Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key
Are you a biology student in search of a reliable and comprehensive resource to practice your knowledge of the cell cycle? Look no further, as this Cell Cycle Worksheet Answer Key is guaranteed to help you reinforce your understanding of this crucial aspect of cellular biology. With clear and concise explanations, this worksheet provides a valuable tool for learners who are looking to review and test their knowledge on the entity and subject of the cell cycle.
Table of Images 👆
- Cell Cycle Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
- Cell Cycle and Mitosis Worksheet Answers
- Cell Cycle Review Worksheet Answers
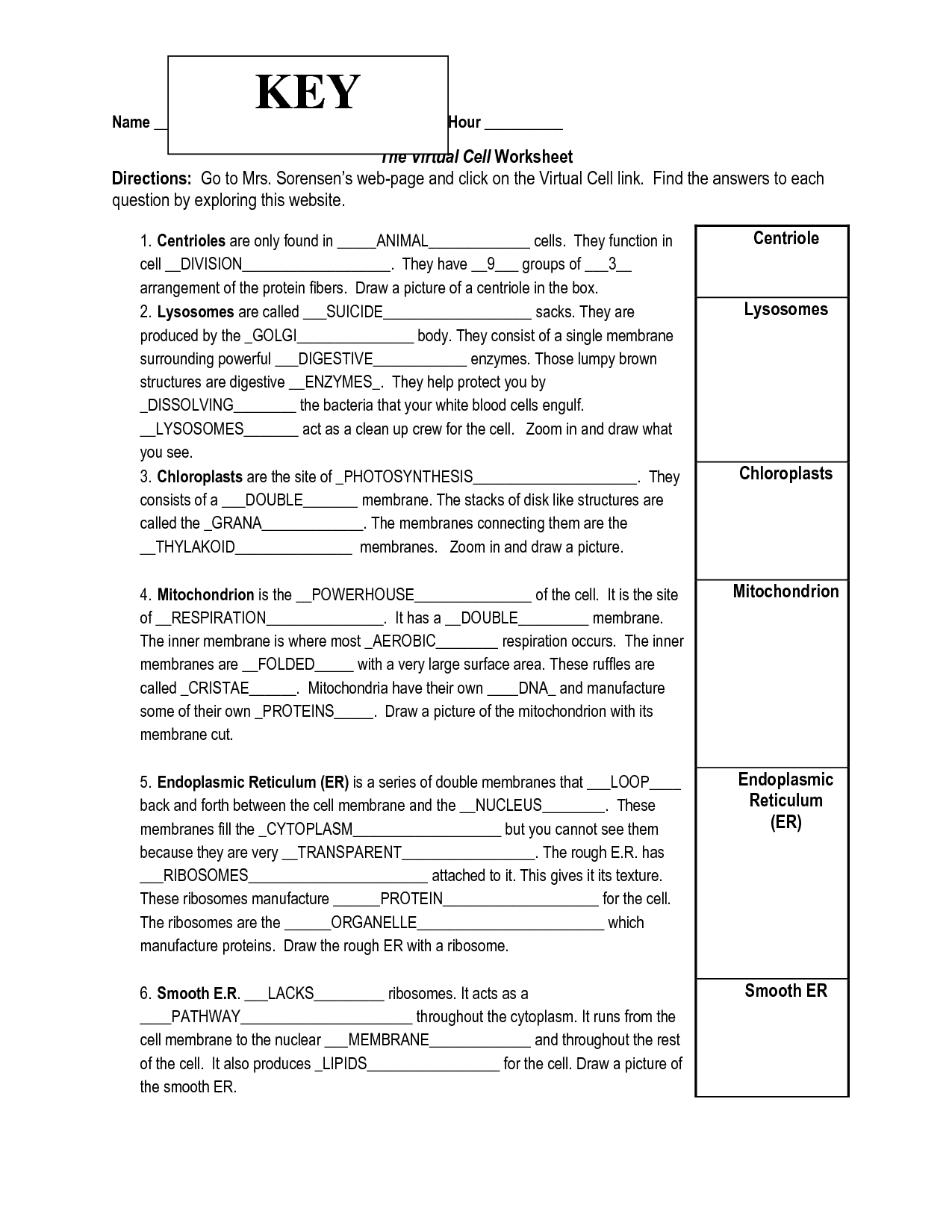
- Virtual Cell Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Worksheet Answer Key
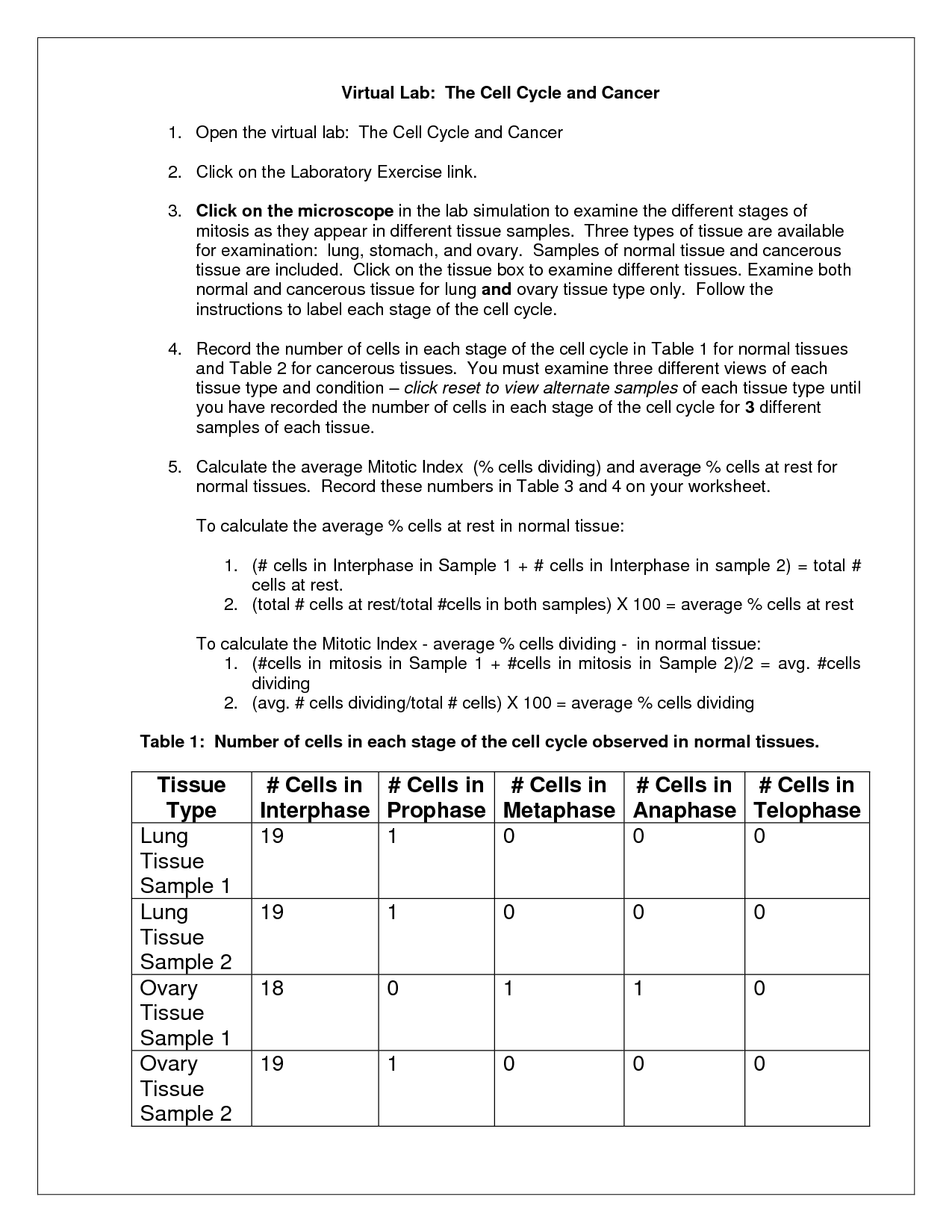
- Cell Cycle and Cancer Virtual Lab
- Cell Membrane Worksheet Answer Key
- Cellular Respiration Worksheet Answer Key
- Mitosis Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?
The purpose of the cell cycle is to ensure the growth, development, and reproduction of cells in an organized and controlled manner. It involves a series of stages, including growth, DNA replication, and cell division, to produce two new daughter cells with identical genetic material. By regulating the cell cycle, cells can maintain proper function, repair damage, and proliferate as needed for tissue growth and maintenance in organisms.
What are the main phases of the cell cycle?
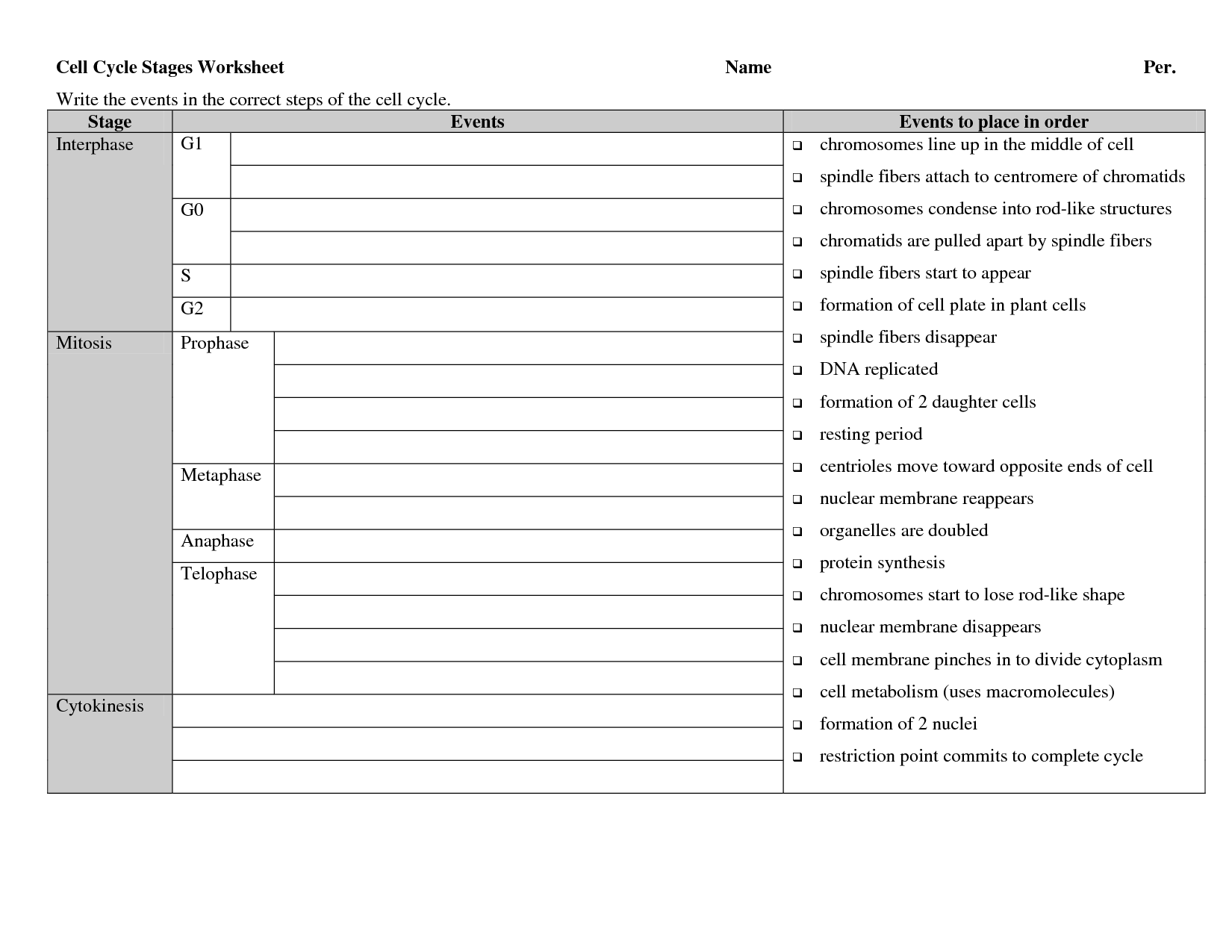
The main phases of the cell cycle are interphase, which includes stages G1 (growth), S (DNA synthesis), and G2 (preparation for cell division), followed by mitosis (division of the cell's nucleus) and cytokinesis (division of the cell's cytoplasm), resulting in two daughter cells with identical genetic material.
Describe the G1 phase.
The G1 phase, also known as Gap 1 phase, is the first stage of the cell cycle where the cell grows in size, synthesizes proteins, and performs its normal functions. During this phase, the cell prepares for DNA replication by ensuring that it has enough nutrients and energy to support the subsequent phases of the cell cycle. The length of the G1 phase can vary between different cell types and under different conditions, as it plays a crucial role in determining whether the cell will proceed with the cell cycle and divide or enter a non-dividing state called G0.
Explain the importance of the S phase.
The S phase of the cell cycle is crucial as it is when DNA replication takes place. During this phase, the genetic material is duplicated to ensure that each daughter cell receives an identical copy of the DNA. This process is essential for the accurate transmission of genetic information to the next generation of cells. Without proper DNA replication in the S phase, cells would not be able to divide and grow correctly, leading to potential genetic abnormalities and disorders. In essence, the S phase is critical for maintaining the integrity and stability of the genetic material in cells.
What happens during the G2 phase?
During the G2 phase of the cell cycle, the cell prepares for division by continuing to grow and synthesizing proteins necessary for cell division. The DNA is also checked for errors and any damages are repaired before entering the next phase, which is mitosis. This phase serves as a checkpoint to ensure that the cell is ready to divide and that the DNA is intact and correctly replicated.
How do checkpoints regulate the cell cycle?
Checkpoints regulate the cell cycle by ensuring that each step is completed accurately before progressing to the next. There are several checkpoints throughout the cell cycle, including the G1/S, G2/M, and metaphase checkpoints, which monitor DNA integrity, cell size, and chromosome attachment to the mitotic spindle. If abnormalities are detected at these checkpoints, the cell cycle can be paused to allow for repair or trigger apoptosis to prevent the propagation of damaged cells. Overall, checkpoints play a crucial role in maintaining genomic stability and preventing the proliferation of faulty cells.
What is mitosis and why is it important?
Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. It is crucial for various important functions in multicellular organisms, including growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction. Mitosis ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic material from the parent cell, allowing organisms to develop and maintain their structure and function.
Describe the stages of mitosis.
Mitosis is divided into four main stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During prophase, chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the spindle fibers form. In metaphase, chromosomes align along the center of the cell. Anaphase follows, where the sister chromatids separate and move towards opposite poles of the cell. Finally, in telophase, the nuclear envelope reforms around the separated chromosomes, the chromosomes decondense back into chromatin, and the cell undergoes cytokinesis to divide into two daughter cells.
What is cytokinesis and when does it occur?
Cytokinesis is the process in which a cell divides its cytoplasm and organelles to form two daughter cells following mitosis or meiosis. It occurs after the completion of nuclear division when the genetic material has been evenly distributed to the daughter cells. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of organelles and cytoplasm, allowing them to function independently.
How does the cell cycle relate to cell division and the growth of tissues and organisms?
The cell cycle is a series of stages that a cell goes through to divide and produce new cells. Cell division is a critical part of the cell cycle, as it allows for growth, repair, and development of tissues and organisms. As cells divide and replicate their DNA during the cell cycle, they contribute to the growth of tissues by increasing the number of cells and ultimately the size of the tissue or organism. Proper regulation of the cell cycle is essential for the maintenance of tissues and the growth of organisms.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






























Comments