Bohr Model Worksheet
A Bohr Model Worksheet is a valuable educational tool that helps students understand the atomic structure of elements. Designed for middle school and high school students, this worksheet provides a thorough overview of the Bohr Model and its significance in the field of chemistry. By using this worksheet, students are able to grasp the concept of energy levels and electron distribution in atoms, aiding them in their pursuit of a strong foundation in chemistry.
Table of Images 👆
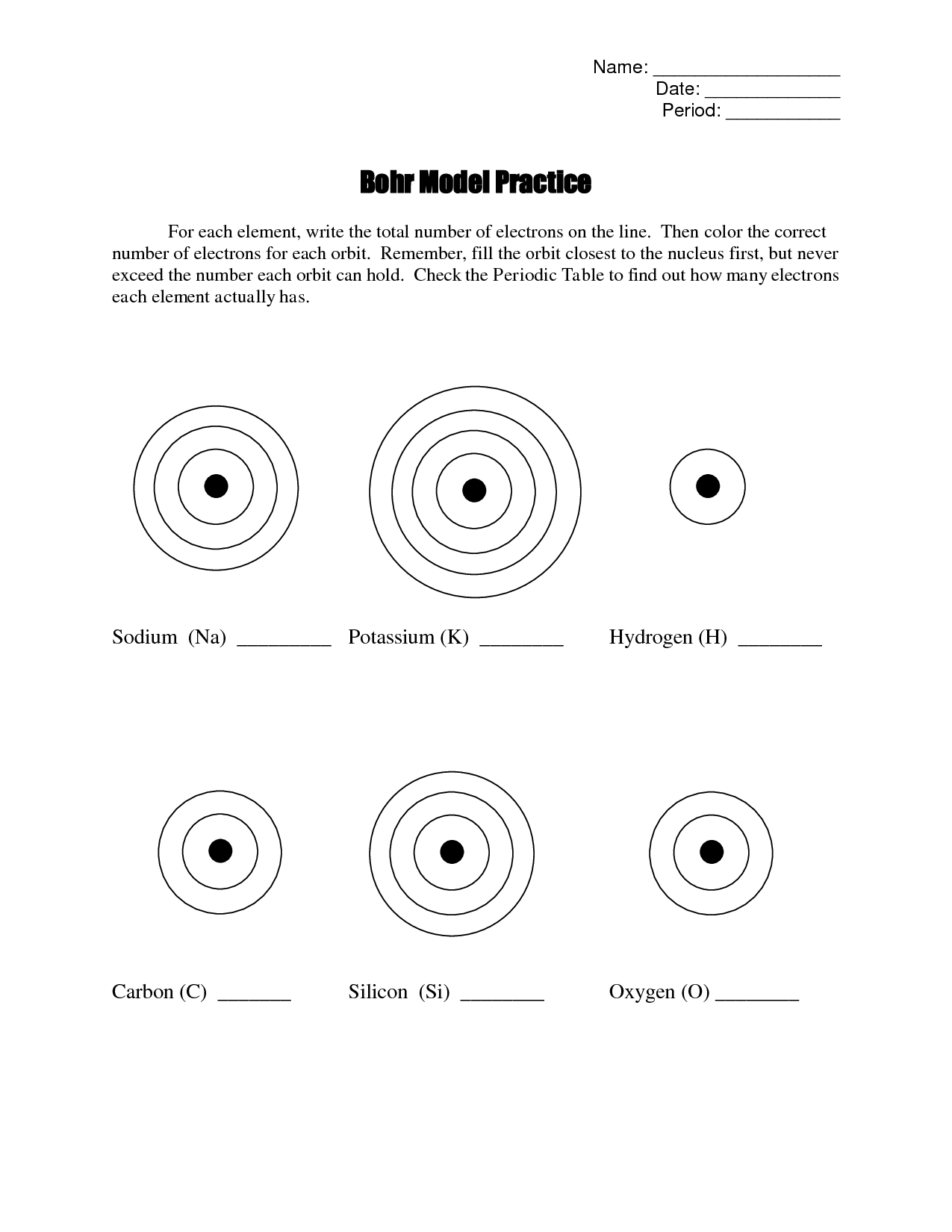
- Bohr Model Worksheet Answers
- Bohr Model Electron Configuration
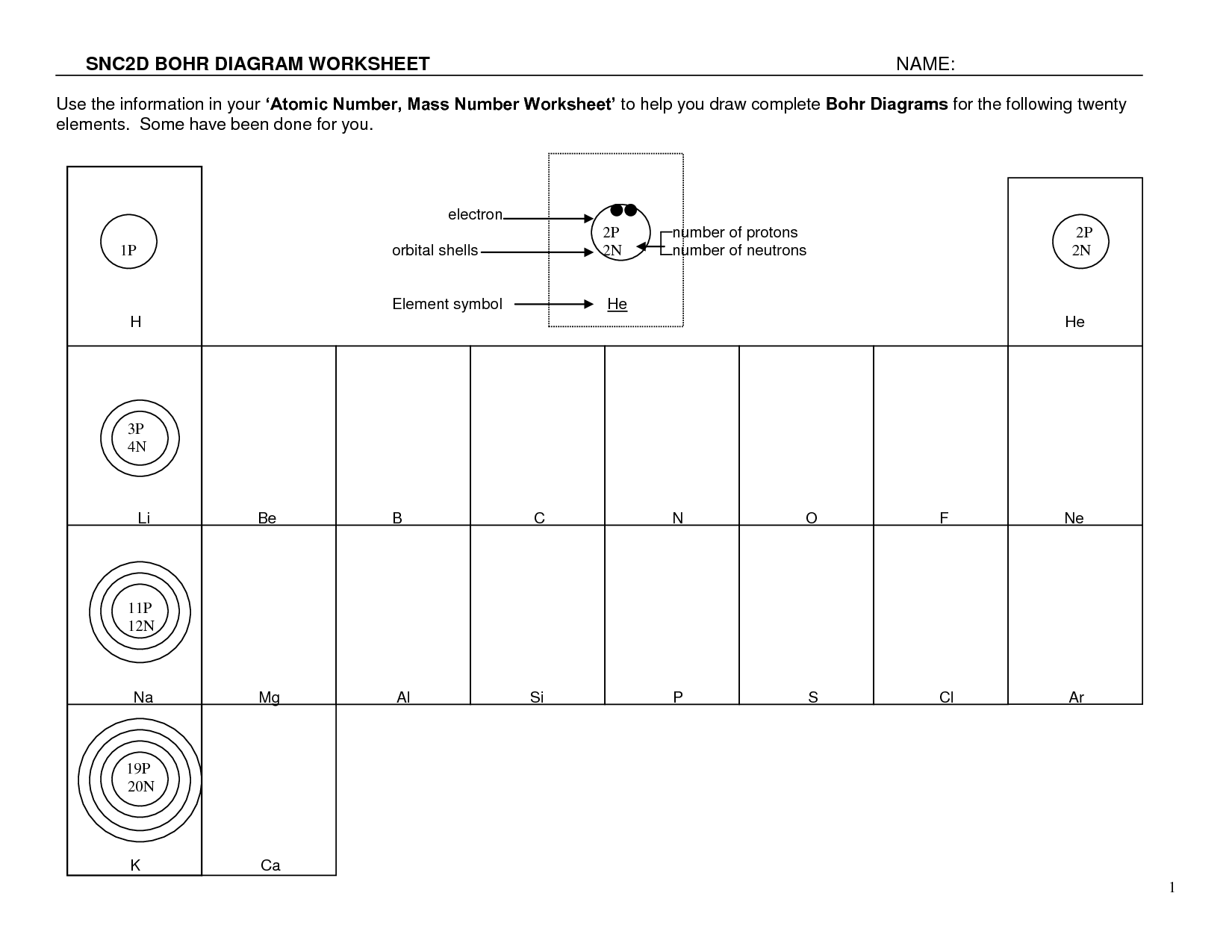
- Bohr Diagram Worksheet
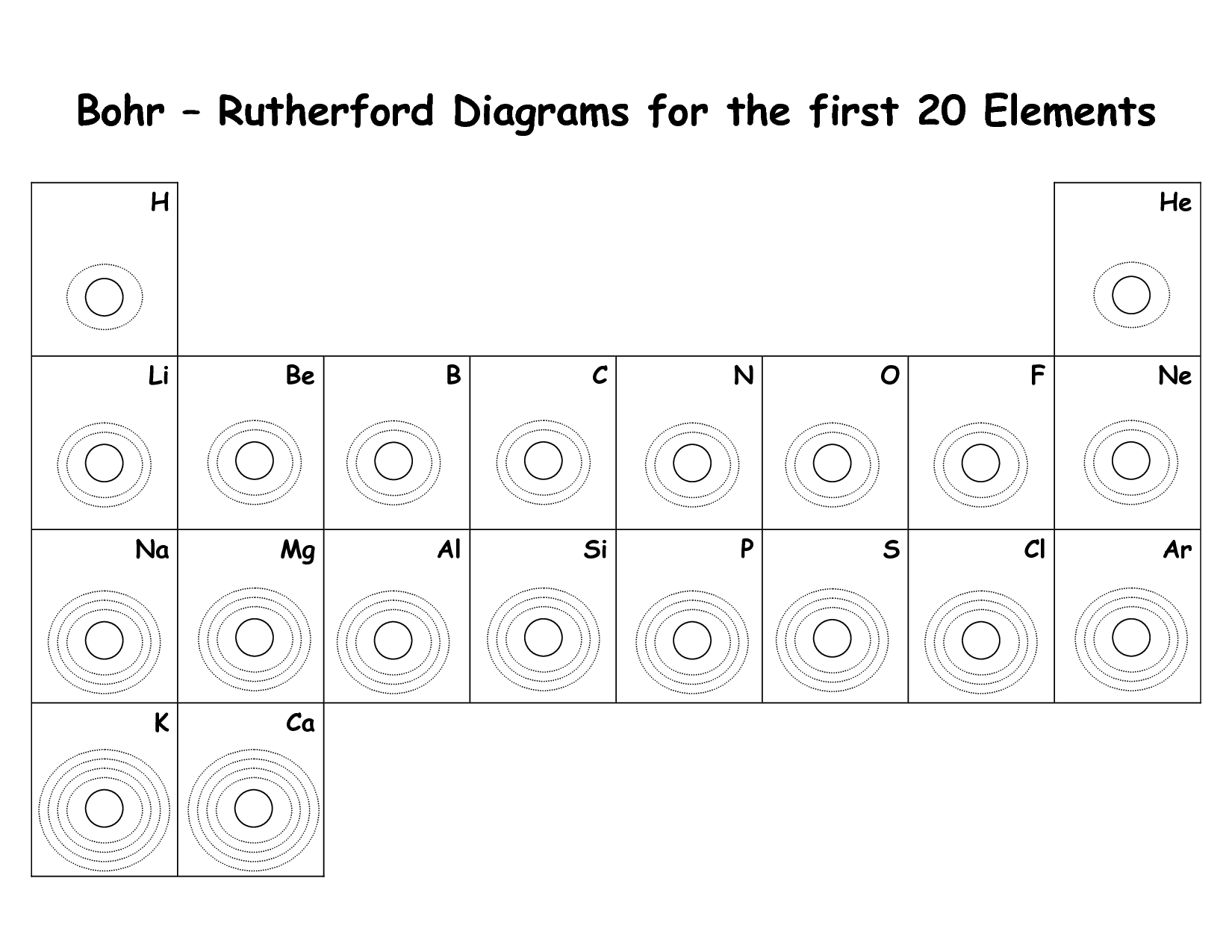
- Diagram of the First 20 Elements Bohr Model
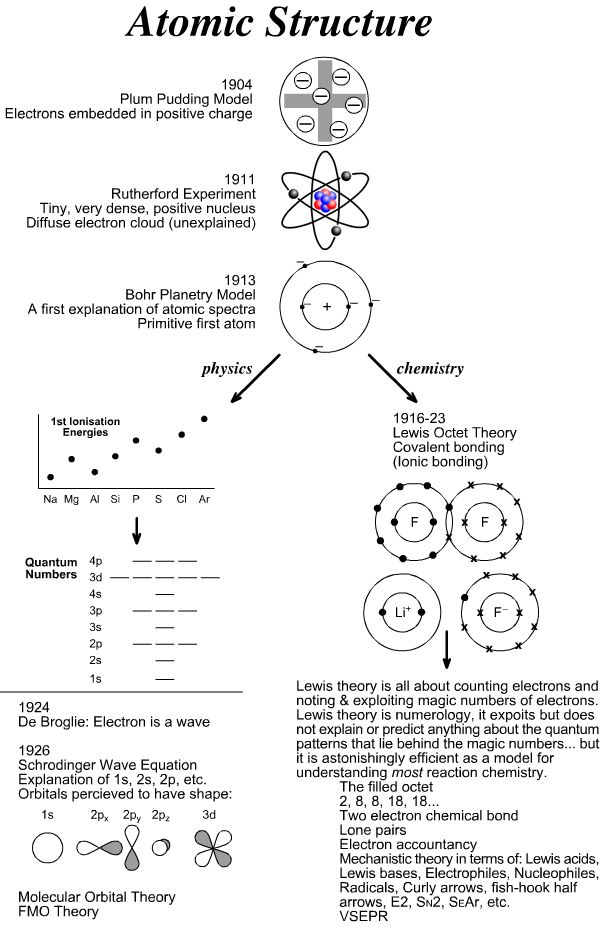
- Atomic Structure Model Timeline
- Bohr Atomic Models Worksheet Answers
- How Do You Draw a Bohr Model
- Metals and Nonmetals Worksheet
- Argon Bohr Model Diagrams
- Basic Atomic Structure Worksheet Answer Key
- Positive-Thinking Worksheet.pdf
- Parent Function Worksheet Answers
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is the Bohr model?
The Bohr model is a scientific model of the atom proposed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913. It describes the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by negatively charged electrons that orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels or shells. This model was revolutionary as it explained the stability of atoms and the emission of spectral lines, laying the foundation for modern atomic theory.
Who developed the Bohr model?
The Bohr model of the atom was developed by Danish physicist Niels Bohr in 1913.
What is the basic structure of the Bohr model?
The Bohr model of the atom proposes a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons, with electrons orbiting the nucleus in specific energy levels or shells. These energy levels are quantized, meaning electrons can only occupy certain distances from the nucleus. The model also suggests that electrons can jump between energy levels by absorbing or emitting specific amounts of energy, such as photons of light.
How does the Bohr model explain the stability of atoms?
The Bohr model explains the stability of atoms by proposing that electrons orbit the nucleus in fixed energy levels or shells. Electrons emit or absorb energy when they move between these energy levels. An atom is most stable when its electrons are in their lowest energy level or ground state. This stability is maintained by the balancing of the attractive force between the positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons with the centrifugal force of the orbiting electrons.
What is the role of electrons in the Bohr model?
In the Bohr model of the atom, electrons revolve around the nucleus in specific orbits or energy levels. Electrons play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of an element as they are involved in forming chemical bonds and determining the reactivity of the atom. Additionally, the movement of electrons between energy levels is responsible for the absorption or emission of light, which is the basis of atomic and molecular spectroscopy.
What are energy levels in the Bohr model?
In the Bohr model, energy levels are specific, quantized orbits around the nucleus where an electron can exist without emitting energy. These energy levels are represented by integer values and are related to the distance of the electron from the nucleus. Electrons can move between energy levels by absorbing or emitting photons of specific energy.
How are electrons arranged within the energy levels?
Electrons are arranged within energy levels based on the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first before moving to higher energy levels. Each energy level can hold a specific number of electrons, with the closest energy level to the nucleus holding the least electrons and subsequent energy levels holding more. This arrangement of electrons within energy levels follows the principles of quantum mechanics and the periodic table, influencing the chemical properties of elements.
What happens when an electron jumps between energy levels?
When an electron jumps between energy levels within an atom, it either absorbs or emits a photon of energy corresponding to the difference in energy between the initial and final energy levels. This process is known as electronic transition or quantum leap and is responsible for the emission and absorption of light in atomic spectra. The specific energy levels that an electron can occupy are determined by the atom's unique set of allowed energy states, and the transition of electrons between these levels plays a crucial role in the behavior and properties of atoms.
How does the Bohr model explain the emission and absorption of light by atoms?
The Bohr model explains the emission and absorption of light by atoms through the concept of quantized energy levels. According to the model, electrons orbit the nucleus in specific energy levels, and when an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, it emits light in the form of photons. Conversely, when a photon of the right energy interacts with an atom, it can be absorbed, causing an electron to move to a higher energy level. This precise matching of energy levels accounts for the specific wavelengths of light that are emitted or absorbed by atoms, supporting the foundation of spectroscopy.
What are the limitations of the Bohr model?
The Bohr model of the atom has several limitations, including its inability to explain the spectral lines of atoms with more than one electron, it does not account for the phenomenon of electron spin or the magnetic properties of atoms, and it ignores the concept of wave-particle duality inherent in quantum mechanics. Additionally, the model is limited in its treatment of electron motion as circular orbits, which is inconsistent with the Heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments