Bill Nye Food Web Worksheet
Worksheets are a valuable and efficient educational tool for students to reinforce their understanding of a subject. When it comes to studying the interconnections within ecosystems and the relationships between different organisms, the Bill Nye Food Web Worksheet is an excellent resource. Specifically designed for middle school students, this worksheet provides a clear and informative way to explore the intricate web of life and how energy flows through a food chain.
Table of Images 👆
More Food Worksheets
Printable Worksheets for French FoodDaily Food Intake Worksheet
5 Food Groups Worksheet
Food Production Worksheet Template
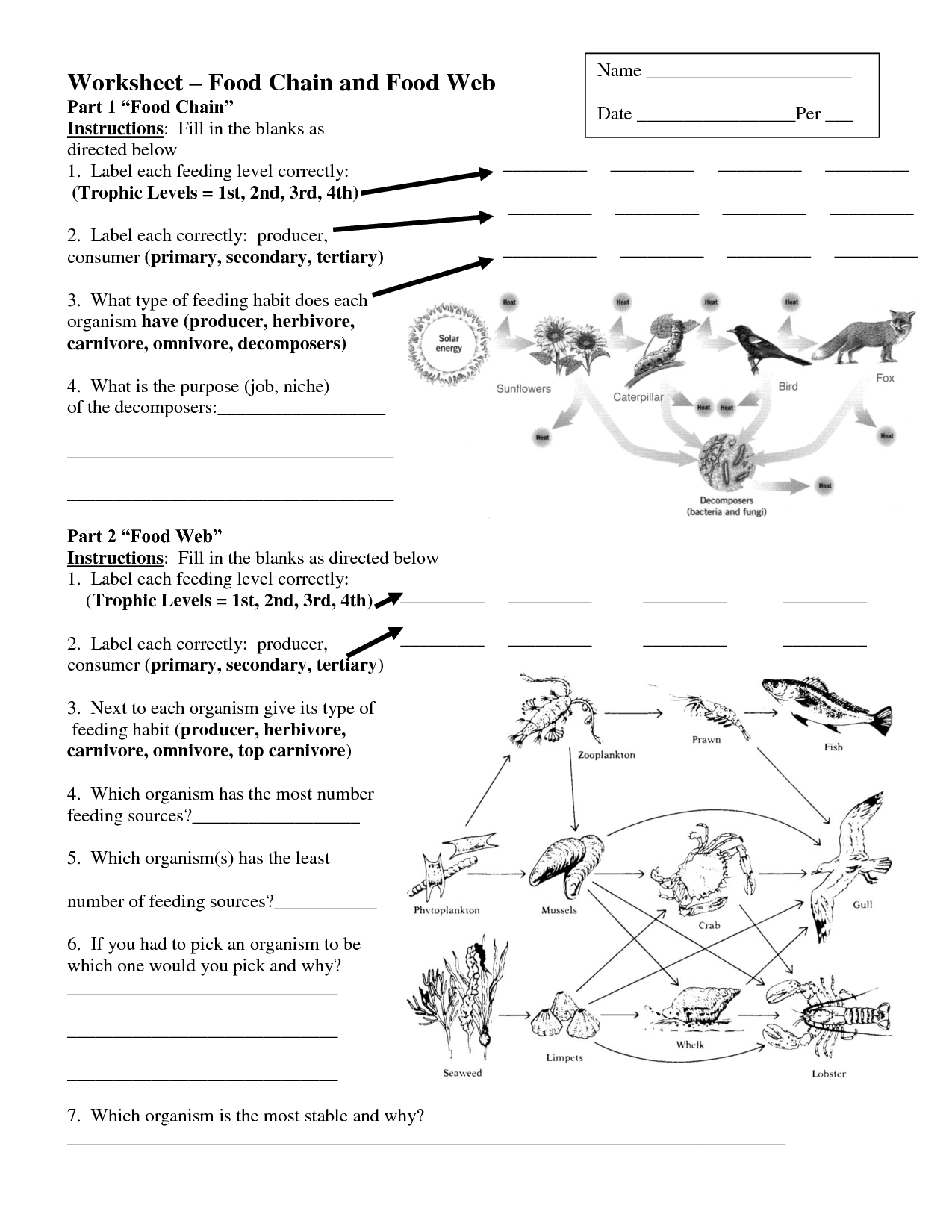
What is a food web?
A food web is a visual representation of interconnected food chains that show the complex network of feeding relationships in an ecosystem. It illustrates how energy and nutrients flow through various organisms in an ecosystem, highlighting the interactions between producers, consumers, and decomposers in a given habitat.
How do producers contribute to the food web?
Producers play a vital role in the food web by converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis, producing organic compounds that serve as the foundation of all ecosystems. They are essential for providing food and energy to primary consumers, such as herbivores, which in turn are consumed by secondary consumers, creating a chain of energy transfer throughout the food web. Without producers, such as plants and algae, the entire food web would collapse due to the lack of energy input at the base of the ecosystem.
Give an example of a primary consumer.
An example of a primary consumer is a rabbit, which feeds on plants and serves as a source of food for higher level consumers in a food chain or web.
What is the role of decomposers in a food web?
Decomposers play a crucial role in a food web by breaking down organic matter from dead organisms into simpler nutrients. This process releases essential elements back into the ecosystem, such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus, that can then be reused by plants for growth. Without decomposers, the ecosystem would become clogged with dead organic material, hindering the recycling of nutrients and the overall health and balance of the ecosystem.
Explain the importance of apex predators in a food web.
Apex predators play a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of an ecosystem by regulating the population of other species in the food web. Their presence helps control the numbers of herbivores, preventing overgrazing and disruption of plant communities. This in turn impacts the entire food web, ensuring the survival of various species and promoting biodiversity. Additionally, apex predators are indicators of ecosystem health, as their decline can signal potential issues within the environment. Their role in maintaining a stable and functioning ecosystem highlights their importance in the overall balance of natural systems.
How do humans impact food webs?
Humans impact food webs in various ways, such as overfishing, hunting, habitat destruction, pollution, and introducing invasive species. Overfishing and hunting can deplete certain species, leading to imbalances in the food chain. Habitat destruction disrupts the natural environment and can cause species to decline or go extinct. Pollution, including chemicals and plastics, can contaminate the food chain and harm organisms. Introducing invasive species can outcompete native species for resources, affecting the balance in the food web. Overall, human activities can have significant consequences on food webs and ecosystem dynamics.
What happens if one species is removed from a food web?
If one species is removed from a food web, it could disrupt the entire ecosystem. This could lead to a domino effect where other species that relied on the species that was removed for food, directly or indirectly, may struggle to survive. This disruption could lead to imbalances in population sizes, changes in predator-prey relationships, and ultimately affect the overall health and stability of the ecosystem.
Briefly describe the concept of trophic levels in a food web.
Trophic levels in a food web refer to the hierarchical levels of organisms in an ecosystem based on their feeding relationships. Producers, such as plants, are at the first trophic level, followed by primary consumers, then secondary consumers, and so on. Each level represents the transfer of energy and nutrients from one group of organisms to another through predation, with energy decreasing as it moves up the trophic levels. This concept helps to illustrate the flow of energy and materials through an ecosystem and the interdependence of different organisms within it.
How do food chains differ from food webs?
Food chains are simplified linear models that show the flow of energy and nutrients from one organism to another in an ecosystem, usually depicting a single pathway of consumption. In contrast, food webs are more complex and interconnected models that represent multiple, overlapping food chains in an ecosystem, showing the various relationships and interactions between different organisms and their roles in the flow of energy and nutrients. Essentially, food chains are specific pathways while food webs show a more intricate network of interactions among different species in an ecosystem.
What are some ways scientists study and monitor food webs?
Scientists study and monitor food webs through field observations, laboratory analysis, and modeling. Field studies involve observing interactions between organisms in their natural habitats, while laboratory analysis allows for detailed examination of nutrients, energy flow, and relationships between species. Additionally, scientists use mathematical models to simulate and predict how changes in one component of a food web can impact the entire system. These methods help researchers understand the complexity of food webs and the effects of human activities on ecosystem dynamics.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.






















Comments