Cell Organization Worksheet
Are you searching for a powerful tool that will help you better understand the complex world of cell organization? Look no further! Our cell organization worksheet is designed to provide a clear and comprehensive overview of this fascinating subject. Whether you're a biology student, a teacher, or simply someone with a curious mind, our worksheet is here to guide you through the intricate structure and functions of cells.
Table of Images 👆
- Biology Cell Organelles Worksheet
- Levels of Organization Worksheet
- DNA Genes and Chromosomes Relationship
- Human Liver Cell Diagram
- Cell Organelle Quiz Worksheet
- Protist Lab Worksheet
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Worksheet
- Blank Animal Cell Diagram to Label
- Frog Dissection External Anatomy Worksheet
- Free Printable 13 Colonies Map
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is cell organization?
Cell organization refers to the arrangement and structure of organelles within a cell that allows it to carry out specific functions. It involves the segregation of organelles into distinct compartments, such as the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, each performing specialized tasks to maintain the overall functionality and efficiency of the cell. This organization is crucial for the coordination of cellular processes, signaling pathways, and regulatory mechanisms that enable cells to function properly and adapt to changing environments.
What are the different levels of cell organization?
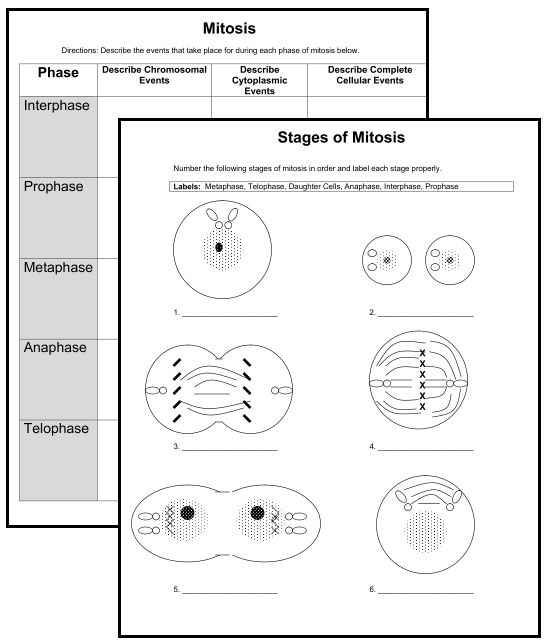
The different levels of cell organization are cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. Cells are the basic units of life, which come together to form tissues with specific functions. Tissues then combine to create organs, which work together to form organ systems that carry out various functions necessary for the organism's survival and wellbeing.
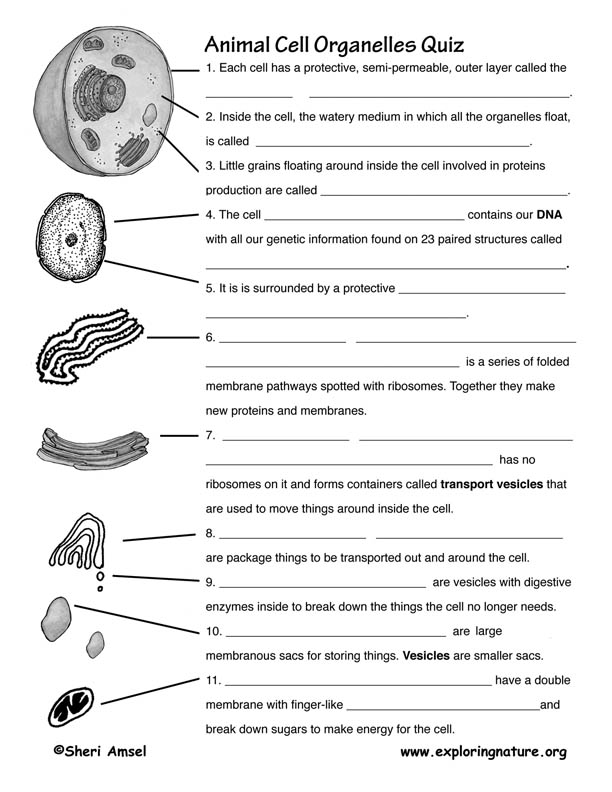
What is the cell membrane?
The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a semi-permeable barrier that surrounds the cell and separates its internal environment from the external environment. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that help regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cell, allowing for the maintenance of cellular homeostasis and communication with the surrounding environment.
How is a cell organized internally?
A cell is organized internally with the help of various structures and organelles that perform specific functions. The nucleus contains the genetic material and regulates cell activities, while the cytoplasm houses organelles like mitochondria for energy production, endoplasmic reticulum for protein synthesis, and Golgi apparatus for processing and packaging molecules. Additionally, cells have a cell membrane that separates the internal environment from the external surroundings and regulates the passage of substances in and out of the cell. Overall, the internal organization of a cell ensures proper functioning and maintenance of cellular processes.
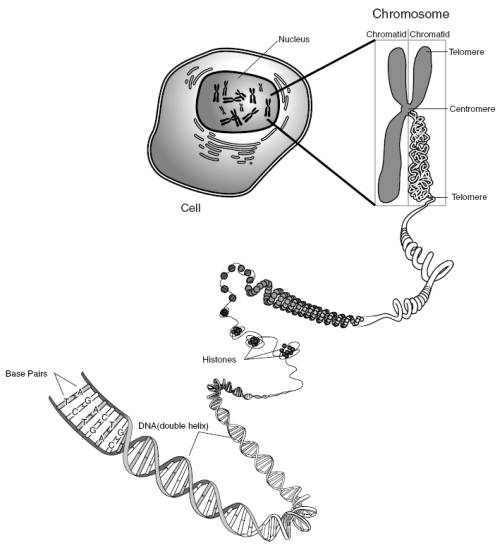
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, housing the cell's genetic material in the form of DNA. It is responsible for regulating gene expression, DNA replication, and the synthesis of RNA. The nucleus also plays a crucial role in cell division and the transmission of genetic information to daughter cells.
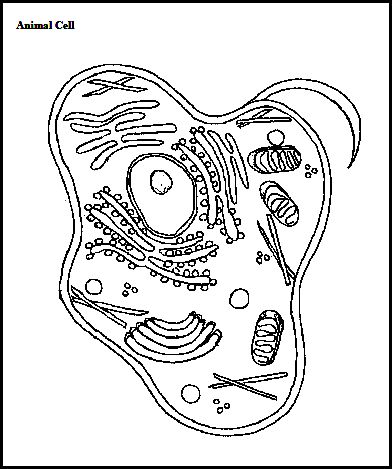
What are organelles?
Organelles are specialized structures within a cell that perform specific functions to ensure the cell's survival and functioning. Examples of organelles include the nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, each with its unique role in maintaining the cell's homeostasis and carrying out essential metabolic processes.
How do organelles contribute to cell organization?
Organelles contribute to cell organization by carrying out specific functions that help maintain the overall structure and organization of the cell. For example, the nucleus contains the cell's genetic material and regulates gene expression, while the endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for protein synthesis and transport. Other organelles like the mitochondria generate energy for the cell, the Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for secretion, and lysosomes break down waste materials. Together, these organelles work in concert to ensure the proper functioning and organization of the cell.
What is the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of tubules and membranes found in eukaryotic cells that plays a crucial role in protein and lipid synthesis, as well as in the transport of molecules within the cell. There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum: rough endoplasmic reticulum, which is studded with ribosomes responsible for protein synthesis, and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, which is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification processes.
How do ribosomes contribute to cell organization?
Ribosomes contribute to cell organization by translating the genetic information from messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins, which are essential for the structure and function of the cell. Ribosomes are responsible for synthesizing proteins that play various roles in cell processes, such as cell growth, repair, and regulation. By producing specific proteins, ribosomes help to organize cellular activities and maintain the overall structure and function of the cell.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in cell organization?
The Golgi apparatus plays a crucial role in cell organization by modifying, sorting, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for delivery to specific destinations within the cell or for secretion outside the cell. It acts as a distribution center where proteins are processed and sorted before being sent to their correct locations, helping to maintain the organization and proper functioning of the cell.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments