Basic Pre -Algebra Worksheets
Pre-algebra can be a challenging subject for many students, but with the right resources, it doesn't have to be. That's why we've compiled a collection of basic pre-algebra worksheets that focus on the fundamental concepts of the subject. These worksheets are designed to provide practice and reinforcement in an organized and structured manner, making it easier for students to grasp and apply the concepts.
Table of Images 👆
- Preschool Shapes Tracing Worksheet
- Basic English Grammar Worksheets
- Rounding Decimal Numbers Worksheets 5th Grade
- Large Tracing Shapes Worksheets
- Preschool Rainbow Coloring Page
- Writing Graphic Organizer Plot
- Printable Shape Coloring Pages
- Preschool Reading Worksheets
- Cute Owl Coloring Pages
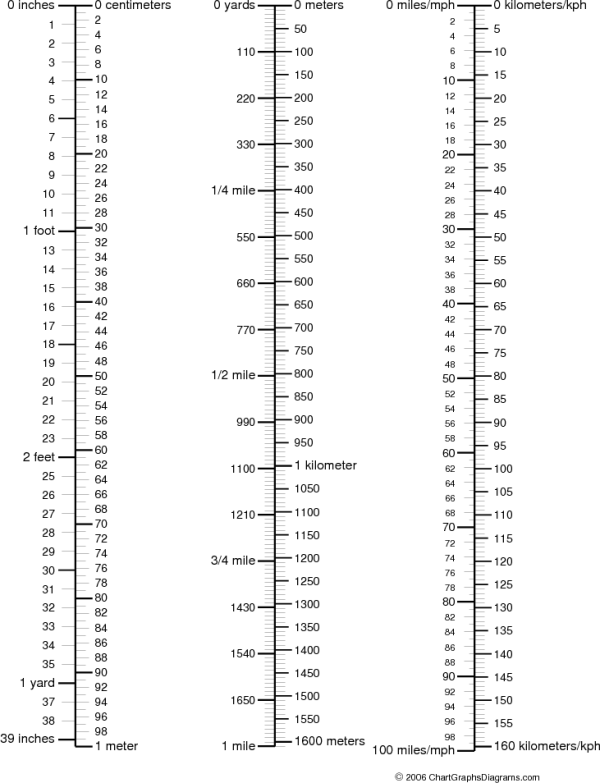
- Metric to Inches Conversion Chart Printable
More Other Worksheets
Kindergarten Worksheet My RoomSpanish Verb Worksheets
Cooking Vocabulary Worksheet
DNA Code Worksheet
Meiosis Worksheet Answer Key
Art Handouts and Worksheets
7 Elements of Art Worksheets
All Amendment Worksheet
Symmetry Art Worksheets
Daily Meal Planning Worksheet
What is a variable?
A variable is a symbol or name that represents a value in programming or mathematics that can change or vary over time. It is a placeholder for data that can be manipulated, stored, and referenced within a program or equation.
How do you solve for a variable in an equation?
To solve for a variable in an equation, you need to isolate that variable on one side of the equation by performing operations that will get it by itself. This involves following the order of operations, combining like terms, and applying inverse operations to both sides of the equation to keep it balanced. Ultimately, the goal is to manipulate the equation until the variable is the only thing on one side, allowing you to determine its value.
What is the order of operations in math?
The order of operations in math is PEMDAS, which stands for Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication and Division (from left to right), and Addition and Subtraction (from left to right). This is the sequence in which operations are carried out when solving mathematical expressions or equations to ensure accuracy and consistency in calculations.
How do you simplify algebraic expressions?
To simplify algebraic expressions, combine like terms by adding or subtracting coefficients of the same variable. Use the distributive property to remove parentheses by multiplying the term outside the parentheses by each term inside. Rearrange terms in a way that isolates variables and constants on one side, simplifying the expression. Lastly, look for opportunities to factor out common factors to further simplify the expression.
What is the distributive property?
The distributive property is a mathematical rule that states that for all numbers a, b, and c, the product of a and the sum or difference of b and c is equal to the sum or difference of the products of a and b and a and c. In other words, a(b + c) = ab + ac and a(b - c) = ab - ac. This property is fundamental in algebra and is used to simplify expressions and equations by expanding them.
How do you solve one-step equations?
To solve one-step equations, isolate the variable by performing the inverse operation. For example, if the equation is x + 5 = 10, you would subtract 5 from both sides to isolate x, giving you x = 5. Conversely, if the equation is 2y = 8, you would divide both sides by 2 to isolate y, resulting in y = 4. Remember, the goal is to get the variable on one side of the equation by undoing the operation that is being performed on the variable.
How do you solve two-step equations?
To solve two-step equations, first isolate the variable term by performing arithmetic operations in reverse order of operations. Start by undoing addition or subtraction by performing the opposite operation, then undo multiplication or division by performing the inverse operation. Remember to perform the same operation on both sides of the equation to keep the equation balanced. Once you have isolated the variable term, solve for the variable by simplifying the equation using basic arithmetic rules.
What is the slope-intercept form of a linear equation?
The slope-intercept form of a linear equation is y = mx + b, where m represents the slope of the line and b represents the y-intercept, which is the point where the line crosses the y-axis. This form is commonly used to represent and graph linear equations.
How do you graph linear equations on a coordinate plane?
To graph a linear equation on a coordinate plane, start by rewriting the equation in the form y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. Plot the y-intercept on the y-axis, then use the slope to find additional points on the line. Connect the points to create a straight line that extends infinitely in both directions. If the equation is in standard form Ax + By = C, solve for y to get it in slope-intercept form before graphing. Remember to label the axes and indicate the scale to accurately represent the relationship between x and y values.
What is the Pythagorean theorem and how is it used in algebra?
The Pythagorean theorem states that in a right triangle, the square of the length of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the lengths of the other two sides. In algebra, the Pythagorean theorem is often used to solve for unknown side lengths or to determine whether a triangle is a right triangle. By utilizing the formula a^2 + b^2 = c^2, where a and b are the two shorter sides of the triangle, and c is the hypotenuse, algebraic equations can be set up and solved to find missing side lengths in right triangles.
Have something to share?
Who is Worksheeto?
At Worksheeto, we are committed to delivering an extensive and varied portfolio of superior quality worksheets, designed to address the educational demands of students, educators, and parents.





















Comments