Cells of the World Worksheet
Are you searching for an engaging and educational tool to teach your students about cells? Look no further! The Cells of the World Worksheet is the perfect resource for science teachers and homeschool parents who are seeking a comprehensive and visually stimulating way to explore this fundamental biological concept.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Organelles Worksheet Answers
- Human Cell Worksheet High School
- Cell Theory Scientist Worksheet
- Cell Theory Worksheet Reinforcement Answers
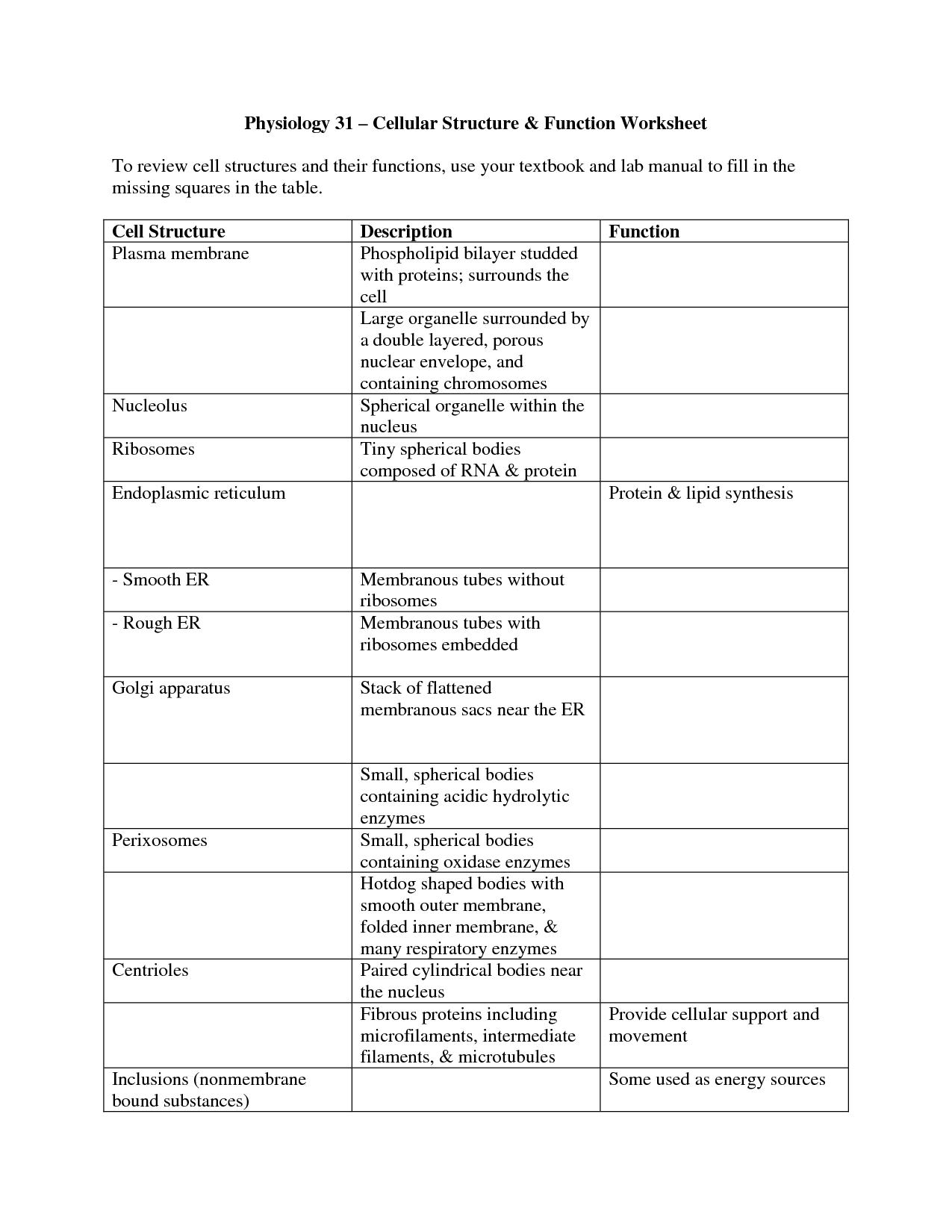
- Cell Structure and Function Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
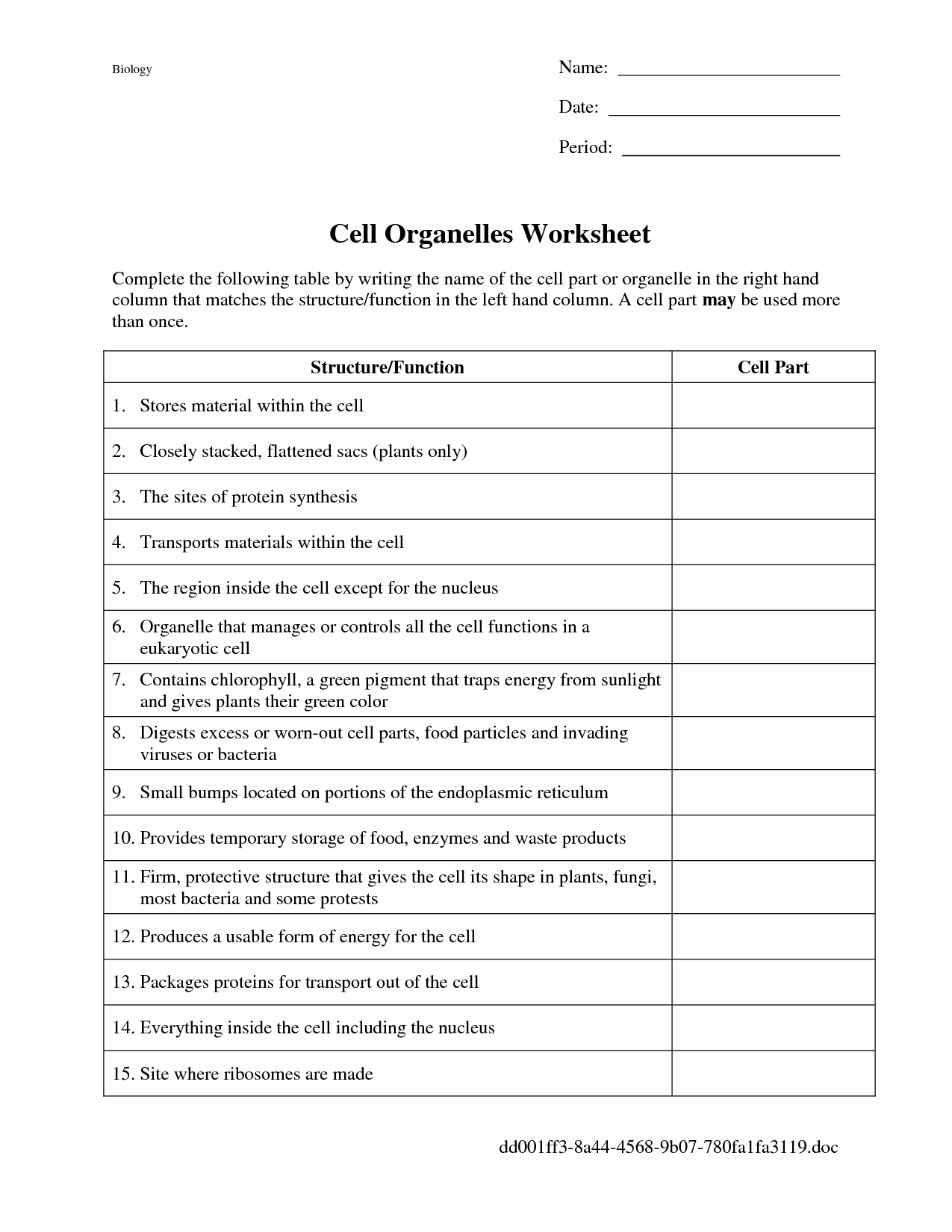
- Cell Parts and Functions Worksheet Answers
- Cell Division Mitosis Worksheet and Answers
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet
- Plant and Animal Cell Worksheet
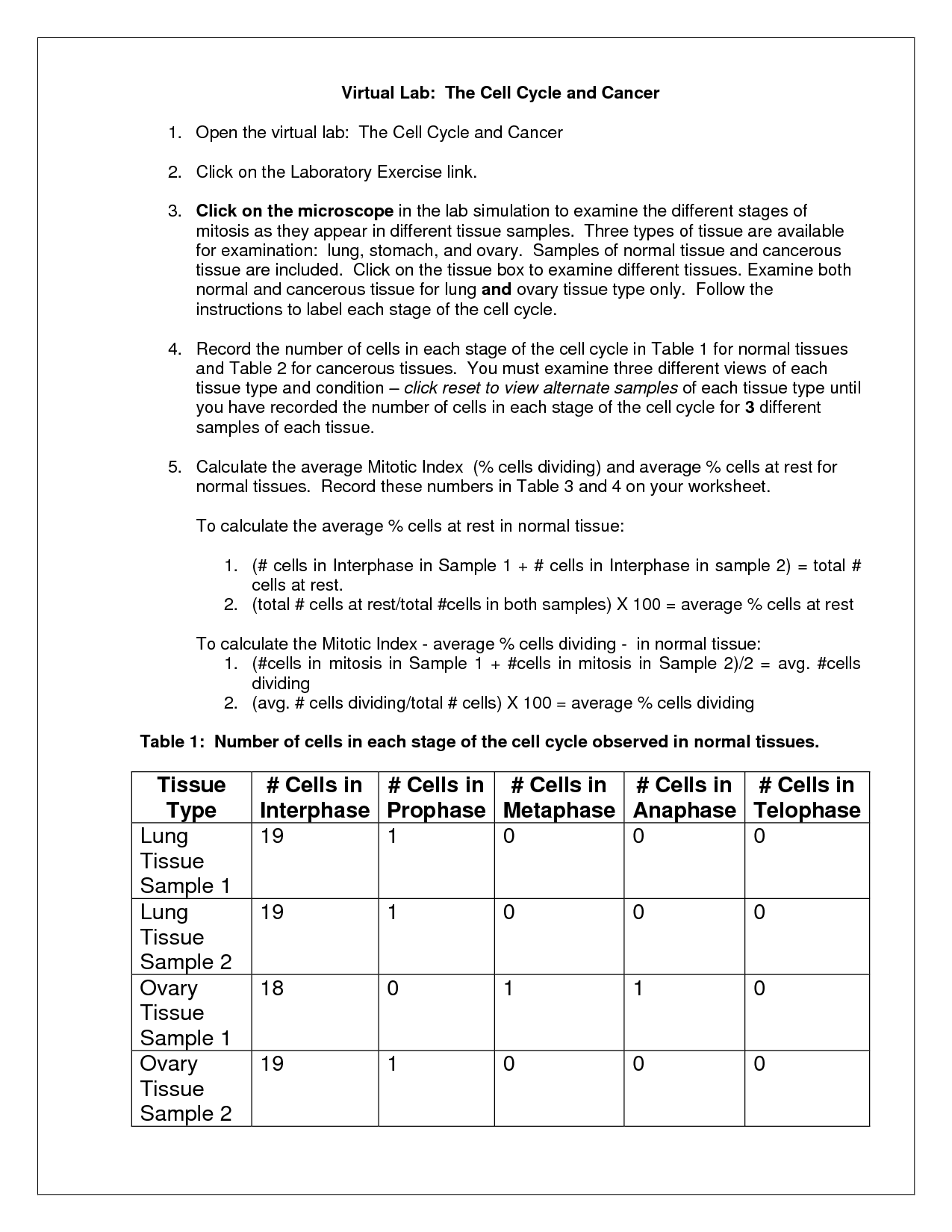
- Cell Cycle and Cancer Virtual Lab
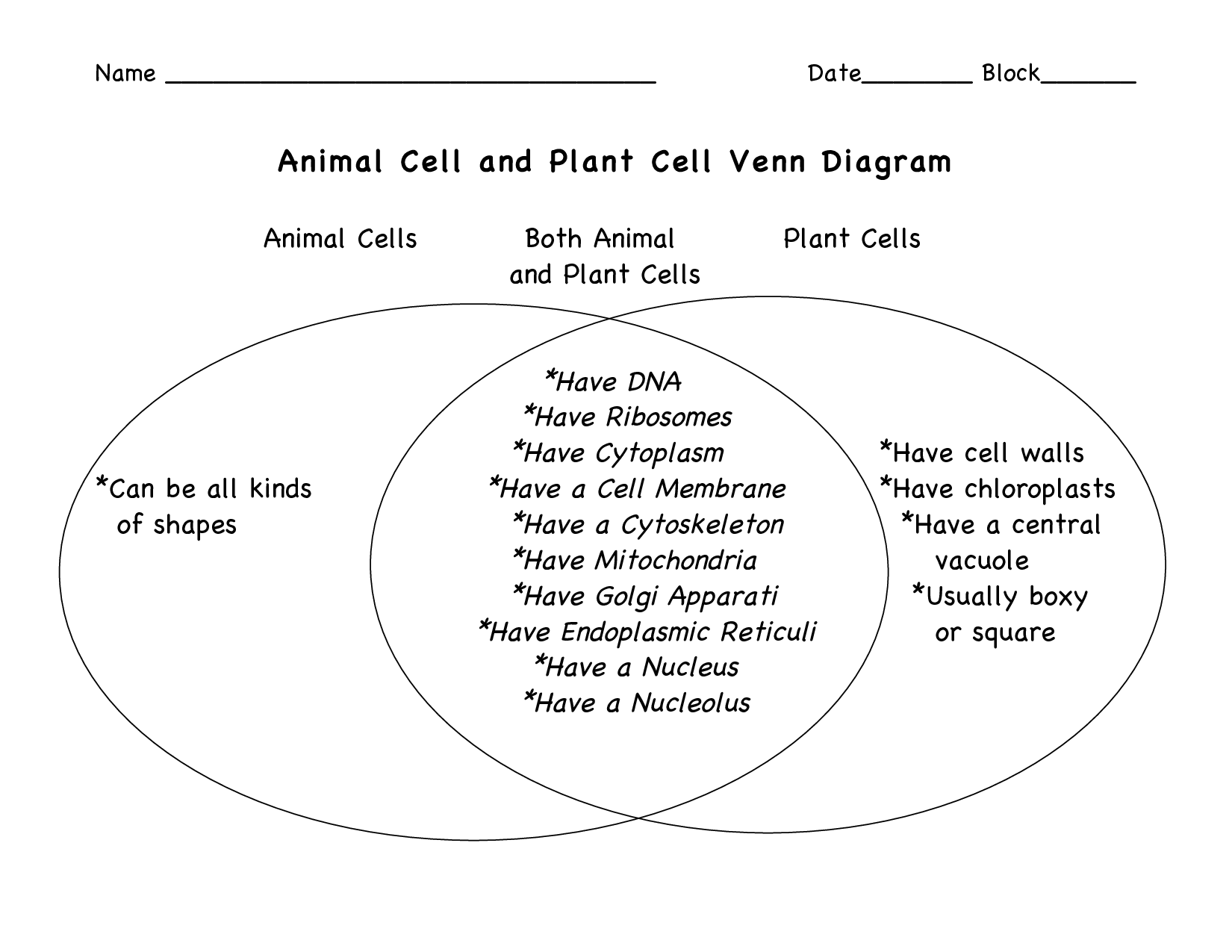
- Plant and Animal Cell Venn Diagram
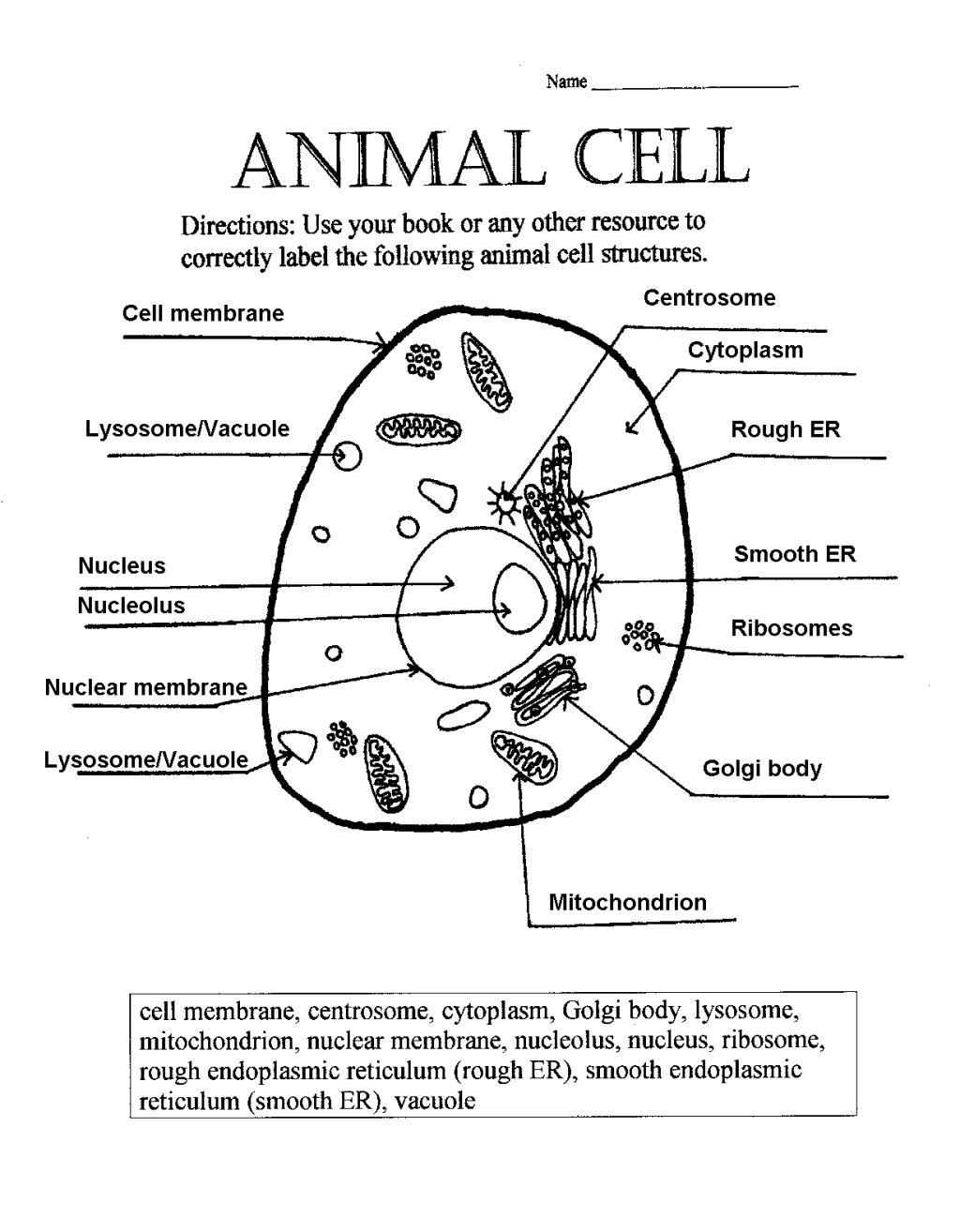
- Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet Answers
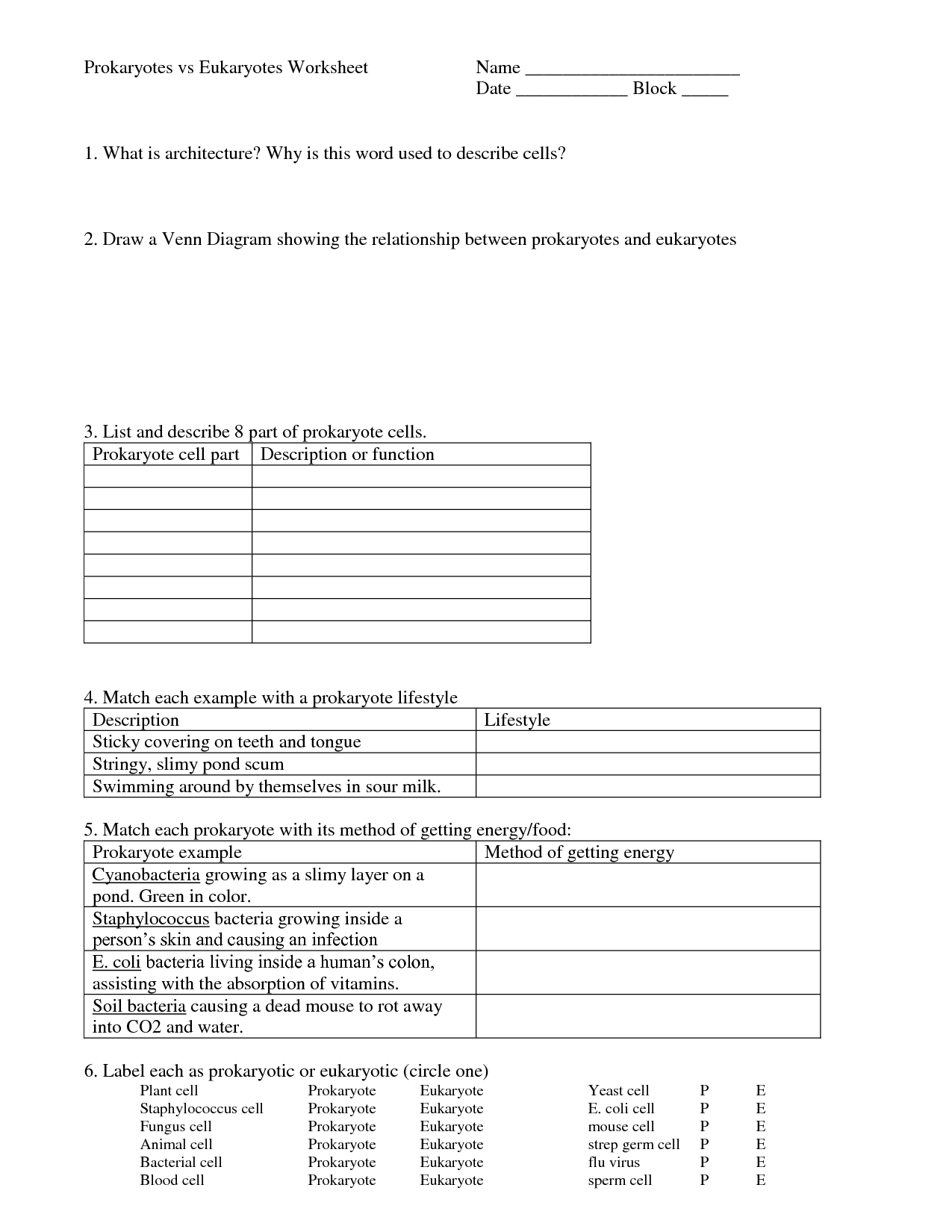
- Prokaryotic Cell Diagram Worksheet
- Cancer Cell Cycle Worksheet and Answers
- Cell Structure and Function Crossword Puzzle
- Cell Structure and Function Crossword
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are cells?
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. They are often referred to as the "building blocks of life" because they contain all the necessary components to carry out essential biological processes. These components include organelles, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, and ribosomes, which work together to support cell functions like metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Cells can vary in size, shape, and function, but all share the fundamental characteristics of life, including the ability to grow, reproduce, respond to stimuli, and maintain homeostasis.
What are the basic building blocks of life?
The basic building blocks of life are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. These elements are essential components of biological molecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids, which are crucial for the structure and function of living organisms.
How do cells differ from one another?
Cells differ from one another in size, shape, function, and specialization. Each type of cell has a specific role in the body, such as muscle cells for movement, nerve cells for communication, and red blood cells for carrying oxygen. Cells also vary in their organelles and structures based on their functions, which allows them to perform unique tasks within the body. Additionally, cells can be classified based on whether they are prokaryotic or eukaryotic, which further distinguishes their characteristics and abilities.
What is the function of a cell membrane?
The cell membrane functions as a semi-permeable barrier that surrounds the cell, regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell. It helps maintain the cell's internal environment by allowing essential molecules to enter and waste products to exit, while also providing protection and structural support to the cell. Additionally, the cell membrane plays a role in cell communication and recognition, as it contains receptors and other proteins that interact with signaling molecules.
What is the role of organelles within a cell?
Organelles within a cell perform various specialized functions that are essential for the survival and functioning of the cell. They help in carrying out specific processes such as energy production, protein synthesis, waste removal, and cellular communication. Each organelle has a specific role that contributes to the overall functioning of the cell, making them crucial for maintaining cellular homeostasis and supporting the various metabolic activities necessary for the cell to survive and function properly.
How do cells reproduce?
Cells reproduce through a process called cell division, which involves two main stages: mitosis and cytokinesis. During mitosis, the cell's nucleus divides into two identical nuclei with the same number of chromosomes. In cytokinesis, the rest of the cell divides, resulting in two daughter cells with the same genetic material as the original cell. This process ensures that genetic information is passed on accurately to new cells, allowing for growth, repair, and the maintenance of organisms.
What is the importance of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is crucial for all living organisms as it is the process by which cells generate energy in the form of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) from glucose and other organic molecules. This energy is essential for carrying out all cellular functions, including growth, maintenance, and reproduction. Without cellular respiration, cells would not be able to produce the energy needed to sustain life processes, leading to cell death and ultimately organism death. Additionally, cellular respiration plays a key role in the carbon cycle by releasing carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which is then used by plants in photosynthesis to produce oxygen, thereby maintaining the balance of gases in the atmosphere.
How do cells communicate with one another?
Cells communicate with each other through various mechanisms such as direct cell-to-cell contact, signaling molecules like hormones, neurotransmitters, and growth factors, and through gap junctions for direct transfer of ions and small molecules. Additionally, cells can also communicate through extracellular vesicles like exosomes that carry proteins, nucleic acids, and other signaling molecules between cells. These communication pathways play a crucial role in coordinating growth, differentiation, and various physiological processes in multicellular organisms.
How do cells contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms?
Cells contribute to the overall functioning of living organisms by performing various specialized functions necessary for survival. They carry out processes such as metabolism, energy production, and waste elimination. Cells also work together to form tissues, organs, and organ systems that coordinate activities and maintain homeostasis in the body. Through communication, division, and differentiation, cells play a critical role in growth, development, and repair of an organism. Ultimately, the combined efforts of all cells in an organism allow for proper functioning and adaptation to the environment.
How does the structure of a cell relate to its function?
The structure of a cell is directly related to its function due to the specialized organelles it contains, which carry out specific tasks necessary for the cell to function. For example, the mitochondria produce energy by cell respiration, the ribosomes synthesize proteins, and the Golgi apparatus packages and distributes molecules. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell, while the cytoskeleton provides structural support and enables movement within the cell. Each organelle plays a crucial role in the overall function of the cell, demonstrating the close relationship between structure and function in biology.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments