Biomolecule Structure Worksheets
Biomolecule structure worksheets are a valuable resource for biology students who want to deepen their understanding of the complex world of biomolecules. By providing a variety of exercises and problems, these worksheets help students develop their knowledge and skills in identifying and visualizing the different types of biomolecules such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids.
Table of Images 👆
- Organic Molecules Worksheet Review Answers
- Biomolecule Review Worksheet Answers
- Biomolecule Review Worksheet
- Biomolecule Chart Review
- Organic Macromolecules Worksheet Answers
- Amino Acids and Proteins Worksheet
- Anatomy and Physiology Worksheets Skull
- Macromolecule Chart Biomolecules
- Using Graphic Organizers in Science
- Macromolecules Chart Answers
- Animal Cell Coloring Worksheet
- Functional Text Worksheets
- Photosynthesis Coloring Sheet
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
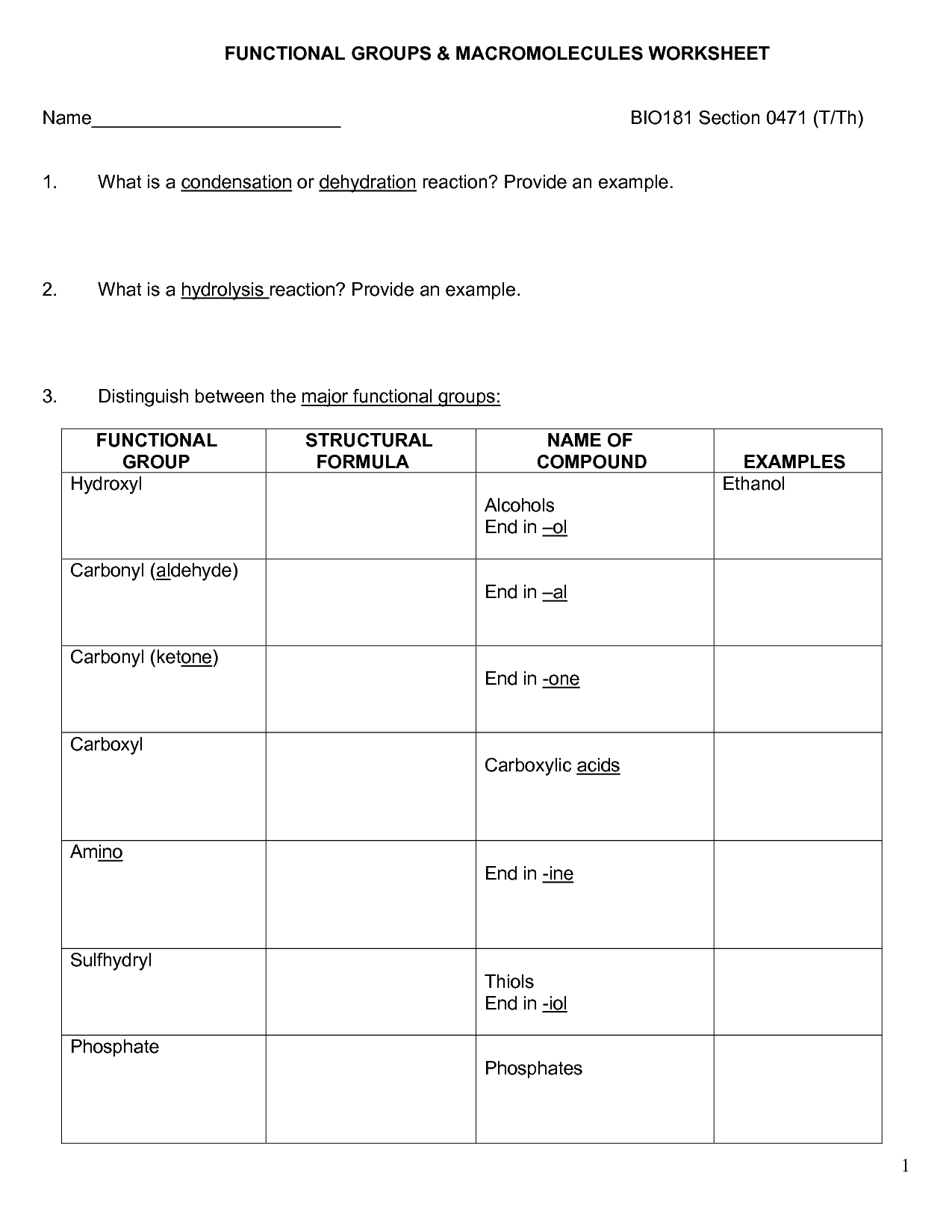
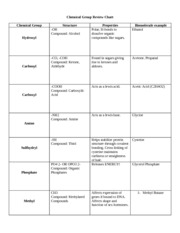
What is the primary structure of a biomolecule?
The primary structure of a biomolecule refers to the linear sequence of individual monomers that make up the molecule. In proteins, for example, the primary structure is determined by the specific sequence of amino acids linked together by peptide bonds. This sequence is essential as it ultimately dictates the higher-order structures and functions of the biomolecule.
What are the main components of a nucleotide?
A nucleotide is composed of three main components: a phosphate group, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a nitrogenous base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, or guanine). The nitrogenous base can be either a purine (adenine and guanine) or a pyrimidine (cytosine, thymine, and uracil). These components are the building blocks of nucleic acids, such as DNA and RNA, which are essential for storing and transferring genetic information in cells.
How are amino acids linked together in a protein?
Amino acids are linked together in a protein through peptide bonds. Peptide bonds form when the carboxyl group of one amino acid reacts with the amino group of another amino acid, releasing a water molecule in a condensation reaction. This process creates a chain of amino acids known as a polypeptide, which folds into a specific three-dimensional structure to form a functional protein.
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids?
Saturated fatty acids have all of their carbon atoms bonded to hydrogen atoms, meaning they have no double bonds in their chemical structure, while unsaturated fatty acids have one or more double bonds between carbon atoms. This difference affects the physical properties of the fats, with saturated fats typically being solid at room temperature, while unsaturated fats are usually liquid. Additionally, unsaturated fats are considered healthier as they are known to lower bad cholesterol levels in the blood compared to saturated fats.
What is the purpose of carbohydrates in living organisms?
Carbohydrates are an important energy source for living organisms, providing fuel for cellular processes and enabling the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) through cellular respiration. They also play a key role in cell structure and in storing excess energy for later use. Additionally, certain carbohydrates serve as signaling molecules and are involved in various biological pathways, such as cell-cell recognition and communication.
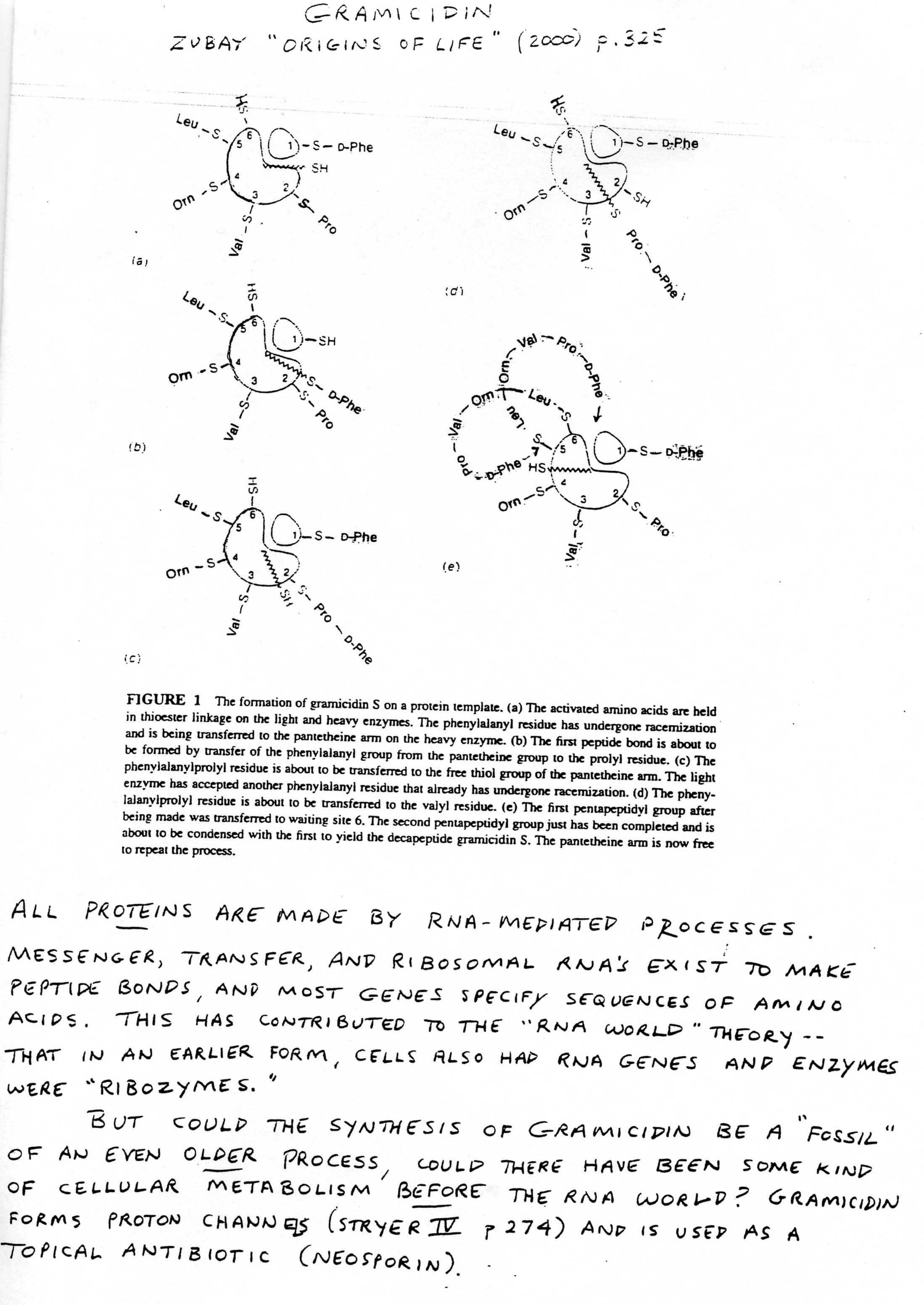
Describe the structure and function of DNA.
DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is a double-stranded helical molecule made up of nucleotide bases (adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine) that encode genetic information. Its primary function is to store and transmit genetic information essential for the development, functioning, and reproduction of all living organisms. The information is inherited from parents and passed on to offspring. DNA is responsible for directing the synthesis of proteins, which play crucial roles in various biological processes. This process is facilitated by the transcription of DNA into messenger RNA and subsequent translation into proteins. DNA also plays a key role in genetic variation and evolution through processes such as mutation and genetic recombination.
What is the role of enzymes in biochemical reactions?
Enzymes act as biological catalysts in biochemical reactions, speeding up the rate at which these reactions occur. They lower the activation energy required for a reaction to take place, making it more efficient. Enzymes are specific to the reactions they catalyze, and they can be reused multiple times. Additionally, enzymes play a critical role in maintaining the metabolic reactions necessary for various cellular processes to occur efficiently.
How is the secondary structure of a protein formed?
The secondary structure of a protein is formed through hydrogen bonding interactions between the amino acid residues in the polypeptide chain. These interactions lead to the formation of two main secondary structures: alpha helices and beta sheets. In an alpha helix, the polypeptide chain forms a coil stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the amide hydrogen and carbonyl oxygen of each amino acid. In beta sheets, the polypeptide chain folds into a series of strands that run adjacent to each other, with hydrogen bonds forming between the strands. These secondary structures are important for the overall folding and stability of the protein.
What are the three types of RNA and their functions?
The three types of RNA are messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), and ribosomal RNA (rRNA). mRNA carries genetic information from the DNA in the cell nucleus to the ribosomes in the cytoplasm, where protein synthesis occurs. tRNA transfers specific amino acids to the ribosome during protein synthesis based on the codons on the mRNA. rRNA is a crucial component of ribosomes, where it helps in the assembly of amino acids into proteins based on the information provided by mRNA and tRNA.
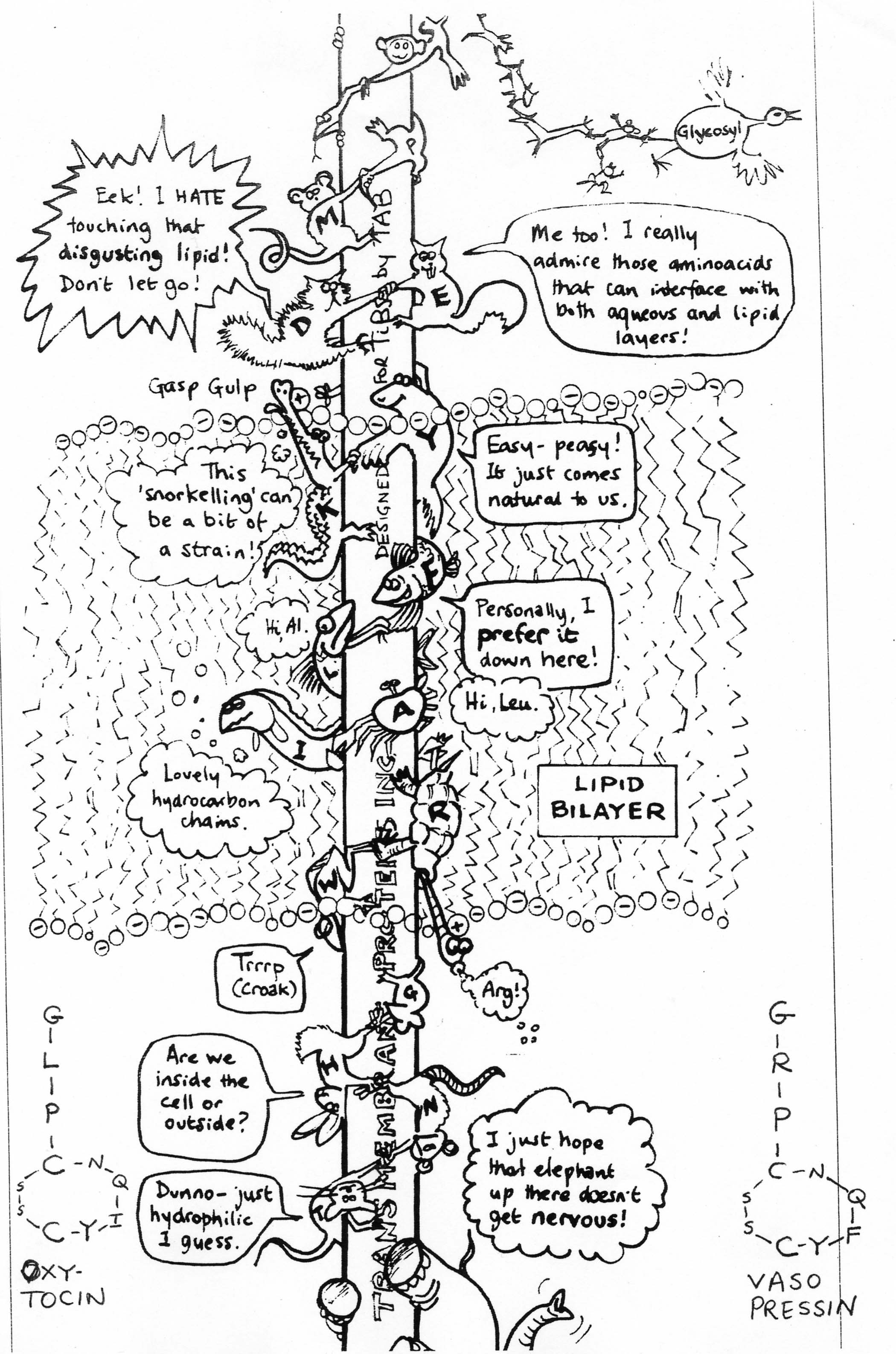
Explain the structure and function of cell membranes.
Cell membranes are composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins that serves as a selectively permeable barrier around the cell, regulating the passage of substances in and out of the cell. The hydrophobic tails of the phospholipids face inward while the hydrophilic heads face outward, ensuring the integrity of the membrane. Membrane proteins can have various functions such as transporting molecules across the membrane, acting as receptors for signaling molecules, or providing structural support. Overall, the cell membrane plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and communication with the environment.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.

























Comments