Biomolecules Worksheet High School
Biomolecules are a fundamental aspect of the study of biology, and for high school students navigating this subject, worksheets can be an invaluable resource. These worksheets provide an entity for students to explore and apply their knowledge of biomolecules, helping them understand the different types and functions of these important substances.
Table of Images 👆
- Worksheets Answer Key
- Using Graphic Organizers in Science
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Photosynthesis Coloring Sheet
- Biology Macromolecules Worksheets
- Genetics Vocabulary Crossword Puzzle Answers Biology
- Current Events Worksheet Template Free
- Bellaire High School
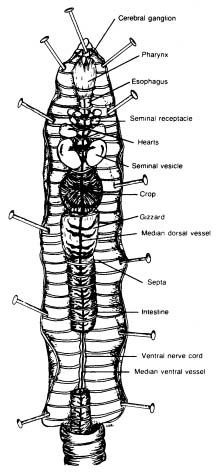
- Earthworm Anatomy Dissection
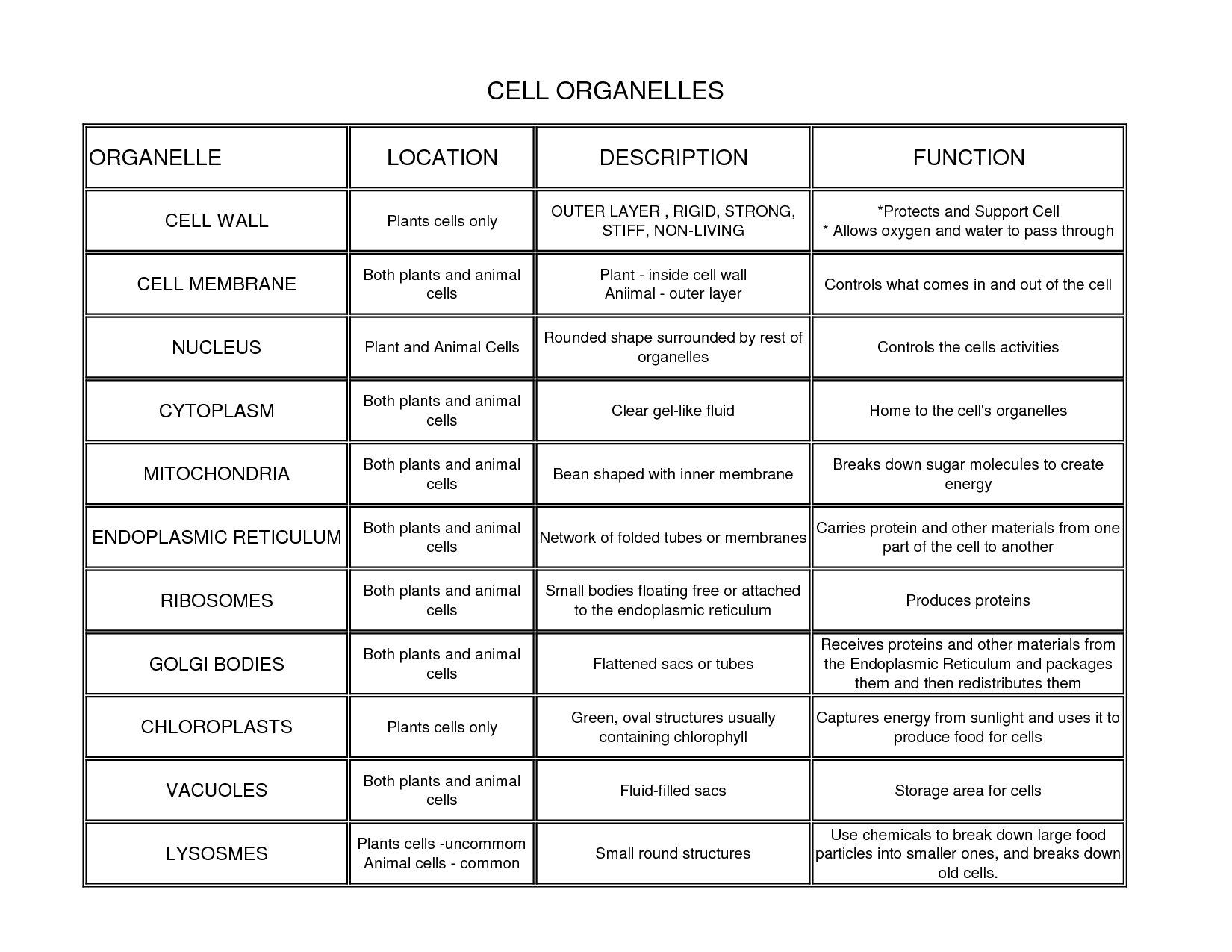
- Animal Cell Organelles Functions
- DNA vs RNA Venn Diagram
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What are biomolecules?
Biomolecules are molecules that are essential for the structure, function, and regulation of living organisms. They include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, which are the building blocks of life and play crucial roles in processes such as metabolism, DNA replication, and cell signaling. These molecules are involved in various biological functions and are vital for sustaining life.
What are the four main types of biomolecules?
The four main types of biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. Carbohydrates are sugars and starches that provide energy; lipids are fats and oils that store energy; proteins are molecules made up of amino acids that perform various functions in the body; and nucleic acids, like DNA and RNA, store and transmit genetic information.
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The primary structure of a protein refers to the linear sequence of amino acids that make up the protein chain. This sequence is held together by peptide bonds between adjacent amino acids and is crucial in determining the overall structure and function of the protein.
How are carbohydrates classified?
Carbohydrates are classified into three main groups: sugars, starches, and fibers. Sugars can be further classified as simple (monosaccharides and disaccharides) or complex (polysaccharides). Starches are long chains of glucose molecules and are a common source of energy in the diet. Fibers are a type of carbohydrate that the body cannot digest, but play a key role in supporting digestion and overall health.
What are lipids and their functions?
Lipids are a diverse group of organic compounds that are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents. They serve various functions in the body, such as storing energy, forming cell membranes, acting as signaling molecules, and serving as insulation for the body. Lipids also play a role in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins and are involved in regulating processes like inflammation and blood clotting.
Describe the structure of nucleic acids.
Nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, are macromolecules composed of nucleotide subunits. Each nucleotide consists of a phosphate group, a sugar molecule (deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, cytosine, guanine, thymine in DNA, and uracil in RNA). These nucleotides are connected through phosphodiester bonds forming long chains. The nitrogenous bases within nucleic acids are responsible for carrying genetic information, with adenine pairing with thymine (DNA) or uracil (RNA), and cytosine pairing with guanine. Overall, the structure of nucleic acids is a double helix in DNA and a single-stranded structure in RNA, which allows for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
What is the function of enzymes?
Enzymes act as biological catalysts in the body, speeding up chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur. They facilitate the conversion of substrates into products without being consumed in the process, allowing essential biochemical reactions to take place at a much faster rate than they would without enzymes.
How are proteins involved in cell signaling?
Proteins play a crucial role in cell signaling by serving as messengers that transmit signals from one part of the cell to another or between different cells. These signaling proteins can interact with receptors on the cell surface, initiating a cascade of molecular events that ultimately lead to a specific cellular response. Protein kinases, for example, are enzymes that add phosphate groups to target proteins, modifying their activity and playing a key role in signal transduction pathways. Overall, proteins are essential components of the complex network of signaling processes that regulate various cellular functions and responses.
Explain the role of carbohydrates in energy storage.
Carbohydrates play a crucial role in energy storage in the human body by being converted into glucose, which is then used for immediate energy production or stored as glycogen in the muscles and liver for later use. When energy is needed, glycogen is broken down back into glucose to fuel various cellular processes and physical activities. Additionally, excess glucose can be converted into fat for long-term energy storage. This dynamic energy storage and utilization system powered by carbohydrates ensures a constant supply of energy for the body's daily functions and activities.
How do lipids contribute to cell membranes?
Lipids contribute to cell membranes by forming a lipid bilayer that provides a barrier between the cell's interior and the external environment. Phospholipids are the primary lipid molecules in cell membranes, with hydrophobic tails that face inward and hydrophilic heads that face outward. This arrangement helps to regulate the passage of molecules in and out of the cell, maintain cell shape and structure, and facilitate cell-cell communication and signaling. Cholesterol molecules are also present in cell membranes and help to maintain membrane fluidity and stability. Overall, lipids are essential components of cell membranes and play a crucial role in the function and integrity of cells.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.
























Comments