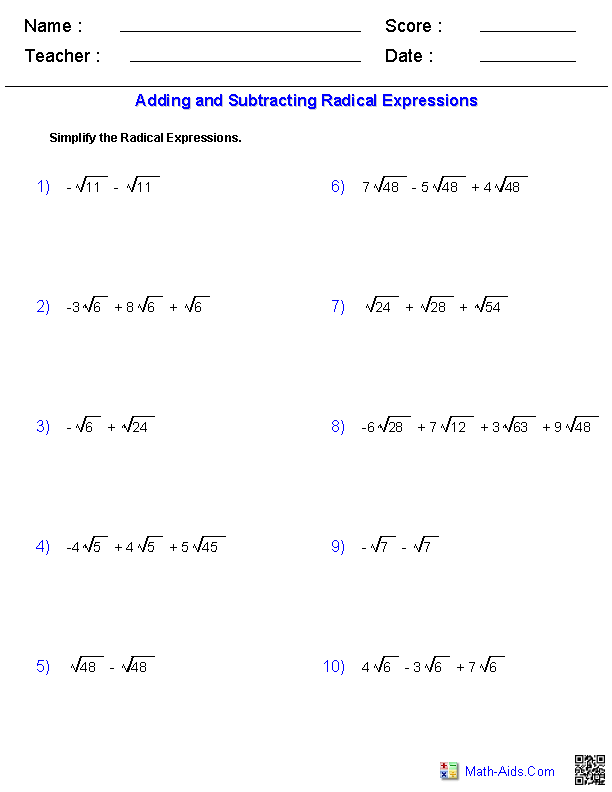
College Algebra and Trigonometry Worksheets
College Algebra and Trigonometry worksheets provide a comprehensive and structured way for students to practice and reinforce their understanding of key mathematical concepts. These worksheets aim to assist college students in mastering essential topics related to algebra and trigonometry. With a focus on subjects such as equations, functions, graphs, and trigonometric functions, these worksheets offer invaluable practice opportunities that cater to the needs of college-level learners.
Table of Images 👆
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the definition of a function in College Algebra?
In College Algebra, a function is a relation between a set of inputs (known as the domain) and a set of outputs (known as the range), where each input is related to exactly one output. A function can be represented by an equation, graph, or set of ordered pairs, and it must satisfy the vertical line test, meaning that no vertical line intersects the graph of the function more than once.
How can you determine the domain and range of a function?
To determine the domain of a function, you need to identify all possible input values (x-values) that the function can accept without causing any mathematical inconsistencies such as division by zero or taking the square root of a negative number. The range of a function, on the other hand, is the set of all possible output values (y-values) that the function can produce based on the given domain. In mathematical terms, the domain and range are often written as sets of numbers between which the function operates.
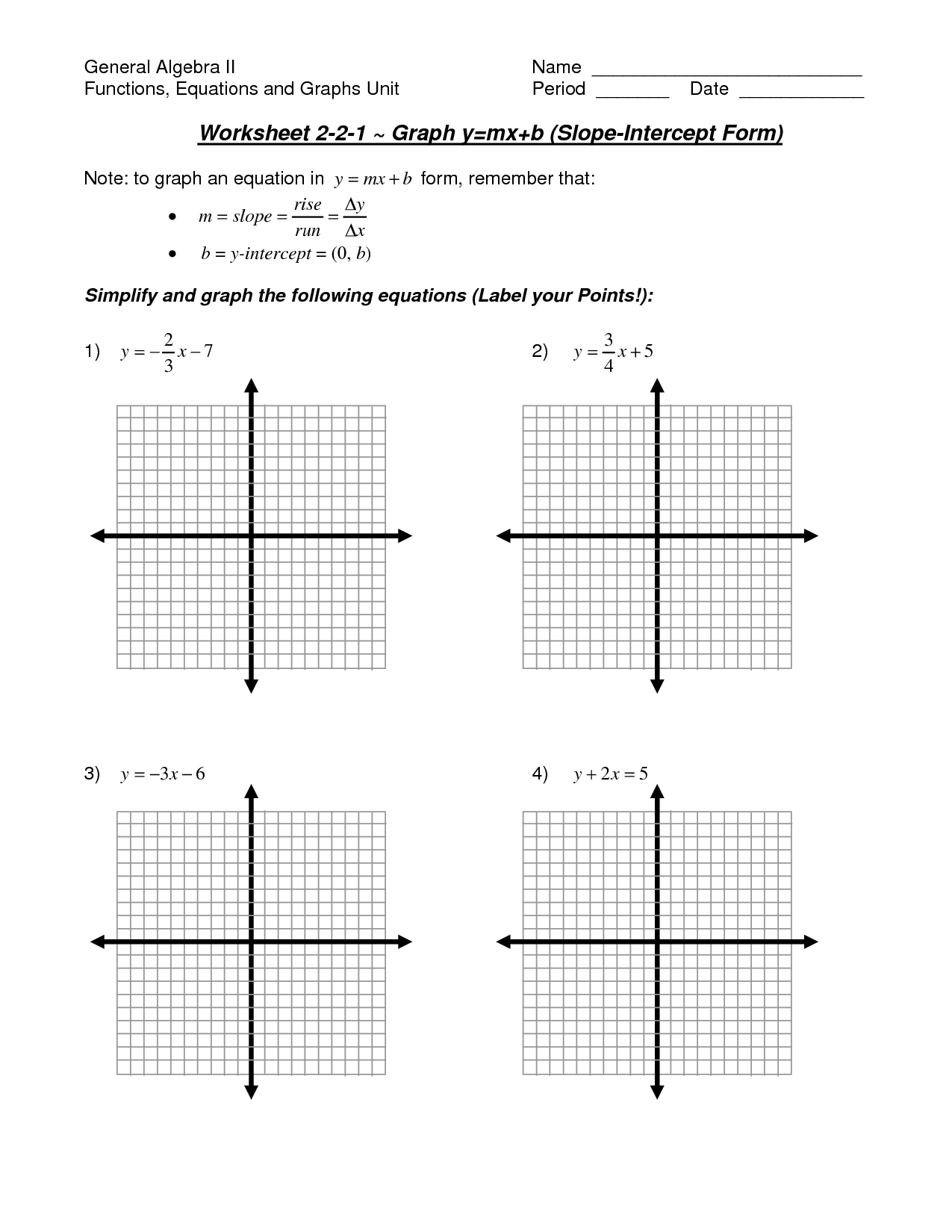
What are the key properties of linear equations?
Linear equations are equations that represent a straight line when graphed. They have two key properties: 1) they involve variables raised only to the first power, and 2) the variables are not multiplied together or divided by each other. This means that the graph of a linear equation is always a straight line, and they can be solved using basic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
How do you solve quadratic equations using factoring?
To solve a quadratic equation using factoring, first set the equation equal to zero. Then factor the quadratic expression to find the two factors. Once the quadratic expression is factored, set each factor equal to zero and solve for the variable. The solutions obtained from setting each factor equal to zero will give the roots or solutions of the quadratic equation.
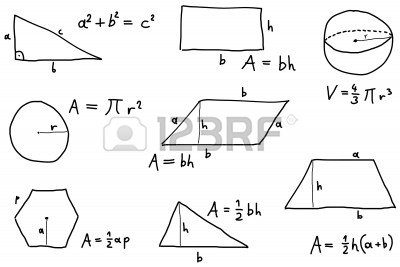
What is the unit circle and how is it used in trigonometry?
The unit circle is a circle with a radius of 1 centered at the origin in a coordinate plane. In trigonometry, it is used to define the values of the trigonometric functions sine, cosine, and tangent at different angles. By using the unit circle, trigonometric identities and relationships can be easily visualized and understood. The coordinates of the points where the unit circle intersects the terminal side of an angle are used to determine the values of the trigonometric functions, making calculations simpler and more intuitive.
How can you find the values of trigonometric functions for special angles?
You can find the values of trigonometric functions for special angles by remembering key trigonometric ratios for common angles such as 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°. By memorizing these ratios, you can easily calculate the sine, cosine, and tangent values for these special angles. Additionally, knowing the unit circle and understanding the definitions of sine, cosine, and tangent functions can also help in finding the values of trigonometric functions for special angles.
What are the primary trigonometric identities and how do they relate to each other?
The primary trigonometric identities are sine squared plus cosine squared equals one, tangent equals sine over cosine, and secant equals one over cosine. These identities are all interrelated through the fundamental Pythagorean theorem relationship between the sides of a right triangle, which is the basis of trigonometry. For example, the first identity can be derived from the Pythagorean theorem, and the other identities can be obtained by manipulating the basic trigonometric functions using this relationship. Overall, the primary trigonometric identities are essential tools for simplifying and solving trigonometric equations and expressions.
How do you solve trigonometric equations algebraically?
To solve trigonometric equations algebraically, first use trigonometric identities and properties to simplify the equation. Then, isolate the trigonometric function by applying algebraic manipulation techniques such as factoring, combining like terms, and solving for the variable. Be sure to check the solutions by substituting them back into the original equation to confirm their accuracy and handle any extraneous solutions that may arise.
What are the properties of exponential functions?
Exponential functions have the general form f(x) = a^x, where a is a constant and x is the variable. They exhibit rapid growth or decay as x increases or decreases, depending on whether a is greater or less than 1. Exponential functions never touch the x-axis but approach it asymptotically as x tends towards negative infinity. They have a single horizontal asymptote at y = 0. Exponential functions are always continuous and differentiable across their domain.
How can you use logarithmic functions to solve exponential equations?
You can use logarithmic functions to solve exponential equations by taking the logarithm of both sides of the equation. When an exponential equation is in the form of y = a^x, you can take the logarithm of both sides to convert it into a form that allows you to solve for the variable x. By applying the property of logarithms that states log(a^x) = x*log(a), you can simplify the equation and solve for x by isolating it on one side of the equation. The most commonly used logarithm to solve exponential equations is the natural logarithm (ln) for base e, but you can also use other logarithm bases depending on the context of the problem.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments