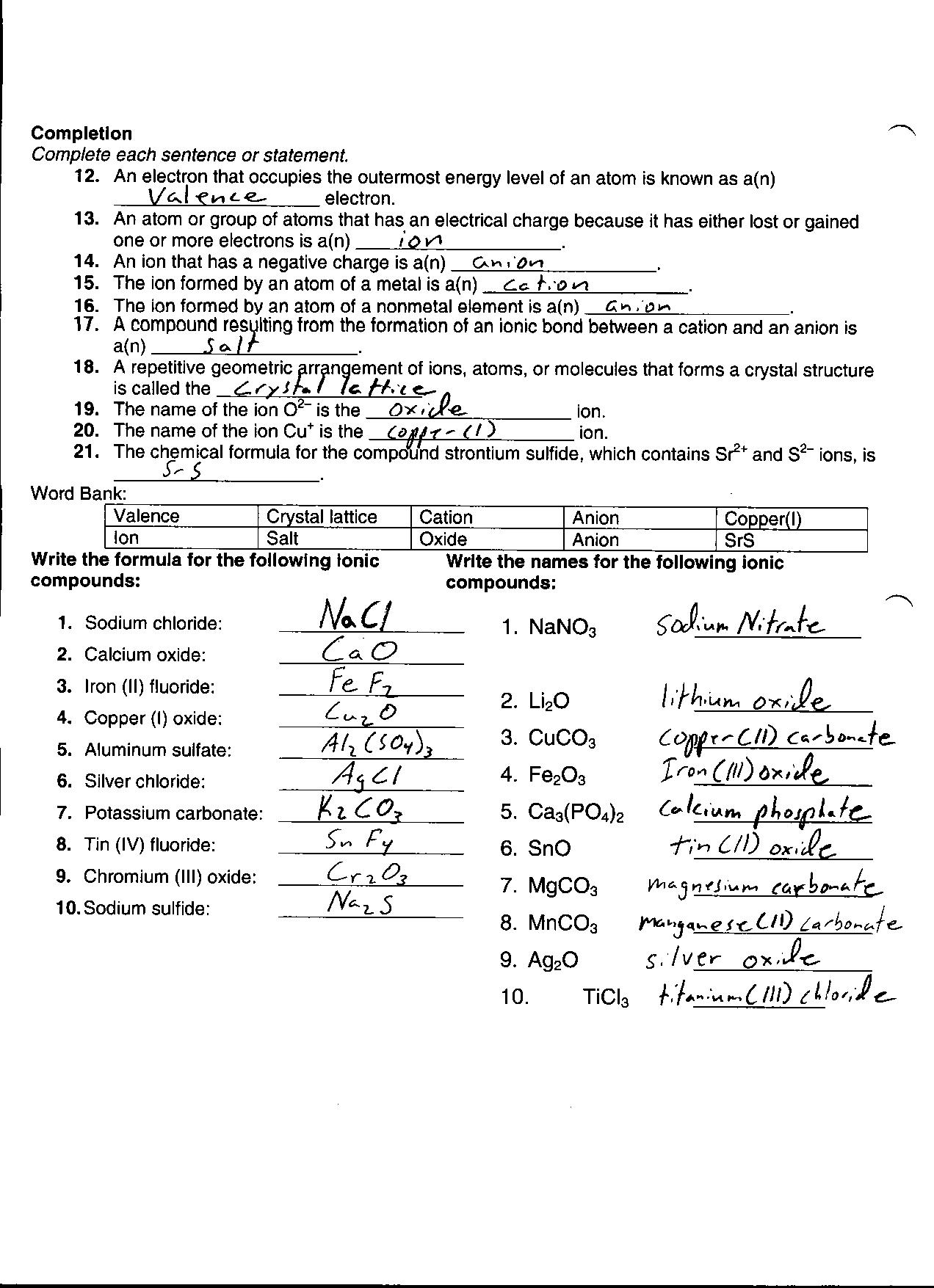
Chemical Bonding Worksheet Answer Key
Chemical bonding worksheets provide a structured way to reinforce learning about the nature and types of chemical bonds. These worksheets are designed to cater to the needs of students studying chemistry, particularly those at the high school and introductory college levels. By offering an answer key, these worksheets allow students to gauge their understanding of the subject matter and identify areas that require further clarification or practice.
Table of Images 👆
- Chemical Reaction Worksheet Answer Key
- Ionic Bonds Gizmo Answer Key
- Biology Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Matter Worksheet Answer Key
- Balancing Equations Worksheet
- Physical and Chemical Properties Worksheet Answer Key
- Writing Formulas Criss Cross Method Worksheet Answers
- Practice Naming Ionic Compounds Worksheet Answers
- Carbohydrates Worksheet Answers
- Periodic Table Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is chemical bonding?
Chemical bonding is the process by which two or more atoms are held together by attractive forces, leading to the formation of molecules and compounds. This bonding occurs through the sharing or transfer of electrons between atoms, resulting in the creation of stable arrangements of atoms with full outer electron shells. There are different types of chemical bonding, including ionic bonding, covalent bonding, and metallic bonding, each playing a key role in the structure and properties of substances.
What are the three main types of chemical bonds?
The three main types of chemical bonds are ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms, covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms, and metallic bonds occur between metal atoms where electrons are delocalized throughout the structure.
How are ionic bonds formed?
Ionic bonds are formed when one atom transfers one or more electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions. The electrostatic attraction between the oppositely charged ions then holds them together in a stable bond.
How are covalent bonds formed?
Covalent bonds are formed when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, resulting in the atoms being held together by the attractive forces between the shared electrons and the positively charged nuclei of the atoms. This sharing of electrons allows both atoms to achieve a more stable electron configuration by filling their valence shells, resulting in a stronger bond between the atoms.
What is a polar covalent bond?
A polar covalent bond is a type of chemical bond where two atoms share electrons unequally due to differences in electronegativity, leading to a partial positive charge on one atom and a partial negative charge on the other. This unequal sharing of electrons results in a separation of charges within the molecule, creating a dipole moment and making the molecule polar.
What is an electronegativity?
Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract and hold onto electrons in a chemical bond. It helps to predict the type of bond that will form between two atoms, with higher electronegativity values indicating a stronger pull on electrons. This concept is crucial in understanding how atoms interact and form compounds in chemistry.
How does electronegativity affect bond polarity?
Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond. When atoms with different electronegativities bond, the electrons are unequally shared, creating a polar covalent bond. The greater the electronegativity difference between the atoms, the more polar the bond will be. This results in one atom having a partial negative charge and the other a partial positive charge, leading to the formation of a dipole within the molecule.
What is a metallic bond?
A metallic bond is a type of chemical bond that occurs between metal atoms in a metal lattice. In this bond, metal atoms share their electrons in a "sea of electrons" that move freely within the metal structure, essentially creating a network of positively charged metal ions surrounded by a mobile "sea" of delocalized electrons. This arrangement gives metals their unique properties such as high electrical conductivity, malleability, ductility, and high melting points.
What are intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are the physical forces of attraction or repulsion between molecules. These forces include hydrogen bonding, dipole-dipole interactions, and London dispersion forces. They play a crucial role in determining the physical properties of substances such as melting point, boiling point, and solubility.
How do intermolecular forces differ from chemical bonds?
Intermolecular forces are weak attractions between molecules that do not involve the sharing or transfer of electrons, whereas chemical bonds are strong attractions between atoms within a molecule that involve the sharing or transfer of electrons. Intermolecular forces are responsible for holding molecules together in a substance, while chemical bonds hold atoms together within a molecule. Intermolecular forces are temporary and easily broken, whereas chemical bonds are strong and stable.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments