membrane reforms around the newly formed daughter nuclei.
How are sister chromatids separated during mitosis?
During mitosis, sister chromatids are separated when the mitotic spindle fibers attach to the kinetochores located on each chromatid. This attachment provides the pulling force needed to separate the sister chromatids and move them towards opposite poles of the cell. Once separated, the chromatids are considered individual chromosomes and are eventually enclosed within separate nuclei during telophase of mitosis.
What is the role of spindle fibers in mitosis?
Spindle fibers are key structures in mitosis that help separate chromosomes during cell division. They attach to the centromere of each chromosome and align them along the metaphase plate. As the cell progresses through mitosis, the spindle fibers shorten and pull the sister chromatids apart, ensuring that each daughter cell receives the correct number of chromosomes. Overall, spindle fibers play a crucial role in ensuring the accurate distribution of genetic material to daughter cells during mitosis.
How does cytokinesis differ between animal and plant cells?
Cytokinesis in animal cells involves the formation of a cleavage furrow, which pinches the cell into two daughter cells, while in plant cells, a cell plate forms between the two daughter cells. Additionally, animal cells lack a cell wall, allowing them to physically divide by cleavage, whereas plant cells have a rigid cell wall that requires the formation of a cell plate to separate the daughter cells.
What is the end result of mitosis?
The end result of mitosis is the formation of two identical daughter cells, each with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. This process ensures that genetic material is evenly distributed between the two daughter cells, allowing for growth, repair, and reproduction in multicellular organisms.
How does mitosis contribute to growth and repair in multicellular organisms?
Mitosis is the process by which a single cell divides to create two genetically identical daughter cells. In multicellular organisms, mitosis is crucial for growth and repair as it allows for the production of new cells to replace old or damaged cells. During growth, mitosis enables an organism to increase in size by producing more cells, while during repair, mitosis facilitates the regeneration of tissues and organs by replacing injured or dead cells with healthy ones. Thus, mitosis plays a fundamental role in the continuous renewal and maintenance of the body in multicellular organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments